Lecture 4 - Communication
advertisement

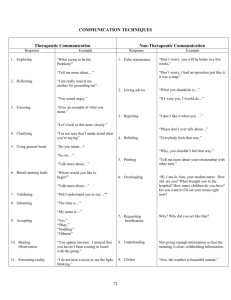
Communication Life span - Chapter 4 Communication • “Exchange of information, ideas, feelings or emotions between two or more people”. • Do you buy it? Communication Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Message Sender Method Receiver Feedback Message • Expression of your thoughts Sender • Sends our the message Method Receiver • Person to whom the message was sent Feedback! • Response to the message Who’s communicating? What are the 5 steps of the communication process? Types of Communication Verbal • Spoken word • Written word Non-verbal • AKA: body language 8 modes of nonverbal communication 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Physical appearance Body movement & Posture Facial expression Gestures Eye contact Tone & volume or voice Touch Silence Thought questions • What are the 8 modes of non-verbal communication? • Give an example of each Personality types 1. Passive 2. Aggressive 3. Assertive Style of Communication Intrapersonal • Thinking to your self Interpersonal • Communication between others Style of Communication Social Therapeutic • Family • Friends • Purposeful • Goal oriented 6 components of therapeutic communication 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Listening & observing Warmth Genuineness Attentiveness Empathy Positive reward 1. Listening & observing • Cognitive & affective domains • Words & feeling Stages of Listening 1. Sensation – Ears pick up sound waves 2. Interpretation – Attaches meaning 3. Evaluation – Judge message 4. Reaction – Feedback Which is a more complex process? A. Hearing B. Listening Active Listening • • • • • • Face them Open posture Lean forward Eye contact Relaxed Respond Rules of listening 1. Don’t talk & listen at the same time! Rules of Listening 2. Open posture Rules of Listening 3. Focus Rules of Listening 4. Listen to understand Rules of Listening 5. Environment control – Quiet – Limit distractions Rules of Listening 6. Show that you care Rules of Listening 7. Validate Rules of Listening 8. Do not criticize Rules of Listening 9. Be non judgmental and accepting Rules of Listening 10. Ask questions 3. Genuineness • Open • Truthful 4. Attentiveness Attentiveness 5. Empathy • Understand feelings • Stay in control 6. Positive Regard • Accepting • Non-judgmental Functions of Therapeutic Communication 1. 2. 3. 4. Create understanding Decrease anxiety Provide information Develop trust Phases of Therapeutic Communication 1. Orientation 2. Working 3. Termination Factors Affecting Communication Congruence • Match – Verbal – Non-verbal Time & Setting • “I’ll be right there” A. B. C. D. Be there within 5 minutes Be there within an hour Be there within a day Be there within a week Proxemics • Personal space Biases • Prejudice • Negative beliefs Physical Handicaps • Deaf • Blind Blocks to Communication Belittling • Dismissing or mocking • 3 yrs old says he is afraid of monsters. • Mom - “You’re acting like a baby, there are no monsters.” Belittling • Dismissing or mocking • Pt “I won’t leave here alive.” • Nrs “That’s ridiculous. You shouldn’t even think that way.” Giving literal responses • Pt: “They’re looking in my head with a TV”. • Nrs: “What channel?” • Patient: “That doctor is a pain in the neck.” • Nurse: “Would you like your pain medication?” Challenging • “If you’re dead, why is your heart beating?” Disagreeing • Response that indicates you believe the person is incorrect • Teenage girl “My boyfriend is terrific” • Mom – “I think he is a loser. You can do better.” Disagreeing • Response that indicates you believe the person is incorrect • Pt “Why am I here? Nothing is being done for me and I’m not getting any better.” • Nrs – “You are getting better.” Disagreeing • Expressing disapproval • ‘You should stop worrying like this.” Agreeing • Statements that show you believe the person is correct. • To neighbor “I’m thinking of divorcing my husband.” • “I’d get rid of him too.” Agreeing • Statements that show you believe the person is correct. • Pt – “I don’t think the doctor will send me home tomorrow.” • Nrs – “I am sure you are correct. I doubt he will let you go home so soon.” Defending • Justification • Counter reply to a verbal attack • Teenage to day “I don’t get as much of an allowance as Paul does.” • Dad – “I’m doing the best I can.” Defending • Justification • Counter reply to a verbal attack • Pt – “I’ve had my call light on for 15 minutes.” • Nrs – “I am doing the best I can. You are not the only patient here.” Stereotyping • Clichés • Superficial • “I know what is happening to you.” • “All 2 year olds are terrible.” Stereotyping • Clichés • Superficial • Pt - “I am really worried about my