Functional Groups
advertisement

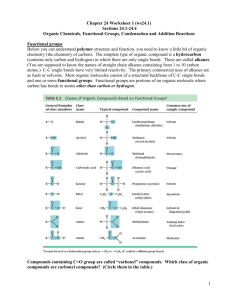
Functional Groups Functional Groups • An atom or group of atoms on a molecule that always reacts in the same manner. The functional groups we will study • • • • • • • • • Halocarbons Alcohols Ethers Aldehydes Ketones Amines Carboxylic acids Esters Amides Halocarbons •General form: R X R is any chain or ring attached to the halogen X is one of the halogens: Cl, F, Br, or I Halocarbons •Alkyl halide •Halogen(s) attached to any aliphatic compound. Cl H2C Cl CH CH3 1,2-dichloropropane Halocarbons •Aryl halide •A halogen attached to any aromatic compound. Cl 1,3-dichlorobenzene (m-dichlorobenzene) Cl Alcohols •General form: R O H O-H is a hydroxyl group R is any chain or ring attached to the hydroxyl group Naming alcohols 1. Count the carbon atoms. 2. The name used is the 3 same as for alkanes. 1 carbon: methane 3. Remove the –e ending and add –ol. 1 carbon alcohol: 4. If necessary, identify methanol the carbon atom to which the hydroxyl is attached. HC O H You try it! •Name this alcohol: H3C CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 O H 1-Pentanol You try it! •Name this alcohol: H3C CH2 CH H O CH2 CH3 3-Pentanol Ethers •General Form: R O 1 R Note the central oxygen atom Naming Ethers Count the carbon atoms separately on either side of the oxygen. Use the branch name for each side, listed alphabetically. Add the word “ether” to complete the name. Naming Ethers 1 carbon on left: 2 carbons on right: oxygen atom in between H3C methyl O CH2 CH3 ethyl ethylmethyl ether You try it! •Name this ether: H3C CH2 O CH2 CH2 CH3 ethylpropyl ether Aldehydes •General form: •Contains a carbonyl group with one hydrogen O carbonyl group R hydrogen C H Naming Aldehydes Count the carbon atoms. Use the same name as you would for an alkane with the same number of carbons. Remove the –e at the end and replace it with –al. hydrogen attached to carbonyl carbonyl group H3C O C H 2 carbons Ethane – e + -al = ethanal You try it! Name this aldehyde O H C CH2 CH2 CH3 butanal Ketones •General form: O carbonyl group C R R 1 Chains or rings attached to either side of the carbonyl Naming ketones Count the carbon atoms. Use the name of the alkane with the same number of carbons. Number the carbon atoms so that you identify the carbon to which the carbonyl is attached. Remove the –e and add –one. Naming ketones carbonyl group O carbonyl attached to 2nd carbon C H3C Four carbons = butane butane – e + one = CH2 CH3 2-butanone Is a number really necessary for this ketone? You try! •Name this ketone: O C H3C CH3 Is a number necessary for this ketone? propanone Amines •Amines are simply ammonia molecules in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been substituted with a branch or ring. •General form: Central nitrogen atom R1 , R2 R, and are either hydrogen atoms, branches, or rings. R R N R 2 1 Naming Amines Look for the central nitrogen. Count the number of carbons on each branch attached to the nitrogen. List each branch by its name in alphabetical order. Add the word “amine” to the end of the name. Naming Amines Central nitrogen H3C methyl group H3C H N CH2 ethylmethyl amine ethyl group Naming Amines Central nitrogen H3C methyl group N ethyl group CH2 CH3 CH3 ethyldimethyl amine You Try! •Name this amine: H N H3C CH2 CH3 CH2 diethyl amine Carboxylic Acids •General form: carboxyl group O carbonyl group C R hydroxyl group O H When a carbonyl AND a hydroxyl are bonded together, it is known as a carboxyl group. Naming Carboxylic Acids Identify the carboxyl group. Count the carbon atoms. Begin with the name of the alkane that has the same number of carbons. Remove the –e and add –oic and the word “acid” to the name. If necessary, identify the carbon to which the carboxyl group is attached. Naming Carboxylic Acids carboxyl group O C H O H 1 carbon atom methane – e + oic acid = methanoic acid You Try! O C H3C CH2 O H propanoic acid Name this carboxylic acid H3C O HC CH3 C O H 2-methylpropanoic acid Name this carboxylic acid H3C H3C CH2 CH CH H3C O C O H 2,3-dimethylpentanoic acid Noteworthy Carboxylic acids O H C methanoic acid O is called “formic acid” H Stinging ants use formic acid as a defense mechanism. O H3C C ethanoic acid is called “acetic acid” O H This is the acid found in vinegar. Esters •General Form: hydrogen is replaced by a chain or ring O R C Ester group O R 1 Naming Esters Name the alkyl group Identify the ester group and use the acid name. Remove the –ic and add –ate to the end. Naming Esters ethanoate group (acetate group) O C methyl group O H3C CH3 methyl ethanoate or methyl acetate Naming Esters •Name this ester: propanoate group ethyl group O CH2 H3C C O CH3 CH2 ethyl propanoate Amides •General form: O R C H N H The oxygen in the carboxyl group is replaced by a nitrogen atom bonded to other atoms. Naming Amides Count the carbons. Use the name of the alkane with the same number of carbons. Replace the final –e with –amide. Naming Amides O CH2 C H 3 carbons = propane N H3C propane – e + amide = H propanamide You Try! •Name this amide: O H3C CH2 CH2 C H N H butanamide A Noteworthy Amide: O CH CH H3C C N H C C OH CH CH If you’ve ever had a headache, chances are that you’ve taken this. This is acetaminophen. (Also labeled Tylenol.)