Exam 3 Review Answer Key
advertisement

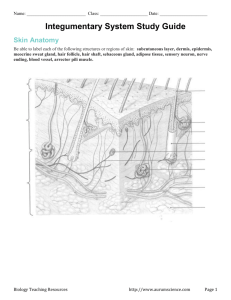
Exam 3 Review: Chapter 5 Integumentary System Short Answer 1. Functions of the skin: body temperature regulation, protection, excretion and absorption, synthesis of vitamin D, cutaneous sensations 2. If a needle pricks your forearm what is the correct order of epidermal layers it would go through: stratum corneum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale 3. When exposed to UV rays this pigment can cause our skin to darken: melanin 4. Explain what happens as keratinocytes move up from the stratum basale: As they move up from the basale they are getting further away from the blood and nutrients in the dermis so as they move up they begin to die 5. What is eccrine sweat composed of: water, ions (salt, chlorides) urea, ammonia, glucose 6. List the accessory organs of the integumentary system: hair, nails, glands (sebaceous glands, sudoriferous glands) 7. What causes goosebumps: contraction of the arrector pili when cold or nervous 8. What is the type of tissue found in the epidermis (think of the 4 types of tissues covered in Chap. 4) : epidermal tissue 9. What is the type of tissue found in the dermis (think of the 4 types of tissues covered in Chap. 4) : connective tissue 10. Explain how the epidermis receives blood and nourishment: the epidermis contains NO blood vessels, but the dermis contains blood vessels. The blood from the 11. How does sweat help cool the body down: sweat evaporates off the body causing it to cool down Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Hair shaft: part of the hair which is visible Stratum lucidum: clear layer of the epidermis which is only found in thick skin Sebaceous glands: Produce sebum, also known as oil glands Langerhans cells: Epidermal cells which are involved in immunity Arrector pili: smooth muscle found in the dermis which cause your hair to stand on end when you’re cold or nervous Keratin: protein produced by the keratinocytes of the epidermis, helps in protection. Nails and hair are composed of keratin Hair follicle: Sheath which surrounds the hair root, composed of epithelial and connective tissue Nail matrix: where nail growth occurs Cutaneous receptors: Specialized nerve endings that respond to temperature, touch and pain Sudoriferous glands: sweat glands True or False: If the statement is false, change the bolded term to make it true 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. The presence of keratin protects the skin from damaging effects of the sun: False; Melanin The skin is also known as the cutaneous membrane: True Keratinocytes are the most numerous type of cell found in the epidermis: True In order to produce Vitamin D, the skin needs to be exposed to heat: False; UV rays Dark-skinned people have the same number of melanocytes as light-skinned people: True Merkel cells are responsible for producing keratin: False; Keratinocytes Eccrine glands are the most common type of sweat gland: True The hypodermis is considered to be part of the skin: False; Hypodermis is not part of the skin The epidermis is responsible for most of the skin’s structural strength: False; Dermis Matching: Some of these can be used more than once 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Cell division occurs in this layer of the epidermis: G Layer of the skin which is composed of dense connective tissue: A Glands which respond to elevated body temperatures: D Sensory receptor which respond to the stimulus of touch: E The secretions of ______________ glands are thought to function as a sexual attractant: C Layer of the epidermis where cells go through apoptosis (programed cell death): F Portion of the hair which is below the surface of the skin: B Most cutaneous sensory receptors are found in the: A This type of gland is most commonly found in the axilla and the groin: C A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Dermis Root Apocrine Eccrine Meissners corpuscles Stratum granulosum Stratum basale Labeling: Label the following picture Hair Shaft Epidermis Stratum Basale Hair Shaft Sebaceous Gland Arrector Pili Dermis Hair Follicle Sudoriferous gland