Reconstruction (1865
advertisement

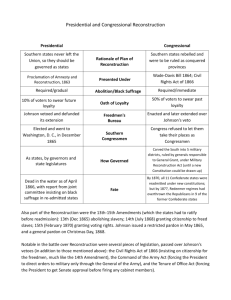
President Lincoln’s Plan
10% Plan
*
“Proclamation of Amnesty and
Reconstruction” (December 8, 1863)
*
Presidential Pardons to: 1) took loyalty
oath to the Union and Constitution &
2) agreed to emancipation.
*
When 10% of the voting pop. in the 1860
election were “loyal” the state could be
reestablished.
*
He didn’t consult Congress regarding
Reconstruction.
President Lincoln’s Plan
1864 “Lincoln
Governments” formed in LA,
TN, AR
*
“loyal assemblies”
*
They were weak and
dependent on the
Northern army for
their survival.
Wade-Davis Bill (1864)
Many Republicans in Congress
felt Lincoln’s plan too lenient.
Required 50% of the number
of 1860 voters to take oath
Senator
Benjamin
Wade
(R-OH)
“Iron-clad Oath” only nonConfederates could vote only
if they never voluntarily
aided the rebellion.
Enacted specific safeguards
of freedmen’s liberties.
Lincoln “pocket” vetoed it.
Congressman
Henry
W. Davis
(R-MD)
Jeff Davis Under Arrest
th
13
Amendment
Ratified in December, 1865.
Slavery abolished.
Congress has the power to enforce it.
Freedmen’s Bureau (1865)
“Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen,
and Abandoned Lands”
Provided food, schooling, and
attempted land. “Forty Acres
and a mule”?
Headed by General Oliver O.
Howard
Many former northern
abolitionists risked their lives
to help southern freedmen.
Called “carpetbaggers” by
white southern Democrats.
Freedmen’s Bureau School
•Established 3,000 schools and several black
Colleges - educated 200,000 by 1870
Freedmen’s Bureau Seen
Through
Southern
Eyes
Plenty to
eat and
nothing to
do.
President Andrew Johnson
Jacksonian Democrat.
Anti-Aristocrat.
White Supremacist.
Agreed with Lincoln
that states had never
legally left the Union.
“Damn the negroes! I am
fighting these traitorous
aristocrats, their masters!”
President Johnson’s Plan (10%+)
Offered amnesty with oath to most southerners
Confederate civil and military officers and the wealthy
($20,000 or more in property) had to apply directly to
Johnson
States had to ratify 13th Amendment.
Johnson granted 13,500 special pardons.
None of the new state constitutions extended voting
rights to blacks - result?
Congress Breaks with the
President
Congress bars Southern
Congressional delegates.
Joint Committee on
Reconstruction created.
February, 1866 President
vetoed the Freedmen’s
Bureau bill.
March, 1866 Johnson
vetoed the 1866 Civil Rights Act.
Congress passed both bills over
Johnson’s vetoes 1st in
U. S. history!!
Johnson the Martyr / Samson
“If my blood is to be shed
because I vindicate the
Union and the preservation
of this government in its
original purity and character,
let it be shed; let an altar to
the Union be erected, and
then, if it is necessary, take
me and lay me upon it, and
the blood that now warms
and animates my existence
shall be poured out as a fit
libation to the Union.”
(February 1866)
“slavery is dead?”
Black Codes
Couldn’t own land
“Vagrants” could be arrested
and forced into labor
Purpose:
*
Guarantee stable labor
supply.
*
Forced many blacks to
become sharecroppers
[tenant farmers].
The 1866 Bi-Election
A referendum on Radical Reconstruction.
Johnson made an ill-conceived propaganda
tour around the country to push his plan.
Republicans
won a 3-1
majority in
both houses
and gained
control of
every northern
state.
Johnson’s “Swing around
the Circle”
14th Amendment
Late 1866 (Ratified in July, 1868).
*
Citizenship Clause: All persons born or
naturalized in U.S. are citizens.
*
Due Process Clause: States can’t deny
citizen rights, “equal protection” or “due
process” to any U.S. citizen
*
Disqualified former Confederate political
leaders from holding state or fed. office.
*
Confederate states must pay off debts.
*
Equal Protection Clause: Punished states
that denied black suffrage by reducing
members of Congress & electoral college
Radical Plan for Readmission
Military Reconstruction.
Required new state constitutions,
including black suffrage and ratification
of the 13th and 14th Amendments.
In March, 1867, Congress authorized the
military to assist enrollment of black
voters.
Reconstruction Acts of 1867
Military Reconstruction Act
*
Restart Reconstruction in the 10 Southern states
that refused to ratify the 14th Amendment.
*
Divide the 10 “unreconstructed states” into 5
military
districts.
The Balance of Power in
Congress
State
White Citizens
Freedmen
SC
291,000
411,000
MS
353,000
436,000
LA
357,000
350,000
GA
591,000
465,000
AL
596,000
437,000
VA
719,000
533,000
NC
631,000
331,000
Reconstruction Acts of 1867
Command of the Army Act
*
The President must issue all
Reconstruction orders through
the commander of the military.
Tenure of Office Act
*
The President could not remove
any officials [esp. Cabinet members]
without the Senate’s consent, if the
position originally required Senate
approval.
