World Geography
advertisement

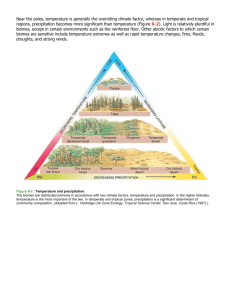
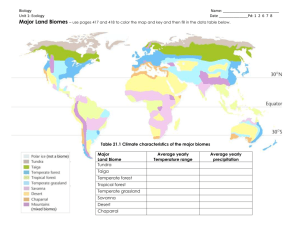
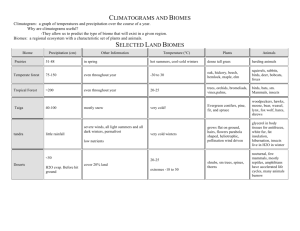
World Geography Objective: Climate and Biomes Learning Goal 3: Explain how physical processes create climate regions and explain how climate influences the distribution of biomes. (TEKS/SE’s 3A,4A, 4C) cli·mate noun \ˈklī-mət\ the average course or condition of the weather at a place usually over a period of years as exhibited by temperature, wind velocity, and precipitation What is a climograph? World Climate Regions Warm Up: Write these down on the back of your cornel notes Review this map and tell me the following. List the three continents with the driest climate List the two continents with the most tropical weather List the three continents with the most cool and subarctic climate regions What is the relationship between weather conditions, climate and the Earth-Sun relationship? Earth’s Tilt and Revolution The earth is tilted at an angle of 23 ½ as it revolves around the sun. Because of this, different areas of the earth receive different amounts of sun which creates the different seasons on earth. 3A The Tropics The Tropic of Cancer (23 ½ N) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23 ½ S) mark the areas on the earth known as the Tropics which are the areas farthest north and south where the sun’s rays shine directly overhead. 3A Polar Areas Areas around the poles (north and south) receive less direct sunlight due to the earth tilt and are thus much cooler than other places on earth. How do elevation, latitude, wind systems, ocean currents, position on a continent, and mountain barriers influence temperature, precipitation, and distribution of climate regions? 4A LAMECOW: ACRONYM L-atitude A-ir Masses M-ountain Barriers E-levation C-ontinent Position on O-cean Currents W-ind Factor #1 Elevation Temperature Areas of higher elevation are much cooler due to thinner air’s inability to hold heat, lack of land to reflect heat, and the conditions of the atmosphere. Precipitation Distribution of Climate Regions Thinner air at higher Areas of high elevations makes it elevation occur difficult for air to around the globe. retain heat/ precipitation causing significant snow at high elevations. Factor #2 Latitude Temperature Precipitation Distribution of Climate Regions Latitude has the Latitude has some -Areas of low elevation greatest impact on influence on precipitation. (areas between the climate since it For example, the hot tropics- 23 ½ N and S) determines the amount of rising air around the are warm due to the sunlight an area equator creates sun’s direct rays. receives. continually moist -The middle latitudes (23 climates. ½ N/S - 66 ½ N/S) have Those closest to the temperate/ seasonal equator receive more climates. sunlight (heat) while -The higher latitudes (66 those farthest away from ½ N/S- 90) have the the equator receive less. coldest climates due to their distance from direct sunlight. Factor #3 Wind Systems Temperature -Wind distributes temperatures across the earth’s surface. Wind that moves across warmer or cool water or land transfers those qualities. Precipitation Precipitation on the earth is moved and distributed by prevailing winds. Distribution of Climate Regions -Areas of high low pressure (rising warm air) tend to receive more rain while areas of low pressure (falling cooler air) tend to get less rain. Factor #4 Ocean Currents Temperature -Waters of the ocean help distribute the earth’s heat. These currents influence the temperature of the areas nearby. -Warm water from the tropics is circulated to the poles and cold water from the poles is circulated to the equator. Precipitation Distribution of Climate Regions -As in the case of wind -Cooler oceans near currents, cool and the poles keep those warm ocean currents areas cool and warmer transfer precipitation waters near the tropics around the world. also hold heat. Factor #5: Position on a Continent Oceans are solar energy collectors Because water heats & cools more slowly than land… 1. Coastline has a more stable temperature 2. Areas along coastlines are influenced by ocean currents, thus they receive more rain.(precipitation) 3. Interior of continent has extreme temperatures (hotter & colder) Factor#6 Mountain Barriers Temperature *See influence of elevation on temperature. Precipitation Distribution of Climate Regions When air moves As mountains over mountains, can occur precipitation anywhere on (orographic) earth, this tends to occur influence on on the windward climate can as side. This well. creates a wet side (windward) and a dry side (leeward). The Hobbit Middle Earth: Apply the climate factors On the menu! 1. Turn in Climographs HM 2. Cornel Notes: Completed with 4 questions for each class. And a summary. Keep track of them. Due Thursday. For a grade 3. One question must use the term Explain 4. Thursday: Quiz on the first three learning goals. 5. After quiz: IDs!!!!!!! 6. Extra Credit Opportunity: 50 points! What am I? Warm up: Use your Phones if you want or P. 594-595 I am a seasonal weather phenomenon in South Asia. I am characterized by massive amounts of rain that cause severe flooding. What causes this weather event? What is a country I am associated with? Temp Stable? What climate factor? Continental Position Latitude Temp Stable? What climate factor? Ocean Currents Latitude How does climate influence Biomes the distribution of biomes in The ecosystems different regions? (community of plants and animal) of a specific region are called biomes. Biomes are divided into four main categories: forests, grasslands, deserts, and tundra 4C Influence of Climate Temperature and precipitation determine the distribution of the world’s biomes. Tropical Biomes: Areas in the lower latitudes are influenced by warmer temperatures and often abundant precipitation. Biomes in these regions include tropical rainforests and tropical grasslands. 4C Influence of Climate Temperate Biomes: Areas in the middle latitudes have biomes adapted to seasonal shifts in temperature in precipitation in temperature. Biomes in these regions include deciduous forests and temperate grasslands. As the latitude increases deciduous forest transition to mixed and coniferous forests. 4C Influence of Climate Polar Biomes: Areas in the higher latitudes tend to be dominated by coniferous forests in the warmer portions that transition to tundra in the cooler areas. Deserts: These biomes occur in areas with limited precipitation requiring plants and animals who have adapted for such conditions. 4C