Fractions
advertisement

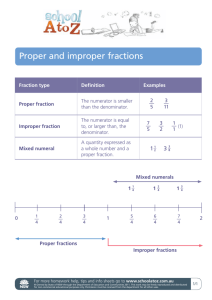
Unit 5 Math Schedule Monday, 12/3: Finish 5.1 - Fraction Review Tuesday, 12/4: 5.2 - Mixed Numbers (you will need the geometric shapes) Wednesday, 12/5: 5.3 - Ordering Fractions Thursday, 12/6: 5.4 - Two (Three) Rules for Finding a Common Denominator (add "quick method") Friday, 12/7: Differentiation Stations/Catch-Up Monday, 12/10: 5.5 – Fractions and Decimals: Part 1 Tuesday, 12/11: 5.6 – Fractions and Decimals: Part 2 Wednesday, 12/12: 5.7 – Fractions and Decimals: Part 3 Thursday, 12/13: 5.8 - Using a Calculator to Convert Fractions to Percents Friday, 12/14: Differentiation Stations/Catch-Up Monday, 12/17: 5.9 - Bar Graphs (No circle graphs yet!) Tuesday, 12/18: Review, slate assessment, etc. Wednesday, 12/19: Review, games, etc. Thursday, 12/20: Unit 5 Test Friday, 12/21: 5th Grade Skating Party Unit 5 Fractions, Decimals, and Percents The objectives are to: Review the meanings of fraction, decimal, and percent. Convert between fractions, decimals, and percents. The secure goals are: Convert between fractions and mixed numbers. Find equivalent fractions. Vocabulary whole denominator improper fraction mixed number equivalent fractions percent numerator simplest form repeating decimal bar graph 5.1 Fraction Review The objectives are to: review fractions; and to find fractional parts of large whole numbers. Vocabulary whole denominator numerator unit fraction Math Message Write any five fractions in your Math spiral. Circle the greatest fraction and the least fraction in your set of fractions. Fractions Fractions were invented to express numbers that are between whole numbers. Fractions can show measures between whole numbers on rulers and scales. Fractions can name part of a whole object (for example, part of a cake or pizza). Fractions can name part of a collection of objects (for example, part of the eggs in a carton). Fractions can compare two quantities as ratios or rates (for example, ½ of the class are boys, the car’s gas mileage was 100 miles/4 gallons, or 25 mi/gal). Fractions can express chance or probability (for example, a probability of 1/6 that a die will land with 6 up). Fractions can represent division (for example, ¾ is equivalent to 3 divided by 4 ). The top number in a fraction is called the numerator. N = North The numerator tells how many parts you are looking at and considering. The bottom or right number in a fraction is called the denominator. D = Down The denominator names the number of equal parts into which the whole is divided. If you have 5/6 of a pizza, then the numerator tells you that five pieces are still left out of six pieces that your pizza is cut into. Solving Parts-and-Whole Problems with Fractions Math Journal page 122 Problems 1 and 2 The whole and the part are given; the fraction needs to be named. Problems 3, 4, and 7 The whole is given and the fraction is named; the part needs to be found. A unit fraction is a fraction with one as the numerator. Problems 5, 6, and 8 A part is given and the fraction is named; the whole needs to be found. 5.2 Mixed Numbers The Objectives are to: review the whole, or ONE; to explore mixed-number concepts; and to convert between mixed numbers and “improper” fractions. Vocabulary improper fraction mixed number Math Message Take the following pattern blocks: 2 yellow hexagons, 2 red trapezoids, 3 blue rhombuses, and 6 green triangles. If a trapezoid is worth ½, what is a rhombus worth? More Pattern Block Problems If the triangle is 1/3, what is the ONE? If the triangle is 1/3, what is the rhombus? If the rhombus is 1/3, what is the ONE? If the rhombus is 1/3, what is the triangle? If the triangle is ½, what is the ONE? If the triangle is ½, what is the trapezoid? Math Journal Page 126 Do you know what these are and how they are different from each other? Proper Fraction – a fraction where the numerator is smaller than the denominator. It is worth less than one. Improper Fraction – a fraction where the numerator is bigger than the denominator. It is worth more than one. Mixed Number – there is a whole number and a fraction. It is worth than one. 5.3 Ordering Fractions The objectives are to: compare and order fractions; review equivalent fractions; explore fraction addition. Vocabulary equivalent fractions fraction stick Math Message Complete problems 1 – 5 on journal page 131. Comparing and Ordering Fractions 1. The Denominators are the Same If the denominators are the same, then all of the pieces are the same size. Only the number of pieces (numerators) need to be compared. 2/10 6/10 1/10 8/10 5/10 2. The Numerators are the Same Since the numerators are the same, there are the same number of pieces for each fraction. Only the size of the pieces (the denominators) needs to be compared. Larger Denominator = Smaller Pieces Smaller Denominator = Larger Pieces 4/10 4/6 4/5 4/12 4/24 3. Compare to Benchmarks If numerators and denominators are different, you can compare each fraction to benchmarks. Is the fraction closer to 0, 1/2, or one? 2/4 5/6 1/10 1/5 4/6 4. Find Equivalent Fractions with the Same Denominators One way to compare fractions is to find a common multiple for the denominator. You can change the fractions to the same denominator by multiplying both the numerators and denominators of the fractions by the same number. 5/12 and 9/24 5/14 and 3/7 5. Fraction Stick Use the Fraction-Sticks Chart in the back of your Math Journal (and your SRB) to compare fractions. 