A population is
advertisement

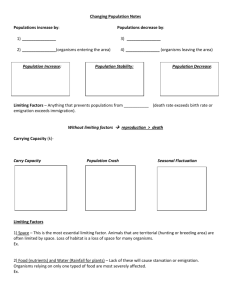
Population Studies Pre-Assessment: 1. What is a population? 2. What might influence population #’s (give 3 things)? 3. How many people are there on Earth? 4. Do you think that the human population can continue to grow forever? Why or why not? http://video.nationalgeographic.com/vide o/player/specials/sitewide-redesign/ngm7billion.html World Population Growth Through History 12 11 2100 10 9 Old Stone 7 Age 8 Billions New Stone Age Bronze Age Iron Age 6 Modern Age Middle Ages 2000 Future 5 4 1975 3 1950 2 1 Black Death —The Plague 1900 1800 1+ million 7000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 A.D. A.D. A.D. A.D. A.D. A.D. years B.C. B.C. B.C. B.C. B.C. B.C. B.C. 1 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Source: Population Reference Bureau; and United Nations, World Population Projections to 2100 (1998). AN ECOSYSTEM IS… All the populations and abiotic factors in an area. SO WHAT’S A POPULATION? A population is…. a group of organisms of the SAME species living in a specific area What is a Species? organisms that are able to interbreed POPULATION ECOLOGY This is the study of how and why populations change and grow. Ecologists try to identify the factors limiting population growth; understanding this helps predict future growth. For populations to survive, many different factors must stay in balance. Limiting Factors for Populations Limiting Factors can affect the number of organisms (i.e. population of people, animal, or plants) in a region/country Limiting Factors for Populations, cont. Limiting factors can be: a. Density Dependent or b. Density Independent Density = number of individuals per unit of area (Ex. = 65 people per square mile) Density Dependent Limiting Factors Density dependent factors (factors affected by the number of people/animals /plants living in the particular area.) Amount of food available Living space Disease Competition Predation Density Independent Limiting Factors Density independent factors (these have nothing to do with the number of people/ animals/plants living in a given area) Weather Seasonal cycles Natural disasters Human activities Specific examples of Density Independent factors Natural disasters Drought Fire Volcanic eruption Human activities Housing development Road building Farming How do we show populations? In a GRAPH!! What are some factors to compare about populations? 1. Total number of individuals during any year 2. Number of women vs number of men 3. Number of individuals that are young, middle aged, or old HOW do we get all this info on 1 graph??? Japan FEMALE Pop (in millions) in year 2000 Japan MALE pop (in millions) in 2000 Comparison of Male & Female Pop in Japan Which parts of the population INCREASE the size of the population? Which part of the poulation DECREASES the size of the population? Population pyramids/ age structure graphs. CARRYING CAPACITY Carrying capacity is the number of # of organisms individuals in a population that an ecosystem can support over a relatively long period of time. time TYPES OF POPULATION GROWTH Exponential growth – “J - curve” Carrying capacity # of organisms time TYPES OF POPULATION GROWTH (cont.) S – curve population growth Carrying capacity # of organisms time POPULATION GROWTH (cont.) Most populations have limited resources – these become limiting factors to population growth. Food Space Water When limiting factors exist, S – curve population growth occurs. When does J – curve population growth occur? Quick Quiz: 8 pts 1. Explain what a population pyramid/age structure graph shows. (think x and y axis). 2. How is it able to predict how a population will change over time? 3. Look at the graph of Mexico: a. Is Mexico stable, increasing or decreasing in the future? b. How do you know?