Edwin Stanton
President Johnson’s
Impeachment
Johnson fired Stanton in February, 1868.
Johnson fired generals who were more
sympathetic to Radical Reconstruction.
The House impeached him on February 24
before even
drawing up the
charges by a
vote of 126 – 47!
The Senate Trial
11 week trial.
Johnson acquitted
35 to 19 (one short of
required 2/3s vote).
The 1868 Republican Ticket
The 1868 Democratic Ticket
“Waving the Bloody Shirt!”
Cartoonist Thomas Nast
Republican “Southern
Strategy”
“This is a white man’s government”
1868 Presidential Election
What was essential to Grant’s victory in the South?
th
15
Amendment
Passed in 1869 - Ratified in 1870.
The right to vote can’t be denied by the fed
or state government “on account of race,
color, or previous condition of servitude.”
The Congress shall enforce it.
Women’s rights groups were furious - why?
Susan B. Anthony
Grrrr!
Grant Administration Scandals
Grant presided over an era of
unprecedented growth and corruption.
*
Jay Gould & James
Fisk corner the Gold
Market “Black Friday”
*
Credit Mobilier
Scandal
*
Whiskey Ring.
*
The “Indian Ring.”
*
“Grantism”
The Tweed Ring
in NYC
William Marcy Tweed
(notorious head of Tammany Hall’s political machine)
[Thomas Nast crusading cartoonist/reporter]
The Election of 1872
Horace Greeley runs
as a Democrat/Liberal
Republican candidate.
“New Departure”
Democrats
Greeley attacked as a
fool and a crank &
waved the “bloody
shirt” again
Greeley died two
weeks after the
election
“Whoever says this isn’t a real
Elephant is a liar!”
1872 Presidential Election
The Panic of 1873
Sparked by failure of Jay
Cooke & Company & overspeculation of railroads
Lasted 4 years
Raised “the money question.”
*
Greenbacks vs. “sound
currency”
1875 Specie Resumption Act
1876 Greenback Party formed & makes gains in
congressional races The “Crime of ’73’!
Blacks limited success
Reunited with families, many moved to cities.
Rise of Negro Baptist and American
Methodists Episcopal (AME) churches
New black colleges - Howard, Atlanta, Fisk,
Morehouse - train black ministers & teachers
Establishment of Historically
Black Colleges in the South
Sharecropping
Tenancy & the Crop Lien System
Furnishing Merchant
Loan tools and seed
up to 60% interest
to tenant farmer to
plant spring crop.
Farmer also secures
food, clothing, and
other necessities on
credit from
merchant until the
harvest.
Merchant holds
“lien” {mortgage} on
part of tenant’s
future crops as
repayment of debt.
Tenant Farmer
Plants crop,
harvests in
autumn.
Turns over up to ½
of crop to land
owner as payment
of rent.
Tenant gives
remainder of crop
to merchant in
payment of debt.
Landowner
Rents land to tenant
in exchange for ¼
to ½ of tenant
farmer’s future
crop.
Black & White Political Participation
Black Senate & House Delegates
20 blacks served in the House and 2 Senators including
Hiram Revels & Blanche Bruce Senators of Mississippi
The Myth of
Colored
Rule
in the
South?
The “Invisible Empire of the
South”
Ku Klux Klan
Founded in 1867
*Enforcement Acts of 1870 & 1871
(KKK Acts) - fed troops to stop violence
and protect civil rights.
*Grant declared SC “state of lawlessness”
*By 1872 KKK in decline
The Civil Rights Act of 1875
Prohibited discrimination in
public transportation, public
places (hotels, railroads &
theaters) & in jury
selection.
Shortcoming lacked
strong enforcement once
troops were gone.
No new civil rights act was
attempted for nearly 90
years!
Thaddeus Stevens
& Charles Sumner
Return of White Rule
Amnesty Act of
1872
The rise of the
“Redeemers” or
“Bourbon Rule”
By 1876 Democrats
regained all exconfederates except
SC, FL & LA.
Northern Support Wanes
“Grantism” & corruption.
Panic of 1873
[worst depression yet].
Concern over westward
expansion and Indian wars.
Rise of Social Darwinism
1874 Democrats gain House
And They Say He Wants a Third Term
1876 Presidential Tickets
1876 Presidential Election
The Political Crisis of 1877
“Corrupt Bargain”
Part II?
A Political Crisis: The
“Compromise” of 1877
Republicans: Hayes as president
Democrats (& South): end of military Reconstruction,
internal improvements, Southern cabinet member.
Alas, the Woes of
Childhood…
Sammy Tilden—Boo-Hoo! Ruthy Hayes’s got my
Presidency, and he won’t give it to me!
Hayes Prevails
“His Fraudulency” & “Ruther-fraud Hayes”
Rise of the Jim Crow South
• Civil Rights Cases of 1873 - 14th
Amendment didn’t protect from
discrimination by private citizens
• Plessy vs. Ferguson (1896) upheld
segregation on LA railroads
“separate but equal”
• Jim Crow Laws passed in southern
sates
• Cumming v. County Board of Ed.
(1899) segregated schools okay
• Disenfranchisement: poll taxes,
literacy tests, and Grandfather
Clause & rise of lynchings