5.4 Two Rules for Finding Equivalent Fractions The objectives are to: use fraction sticks to find equivalent fractions; formulate multiplication and division rules for finding equivalent fractions. Vocabulary simplest form (lowest terms) Math Message Lisa has a 50-cent piece. Jamal has two quarters. Sam has five dimes. Hunter has ten nickels. Elliot has 50 pennies. Write a fraction to show what part of a dollar each person has. Who has the most money? Name fractions that are equivalent to – 1/2 1/4 1/5 1/10 Multiplication Rule To find an equivalent fraction, multiply both the numerator and the denominator of the fraction by the same number. 5.5 Fractions and Decimals: Part One The objectives are to: rename simple fractions as decimals; review rounding decimals; to find decimals between pairs of numbers. Vocabulary round down round up round to the nearest Math Message Write three decimals between each of the following pairs: 45 seconds and 46 seconds 7 dimes and 8 dimes 9.32 seconds and 9.33 seconds Math Lesson Write each number as a fraction or a mixed number and then as a decimal. Word Form three-fourths four-fifths six-fiftieths five and one-half two and nine twenty-fifths seven and six-twentieths Fraction Decimal Renaming Fractions as Decimals MJ 139 How do you turn fractions into decimals? 1. Benchmark Fractions Benchmark Fraction 1/2, 2/4, 3/6, 50/100 1/3, 2/6, 3/9, 33/99 1/4, 2/8, 3/12, 4/16, 25/100 2/3, 4/6, 6/9, 66/99 3/4, 6/8, 9/12, 75/100 1/5, 2/10, 3/15, 10/50, 20/100 2/5, 4/10, 20/50, 40/100 3/5, 6/10, 30/50, 60/100 4/5, 8/10, 40/50, 80/100 1/1, 2/2, 5/5, 10/10, 50/50, 100/100 Equivalent Decimal 0.5, 0.50, 0.500 0.33, 0.330 0.25, 0.250 0.67, 0.670 0.75, 0.750 0.2, 0.20, 0.200 0.4, 0.40, 400 0.6, 0.60, 0.600 o.8, 0.80, 0.800 1.0 2. Fractions with Denominators of 10, 100, 1000 3. Divide Numerator by Denominator Playing Estimation Squeeze Student Reference Book Page 268 5.6 Fractions and Decimals: Part 2 The objectives are to: use a fraction-stick chart; rename “easy” fractions; to begin a table of decimal equivalents for fractions. Math Message How would you use the Probability Meter to show someone what 1/6 dollar is worth? 5.7 Fractions and Decimals: Part 3 The objectives are to: use a calculator to find decimal equivalents for fractions. Vocabulary repeating decimal Math Message Write 7/16 as a decimal. Converting a Fraction into a Decimal How do you do it? 1. Fraction-Stick 2. Denominators of 10, 100, 1000 3. Dividing the numerator by the denominator When you see a fraction, think “division.” Think of the bar between the numerator and denominator as thought it was the slash, /, for division, and divide. For mixed numbers, students only need to divide the fraction part. You can simply copy the whole number part when you write the decimal name. Some fractions when divided repeat continuously. These decimals are called repeating decimals. Place a bar over the number or numbers that repeat. 2-4-5-10 Frac-Tac-Toe SRB 274 – 276 and MM 62, 63, and 479 5.8 Using a Calculator to Convert Fractions to Percents The objectives are to: use a calculator to convert fractions to decimals and decimals to percents; discuss meanings and uses of percents. Vocabulary percent Math Message Using your calculator, find a way to rename 4/7 as a percent. Do not use a percent key. Meaning of Percent The word percent comes from the Latin per centum: per means “for” and centum means “one hundred.” Allison scored 80% on a test. If the test had exactly 100 questions, Allison answered 80 of them correctly. Allison answered 80/100 questions correctly. If the test had more than 100 questions, Allison correctly answered 80 out of every 100 questions. For every 100 questions, Allison answered 80 correctly. How many questions did Allison answer correctly if: there were 100 questions on the test? there were 50 questions? there were 40 questions? there were 10 questions? there were 20 questions? Emily spent 18% of the money she earned babysitting last summer on school clothes. For every 100 dollars earned, Emily spent 18 dollars on school clothes. If 100 baby-sitting dollars were spent, 18 of those dollars were spent on school clothes. Emily spent $18 out of every $100 earned on school clothes. Emily spent 18/100 of her money on school clothes. How much would Emily have spent if: she earned $200? she earned $400? she earned $50? The Purpose of Percents Percents are useful for making comparisons between numbers when the whole is not the same. For example, 8 correct on a test could be worse than 4 correct on a different test, depending on how many question were on each test. 8 out of 20 , or 40 %, is worse than 4 out of 5, or 80%. Percent makes comparisons easier when the whoe or ONE differs. Kris earned $167 setting up new computers for her neighbors. She spent $43 on software. Clay earned $219 teaching piano to children. He spent $51 on sheet music. Who spent the larger portion of her or his earnings? Changing Fractions to Percents Step One Divide the numerator by the denominator by the numerator. Step Two Round the decimal to the hundredths place. Step Three Multiply the decimal by 100 (move the decimal two places to the left). 5.9 Bar Graphs The objective is to: construct and label bar graphs. Vocabulary bar graph Math Message Answer problem 1 on journal page 152. Parts of Bar Graphs A bar graph should have the following parts: 1. A title that describes what is being graphed. 2. A list of the groups or categories for which bars are drawn. 3. A number line with a scale. The scale is used to draw bars of lengths that show the amount of data in each group or category. The scale is usually labeled.