Foldable Notes
advertisement

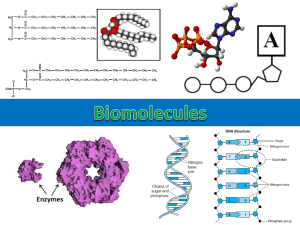
Objectives: • Today, you the student, will define and arrange information of carbohydrates into graphic organizer. • You will organize this information on a graphic organizer as you see it and hear it. I will assess your comprehension of this information by a written ticket-out-thedoor for a grade. WHAT'S Is it? A carbohydrate is called an organic compound or biomolecule because it contains carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. Sugars, which are carbohydrate-based compounds, provide living things with energy and act as substances used for structure. Basic Building Blocks: • Monomer – monosaccharide (simple sugar) – C6H12O6 – Ex: glucose; fructose; maltose – Notice that they all end in –ose • Polymer – polysaccharide (complex sugar) – Ex: Cellulose (wood, paper); starch (energy storage in plants); glycogen (energy storage in animals) Where does it come from? Carbohydrates come from plants, or plant products, mostly. You EAT it. Your body does not make it. What is it used for? Carbohydrates are major component of cell walls. Carbohydrates are also the cells primary source of energy. When the body (cells) need immediate energy, it burns carbohydrate molecules first. Examples: vegetables, pasta and grains (grasses), any kind of sugar, fruit, etc. Notice the carbon backbone. There is only 1 oxygen to each carbon, making the acronym “CHO” With your highlighter or marker, highlight the acronym “CHO” on the front flap cover of your foldable on the carbohydrate flap Ticket out the Door: Give 3 different names for a carbohydrate: 1. 2. 3. 4. What is a carbohydrate used for? Give 3 examples of a carbohydrate: 5. 6. 7 Warm Up On the outside of your carbohydrate flap, write the 3 other words that a carbohydrate is sometimes called. The basic building block of a lipid is glycerol, with 3 fatty acids attached. Where does it come from? Lipids are another type of organic molecule containing carbon. Some lipids are consumed in your diet. But SOME lipids are made within the body, so they are NOT consumed. What is it used for? Lipids have 3 main functions in the body: • Separation, such as membranes, b/c oil and water doesn’t mix. • Insulation, to help maintain body temp and protect organs • Energy reserve, which is your secondary, or back-up energy source, after carbohydrates. Examples of lipids: • • • • • • Butter oil animal fat Wax, such as ear wax Hormones, such as steroids and others body fat. CHOO Notice the structure of a fatty acid, or lipid. A carbon chain with double or single bond. A steroid has interlocking rings, such as the ones below. It will look like a pentagon or hexagon. Highlight the acronym CHOO on the lipid flap on the front of your foldable Hydrolysis vs Dehydration Synthesis http://youtu.be/_Ai5NyQ_ttE Warm Up Get your journal and have your foldable and your notes out. Basic Building Block: Amino Acids *remember amino acids are built during protein synthesis in DNA replication Where does it come from? 1. Animals and animal products, with the exception of a few plants. 2. Your body combines amino acids during protein synthesis. Amino acids come from the protein you eat. What is it used for? All organisms need some proteins, whether they are used in muscles or as simple structures in the cell. Examples: bacon, eggs, cheese, chicken & Enzymes in your body are also considered proteins. Enzyme Examples: lactase, sucrase, fructase, etc. *Remember that simple carbohydrates, like sucrose, fructose, lactose, end in -ose. The enzymes that break these simple sugars down end in -ase, and they match. Ex: Lactase breaks down lactose sucrase breaks down sucrose Chemical Structure All proteins will have the carbon backbone, but will have an additional amino group Notice that a protein has an element that carbohydrates don’t have. With the original CHO that we had before, when you add the nitrogen, you get CHON! Proteins So, on the front of your foldable, Highlight the acronym CHON on your protein flap. Warm-Up Get a small slip of paper; you may use your foldable to answer the following questions: Bio Group Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids Monomer Function 2 examples Basic building blocks? •Nucleotides are the building blocks of both nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. •Many nucleotides bonded together make an amino acid chain. Where does it come from? The nucleic acids are the building blocks of living organisms. (DNA) Your body MAKES nucleic acids from the molecules you consume in foods. What is it used for? The nucleic acids are the building blocks of living organisms. It is the DNA or RNA located in the nucleus of every cell in your body. This is the “stuff” that they use in CSI to tie a suspect to a crime scene. It is unique to each and every organism. Examples of nucleic acids: DNA is just one type of nucleic acid. Some other types nucleic acids are RNA, mRNA, and tRNA. All of these "Na's" work together to help cells replicate and build proteins. Highlight the acronym CHON P on the Nucleic Acid flap on the front of your foldable. Name That Biomolecule ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?