United States Imperialism
advertisement

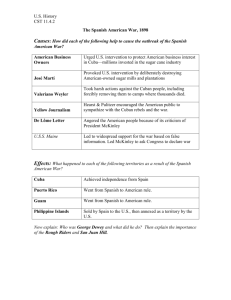
BELLRINGER #4-1 Read “American Expansionism” and “Global competition” on p. 342-343. Answer the following questions. 1. Define Imperialism. 2. On what continent was European imperialism a primary target in the late 19 th century? 3. To what country did nations shift their imperialist goals in the late 1800s? 4. What three factors fueled American imperialism? UNIT 4 HOMEWORK WB pgs. 140-154 IMPERIALISM Unit 4 THE IMPERIALIST VISION IMPERIALISM The political and economic domination of a strong nation over other weaker nations. THREE REASONS FOR IMPERIALISM 1. Political rivalries – Each nation wanted a larger empire than the other, which led to more world power. 2. Desire for new markets – Industrial countries needed markets for their goods. 3. Spread culture – US leaders believed their culture was superior to any in the world (Western). ANGLO-SAXONISM Idea that came from Social Darwinism English-Speaking nations were superior Character Ideas Systems of Government Destined to dominate the planet JOSIAH STRONG Linked Anglo-Saxonism to missionary work Must spread Christianity Convinced many Americans to support Imperialism GROWTH OF A MODERN NAVY Americans became interested in protecting their interests overseas. This required a navy that could compete with Europeans. ALFRED T. MAHAN U.S. naval of ficer who helped convince American leaders of the importance of maintaining a large navy and overseas territories. THE PACIFIC PACIFIC EXPANSION U.S. leaders saw the economic benefit of starting trade with Japan and China. MATTHEW C. PERRY U.S. naval commander who forced Japan to begin trade with the U.S. Japan accepted U.S. influence. COMPARE THE VERSIONS Japanese Version The real Matthew Perry PERRY ARRIVES IN JAPAN PERRY MEETS WITH THE JAPANESE AMERICANS SIGN TRADE AGREEMENT WITH THE JAPANESE RESULT OF JAPANESE TRADE AGREEMENT Japan adopted Western technology Had an industrial revolution IMPORTANCE OF HAWAII Midway between the U.S. and Asia. Climate allowed for growing sugar, fruit. U.S. began trade and settlement of Hawaii in 1887. LOCATION OF HAWAII QUEEN LILIUOKALANI Queen of Hawaii who disliked American intervention. Americans forced the Queen to give up power and Hawaii became a U.S. territory in 1893. Annexation-to add on QUEEN LILIUOKALANI ALASKA Purchased from Russia in 1867 Seward’s Folly People felt it was a foolish move by Secretary of State William Seward After Seward's death, gold was discovered in Alaska and many people changed their minds. Became a state in 1959 LATIN AMERICA LATIN AMERICA LATIN AMERICAN TRADE U.S leaders wanted more trade and cooperation with Latin America. Wanted to show Europe that we were the dominant power in Latin America PAN-AMERICANISM Belief that the U.S. and Latin America should work together. LESSON RE-CAP WB. 142 HOMEWORK WB p. 140-142 BELLRINGER #4-2 Look at the maps on p. 349. Answer the following questions. You do not have to write the questions. 1. In what two regions (parts) of the world was the Spanish American War fought? 2. From which city did Dewey attack the Philippines? 3. Where does Cuba lie in relation to the United States? The SpanishAmerican War CUBAN REVOLT In 1895, Cuba began a revolt against colonial power Spain. Americans supported Cuba. JOSE MARTÍ Cuban revolutionary leader Raised money from Americans Planned an invasion of Cuba ECONOMIC TIES TO CUBA Cuban sugar imported into the U.S. Investments in Cuban mines, railroads and sugar plantations YELLOW JOURNALISM Sensational news reporting where writers exaggerate or make up stories to attract readers. Support for Cuban rebels EXAMPLE OF YELLOW JOURNALISM MODERN YELLOW JOURNAL JOSEPH PULITZER Publisher of the New York World. WILLIAM RANDOLPH HEARST Publisher of the New York Journal. MCKINLEY’S POSITION ON THE WAR President William McKinley said the U.S. should not get involved and tried to negotiate a peace. U.S.S. MAINE McKinley sent the battleship U.S.S. Maine to Cuba’s Havana Harbor in case American citizens needed to be evacuated. U.S.S. MAINE U.S.S. MAINE EXPLODES While in Havana Harbor, the Maine exploded suddenly. A navy report declared that a Spanish mine had sunk the ship. U.S.S. MAINE EXPLODES WRECKAGE OF THE MAINE “REMEMBER THE MAINE!” American people blamed Spain. McKinley was under tremendous pressure to declare war. Congress declared war on April 19, 1898. “REMEMBER THE MAINE!” JINGOISM An attitude of aggressive nationalism. Very strong after the Maine incident. CAUSES OF SPANISH AMERICAN WAR American support for Cuban rebels Republican pressure of McKinley Yellow journalism Explosion of the USS Maine WAR ON TWO FRONTS 1. U.S. forces fought the Spanish in two areas: A land war in Cuba. 2. A naval battle in the Spanish Colony of the Philippines. ADVANTAGES OVER SPAIN New and better battleships Spanish were weak from disease and fighting Cubans Spanish were poorly trained WAR ON TWO FRONTS PHILIPPINES GEORGE DEWEY American Admiral who defeated the