children. I came to the hospital so quickly and didn’t get to see them. They just wont understand. I wish I could talk to them” • Nrs - “I know exactly how you feel.” Giving false reassurance • Reassurance without sincerity • “Don’t worry. Everything will be all right. You will feel better soon.” Giving false reassurance • Reassurance without sincerity • Pt – “What will I do if this is malignant?” • Nrs – “Don’t you worry. Everything will work out just fine.” Giving advice • “If I were you…” • “Why don’t you…” Giving Advice • “What you should do is…: Changing the subject • Introducing a new topic • Pt – “They are doing a biospy tomorrow. I hope it isn’t cancer.” • Nrs – “Are these pictures of your children? They are such a nice looking family.” Asking closed-ending questions • Questions with oneword answers Asking “why” questions • Why? • “Why did you fall?” Probing • Seeks information beyond what is necessary. Techniques used to enhance communication Giving information • “Susie is getting an echocardiogram right now which is a test that uses painless sound waves to create a moving picture of her heart structures and valves and should tell us what is causing her murmur”. Validating • A statement or question to verify your perception • “Has the diarrhea stopped?” Clarifying • Seeking information to understand • “Could you explain? • I’m not sure I understand? Clarifying • Seeking information to understand • Pt - “There is no point in asking for pain medication” • “Are you saying no one give you medication when you have pain or do you mean the medication doesn’t help your pain?” Reflecting • Stating you perception of the message in the affective (feeling) domain • Flashback • Pt – “My sister won’t help with our mother’s care.” • Nrs – “You feel angry. Have you discussed this with her?” • Nrs – “I sense that you feel angry” Paraphrasing • Restating • Pt – “I was awake most of the night.” • Nrs – “You have trouble sleeping.” Paraphrasing • Restating • Pt – “I couldn’t eat supper last night.” • Nrs – “You had difficulty eating.” Asking broad questions • Open-ended questions • “Would you like to tell me about it?” • “Is there something you would like to talk about?” Using general leads • 1-2 works to encourage the person to continue • “Go on.” • “And then…” • “You were saying” Stating observations • “You seem tense.” • “You are trembling” Offering self Silence Touch Time • “I'd like to understand.” • “I’ll stay awhile if you’d like.” Focusing • Directing the conversation to a specific topic • "This point seems worth looking at more closely." Using humor • Laughter is the best medicine A = Therapeutic B = Block • Patient: “I don’t know. I hate to have my boyfriend see me looking like this. Just thinking about him coming to visit makes me nervous.” • Nurse: “You really should stop worrying. That may be what’s keeping you from getting the rest you need. And after all, no one expects you to look your best when you’re in the hospital.” A = Therapeutic B = Block • Patient: “You’d think my doctor would have prevented me from getting phlebitis, but he’s too busy to care about what’s happening to me.” • Nurse: “You’re wrong, Mr. Iverson. Of course he cares.” A = Therapeutic B = Block • Nurse: “You seem to be kind of restless tonight.” Patient: “Nobody cares. My doctor wants me to go—just go on home. He doesn’t care?” Nurse: “Go home?” A = Therapeutic B = Block • Patient: “Maybe I should find a hobby or something. I try not to get discouraged; I know I shouldn’t let it get me down.” • Nurse: “That’s the right attitude. It really doesn’t help to worry about it.” A = Therapeutic B = Block • Nurse: “How are you feeling this morning, Mr. Patterson?” • Patient: “Oh, fine, thanks.” (unenthusiastic) • Nurse: That’s good. A = Therapeutic B = Block • Patient: “I can’t go home with this…AIDS. If they want me out of here so bad, why don’t they just let me die?” • Nurse: “You can’t go home because you have AIDS?” A = Therapeutic B = Block • Patient: “Well, I haven’t been able to work for quite a while now, and the doctor says I might not ever work as a carpenter again.” • Nurse: “It must be difficult for you right now, but I’m sure everything will be all right.” A = Therapeutic B = Block • Patient: "I'm just jumpy-I get like this sometimes. I guess it's because I didn't get too much sleep last night." • Nurse: "Yes, when you don't get a good night's sleep it does make you edgy." A = Therapeutic B = Block • Patient: "What's there to talk about? First they say they have to operate, and then when I'm beginning to feel better, I get this infection. I don't think I'm ever going to get out of here!" • Nurse: "I know just how you feel. You know, everyone gets frustrated when things aren't going right."