Fertilization & Development
advertisement

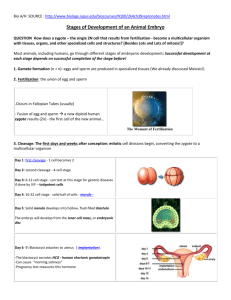
Fertilization & Development • Fertilization occurs in the oviduct • Sperm + Egg Zygote • Haploid +Haploid Diploid Formation of the Zygote Once fertilization has occurred and the genetic material has combined, cell division begins. Is it mitosis or meiosis? Formation of the Zygote Once fertilization has occurred and the genetic material has combined, cell division begins. Is it mitosis or meiosis? Mitosis Formation of the Zygote A special type of mitotic cell division called cleavage occurs. Formation of the Zygote Cleavage results in cells being formed which become progressively smaller. Formation of the Zygote Notice how the over all size remains the same while the number of cells increase. Formation of the Zygote Formation of the Zygote Cleavage occurs while the zygote is moving through the oviduct. Formation of the Zygote As the zygote develops it goes through several specific phases. These are the : – Morula – Blastula & – Gastrula Formation of the Zygote The Morula is a solid ball of cells. This develops during the first few days after conception. Formation of the Zygote The Blastula is a hollow ball of cells. Formation of the Zygote The Gastrula is formed from the blastula. It establishes the three embryonic tissue layers. Formation of the Zygote The three layers are: – Endoderm – Mesoderm & – Ectoderm Formation of the Zygote The ectoderm gives rise to the skin and nervous system. Formation of the Zygote The ectoderm gives rise to the skin and nervous system. The mesoderm gives rise to the muscles, bones, circulatory and excretory systems. Formation of the Zygote The ectoderm gives rise to the skin and nervous system. The mesoderm gives rise to the muscles, bones, circulatory and excretory systems. The Endoderm gives rise to the digestive and respiratory systems. Implantation The Morula secrets a hormone, HcG. This maintains Progesterone levels, preventing menstruation. Implantation HcG is detected early and forms the basis for the home pregnancy test kits . Implantation Implantation occurs in the endometrial lining of the uterus. This occurs by day 7. Associated Structures The umbilical cord connects the embryo to the placenta. Associated Structures The umbilical cord connects the embryo to the placenta. In adults, its scar forms the navel. Associated Structures The placenta is the site of gas and nutrient exchange between the mother and the fetus. Associated Structures The Amniotic Fluid is the liquid that the baby floats in. It serves as a cushion. Multiple Births Multiple births can occur two ways: – The splitting of one fertilized egg that will give rise to identical twins Multiple Births Multiple births can occur two ways: – The splitting of one fertilized egg that will give rise to identical twins – Multiple eggs are fertilized giving rise to fraternal twins (not identical) Twins In Vitro Fertilization Types of Sexual Reproduction The reproductive pattern shown by mammals and marsupials involves internal fertilization and internal development. Types of Sexual Reproduction The reproductive pattern shown by mammals and marsupials involves internal fertilization and internal development. The number of off spring per pregnancy is low but parental care is high. Types of Sexual Reproduction Types of Sexual Reproduction The reproductive pattern shown by reptiles and birds involves internal fertilization but external development (egg) The number of off spring is higher, and parental care is variable. Types of Sexual Reproduction Types of Sexual Reproduction The reproductive pattern shown by amphibians and fish involves external fertilization and external development The number of off spring is much higher, and parental care is usually lacking Types of Sexual Reproduction Types of Sexual Reproduction Regardless of the type of sexual reproduction, the development of the embryo is similar.