Spanish in the Battle of Manila Bay. EMILIO AGUINALDO Filipino revolutionary leader. Unrest developed between Filipino revolutionaries and the Americans. CUBA ROUGH RIDERS American volunteer cavalry unit that fought the Spanish in Cuba. Led by Leonard Wood. Led the capture of Kettle Hill and San Juan Hill. THEODORE ROOSEVELT Second in command of the Rough Rider unit. http://www.history.com/videos/ roosevelt-fights-in-spanishamerican-war#roosevelt-fightsin-spanish-american-war ROOSEVELT AND THE ROUGH RIDERS CHARGE OF THE ROUGH RIDERS END OF THE WAR The war ended on August 12, 1898. U.S. received Guam, Puerto Rico. U.S. paid $20 million for the Philippines. Cuba was granted independence. Historical IRONY Many Filipinos were not happy with the United States taking control of their country. They were treated by the Americans almost the same way the Cubans were treated by the Spanish. Filipinos rebelled, and in order to control Filipino rebels, General Arthur Macarthur set up reconcentration camps which resulted in the deaths of many Filipinos. MCKINLEY’S PRESIDENCY McKinley’s Presidency LESSON RE-CAP P. 351 #2 WB p. 146 HOMEWORK WB p. 143-146 BELLRINGER #4-3 P. 354- Analyzing Political Cartoons #1 -3 (For question #2 you may need to compare presidential portraits on p. R41 in the back of the book) New American Diplomacy ELECTION OF 1896 McKinley vs. William Jennings Bryan. McKinley named Roosevelt Vice President. “CROSS OF GOLD” SPEECH ELECTION OF 1896 William McKinley William Jennings Bryan ELECTION OF 1896 MCKINLEY’S ASSASSINATION McKinley was shot at a pubic appearance by anarchist Leon Czolgosz. Died a few days later. Roosevelt at age 42 became the youngest President. http://www.history.com/videos/theodore -roosevelts-rise-topresidency#theodore-roosevelts-rise-to-presidency MCKINLEY’S ASSASSINATION LEON CZOLGOSZ ROOSEVELT’S PRESIDENCY http://www.history.com/shows/the presidents/videos/roosevelts -big-stick-foreignpolicy#roosevelts-big-stick-foreign-policy SKETCH OF ROOSEVELT’S INAUGURATION POLITICAL CARTOON ROOSEVELT THE OUTDOORSMAN ROOSEVELT DURING AN AFRICAN SAFARI “BIG STICK” DIPLOMACY Roosevelt’s foreign policy. He wanted America to become a major player in the world. WHAT DOES THIS QUOTE MEAN? “Walk softly and carry a big stick.” – Theodore Roosevelt “BIG STICK” DIPLOMACY “BIG STICK” DIPLOMACY “BIG STICK” DIPLOMACY SPHERES OF INFLUENCE An area in China where a foreign country controlled the economic development. SPHERES OF INFLUENCE OPEN DOOR POLICY European countries were wanting to carve up China for their own imperialist needs. Roosevelt wanted all countries to be able to trade freely with China. BOXER REBELLION (1900) Rebellion in China by the Society of the Righteous and Harmonious Fists against foreigners. International force was used to end the uprising. CHINESE BOXER EXECUTION OF BOXERS ROOSEVELT GETS THE NOBEL PEACE PRIZE Russia and Japan almost go to war over Chinese territory Roosevelt negotiated a treaty between Japan and Russia Japan resented American involvement GREAT WHITE FLEET New fleet of modern battleships that Roosevelt had sail around the world as a display of American might. MAP OF THE GREAT WHITE FLEET’S VOYAGE THE REAL GREAT WHITE FLEET PANAMA CANAL Building a canal across Central America would make it easier to ship goods from the east coast to Asia. Begun in 1881 by the French. Malaria, heat and money loss ended the project. U.S. began the project in 1903 and finished 10 years later. VOYAGES WERE CUT SHORTER PANAMA CANAL BUILDING THE CANAL BUILDING THE CANAL BOAT GOING THROUGH THE PANAMA CANAL REVOLT IN PANAMA Panama was part of Colombia and revolted because they believed the Canal would hurt Colombia economically. U.S. sent warships and recognized Panama as a new country. The two countries signed the deal to build the canal. MONROE DOCTRINE (1823) Decision by U.S. President James Monroe that said all of the Western Hemisphere was closed to European colonization. WESTERN HEMISPHERE IS OFF LIMITS ACCORDING TO THE MONROE DOCTRINE ROOSEVELT COROLLARY Addition to the Monroe Doctrine. Said that the U.S. would intervene militarily against any European power to keep Latin America stable (big stick diplomacy). USA was the “policeman” of the Americas OTHER PRESIDENTIAL FOREIGN POLICIES Taft-Dollar diplomacy Trade with Latin America Wilson- Missionary Diplomacy Promoting democracy HOMEWORK WB p. 147-153 LESSON RE-CAP WB p. 150 Prepare for the SATP NUMBERED HEADS TOGETHER REMEMBER? What is an attitude of aggressive nationalism? (Very strong after the Maine explosion) Jingoism REMEMBER? On what two fronts was the Spanish - American war fought? Cuba and Philippines REMEMBER? What was the American volunteer cavalry unit that fought the Spanish in Cuba? (San Juan Hill) Rough Riders REMEMBER? Who was the Cuban revolutionary leader that planned an attack from America? Jose Marti REMEMBER? What were the publications that exaggerated news stories? (Last question) Yellow Journalism BELLRINGER #4-4 Standardized Test Practice p. 369 #1-2