Protein Synthesis
advertisement

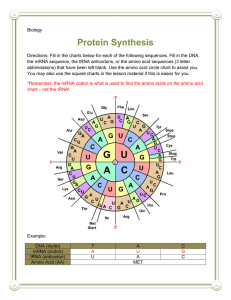
Protein Synthesis From Codes/genes to Proteins/machines Central Dogma- DNARNAProtein It explains how genetic information flows Can you break the code??? 8 5 12 12 15 3 12 1 19 19 Making Proteins Protein Synthesis Process of making proteins Two part process 1. Transcription 2. Translation Remember Reading DNA? The four chemical bases in DNA (A, T, C, G) create a code/gene Ribosomes “read” this DNA code/gene to make proteins. Where are ribosomes located? Where is DNA located? Nucleus Problem Nucleus not permeable to DNA DNA is a large to fit out of pore Double stranded = wide How do we get the code/gene to the ribosomes to make proteins? Copy code into a smaller molecule RNA (ribonucleic acid) RNA vs DNA • What is the difference? • Compare and contrast DNA to RNA DNA BOTH RNA Two Types of Nucleic Acids Deoxyribonucleic Acid Ribonucleic Acid DNA RNA Double Stranded Single Stranded Smaller Nucleotide sugar = Nucleotide sugar = Deoxyribose Ribose Bases = A, T, G, C Bases = A, U, G, C The Tail of Two RNA’s Two RNA types needed for Protein synthesis mRNA messenger RNA tRNA Transfer RNA Protein synthesis Step 1: Transcription Process of making messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA Exactly like Replication (with one small difference) Use base paring rules C pair with G G pair with C T pairs with A BUT A pairs with U (uracil) Which enzyme is used to add nucleotides?? Modifications of Mrna before it can leave nucleus Add5’ cap- protects mRNA and allows it to leave nucleus/find a ribosome Poly (A) tailThey are added to: protect mRNA and allow it to leave nucleus/find a ribosome Introns (non-coding sequences between exons) are removed and exons (amino acid coding sequences) are spliced together mRNA Function Take gene from nucleus to ribosome Disposable copies(often thoughsands) of VERY important information Tells Ribosome how to build protein. Transcription Practice (DNA to mRNA) Cheat Sheet A=U T =A C=G G =C Open DNA: A T G C C G T T A A C G A G T C T mRNA copy: U Step 2: Translation What does it mean to Translate something? Change from one language to another Biology Translation To go from the language of DNA (A, T, C, G, and U) to the language of protein (amino acids) Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins Translation Involves ribosome, mRNA and tRNA (transfer RNA) Ribosome reads mRNA on codon (3 bases) at a time tRNA matches with codon on mRNA Brings amino acid with Ribosome takes amino acid from tRNA and links it to growing protein Translation summary mRNA read by ribosome in groups of 3 bases called CODONS Ex: AUG = Start making protein Ex: UGA = Stop making protein Codon on mRNA match Codon on tRNA Codon tells ribosome what amino acid to attach to protein Decoding mRNA Humans use decoder Codon wheel Codon chart Reading Codon Wheel Using 3 base Codon Start at center of the wheel Find the first nitrogen base in codon Sets what ¼ of circle you will work in Move to the next ring of circle Find second nitrogen base Sets what ¼ of the remaining circle you are in Move to the last ring Find third nitrogen base Arrive at your amino acid Finding Amino acid for Codon GAG Reading Codon Chart Using 3 base Codon Start at left side Find the first nitrogen base in codon Sets what row you are using Move to the top of chart Find second nitrogen base Sets what column you are using Find where column and row meet This is the box you are working in Find matching Codon in this box Find the amino acid for the codon CGU CYU Transcribe this DNA to mRNA Translate the mRNA to amino acids DNA mRNA Amino Acid T A C G G C A T C