Biology Study Guide
advertisement

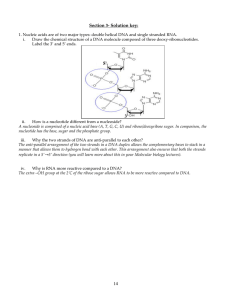
Name: __________________________________ Period: ____________________ Date: _____________ Biology Study Guide Unit 3: Macromolecules and Enzymes Vocabulary Give a brief definition of each of these terms. These words are likely to appear as part of questions on the exam. 1. Macromolecule – 2. Nucleic Acid – 3. Carbohydrate – 4. Polymer – 5. Starch – 6. Cellulose – 7. Glycogen – 8. Lipid – 9. Hydrophobic – 10. Triglyceride – 11. Trans Fat – 12. Phospholipid – 13. Hydrophilic – 14. Bilayer – 15. Steroid – 16. Protein – 17. Enzyme 18. Substrate – 19. Product – 20. Denaturation - Biology Worksheets and Resources http://www.aurumscience.com Page 1 Critical Thinking Questions These questions are similar to those on the test. 1. What element is the backbone of all organic compounds? 2. Proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids are all polymers. What repeating subunit is each made of? 3. Fill out this table comparing the different types of carbohydrates. Carbohydrate Class Root Prefix Meaning Monosaccharide Single or one. Examples Glucose Fructose Galactose Deoxyribose Ribose Disaccharide Polysaccharide 4. Give two structural differences between DNA and RNA. 5. Give an example of where you could find the three classes of lipids (triglyceride, steroid, and phospholipid) in living organisms. 6. The diagram below shows a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid. Label each. Which would be liquid at room temperature, and which would be solid? 7. Sketch a single phospholipid molecule (do not draw the chemical structure, just the shape). Label the phosphate and two fatty acids that make up the molecule. Also, label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic region. 8. Explain why altering the sequence of amino acids that make up a protein could completely alter its ability to function normally. 9. Give five examples of functions served by proteins in living organisms. 10. This illustration shows an enzyme breaking down a substrate. Label the enzyme, substrate, and products. 11. What effect do enzymes have on chemical reactions in living organisms? 12. What are the two most common ways to cause denaturation of a protein?