World LiteratureWeek4
advertisement

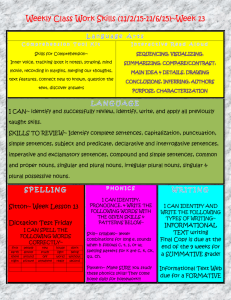
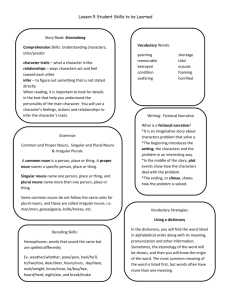
World Literature Week 4 Monday, September 21, 2015 • Write a paragraph (6-8 sentences) about your weekend OR school year thus far. Use 1 compound complex sentence, 2 complex sentences, and two semicolons. Highlight and label the parts of the sentence. Objectives • SWBAT understand the grammar rules for irregular plural nouns. • SWBAT create sentences appropriately using apostrophes with regular and irregular plural nouns. Turn and Talk • What are irregular plural nouns? Regular Nouns • We make regular nouns plural by adding –s to the end of the word • Examples: • cat • chair • shoe cats chairs shoes • However, there are many nouns that do not follow this pattern and they are called irregular nouns Rule # 1 Nouns ending in [s, x, z, ch, and sh] • Form the plural by adding –es to the end of the word • Examples: • • • • • class box buzz watch dish classes boxes buzzes watches dishes Examples Singular Plural beach beaches match matches sandwich sandwiches bush bushes eyelash eyelashes ax axes fox foxes tax taxes kiss kisses Rule # 2 Nouns ending in consonant + [y] • Form plural by changing [y] to [i] and add –es • Examples: • • • • lady city party baby ladies cities parties babies Examples Singular Plural puppy puppies family families story stories library libraries country countries butterfly butterflies discovery discoveries Rule # 3 Nouns ending in [f] or [fe] • Form plural by changing [f] or [fe] to –ves • Examples: • • • • half leaf wife knife halves leaves wives knives • But NOT always! • belief • chef • roof beliefs chefs roofs Examples Singular Plural calf calves loaf loaves scarf scarves thief thieves wolf wolves shelf shelves life lives Rule # 4 Some Nouns that end in [o] • Form plural by adding –es • Examples: • • • • tomato potato hero echo tomatoes potatoes heroes echoes • But NOT Always! • • • • kangaroo piano photo auto kangaroos pianos photos autos Examples Singular Plural potato potatoes kangaroo kangaroos echo echoes tomato tomatoes photo photos auto autos hero heroes piano pianos Irregular forms without –s • Examples: • • • • • • • • man woman child mouse goose foot ox tooth men women children mice geese feet oxen teeth • These nouns just need to be memorized because they do not follow a rule Examples Singular Plural woman women goose geese man men mouse mice ox oxen tooth teeth child children foot feet Some nouns have the same singular and plural form • Examples: • • • • • • a shrimp a series a fish a deer a sheep a moose two shrimp two series two fish two deer two sheep two moose • These nouns are determined plural or singular by the context of the sentence Think, Walk, Pair, and Share • What are the different ways to use apostrophes? 2 Main Uses of Apostrophes: 1. To form a contraction: ’ don t ’ ’ can t wouldn t 2. To show possession ’ ’ John s car the boy s bike ’ the workers contract 2 rules for adding an apostrophe to form a possessive 1. If a word ends in –s already, add only the apostrophe: ’ The students backpacks were stolen from the classroom during the break. 2. If the word does not end in –s, add ’s: The instructor ’s parking permit was stolen. ALERT: Some words are possessive without the apostrophe. These words are the possessive pronouns: Tip: Be careful not to confuse it’s and its. it’s = it is my, mine its his her, hers your, yours our, ours their, theirs whose Practice • Practice using irregular plural nouns and apostrophes with the handout. Homework • Complete the worksheet. Tuesday, September 22, 2015 • Complete the Exit Ticket and then SSR (20 minutes) Objectives • SWBAT Distinguish the differences between informal and formal tones while reading short passages. • SWBAT write a letter displaying the differences in informal and formal tones. Think, Pair, and Share • Reflecting on your background knowledge and personal experience what do you already know about tone? Tone The attitude that an author takes toward the audience, the subject, or the character. Conveyed through the author’s words and detail. How to identify the TONE? Tone must be inferred through the use of descriptive words You can recognize the tone/ attitude by the language/ word choices the author uses Words that describe tone POSITIVE - Optimistic - Formal -Humorous , witty - Amused, Cheerful - Joyful, jubilant - Complimentary - Compassionate -Reverent; respectful NEGATIVE - Pessimistic - Informal - Sarcastic, Ironic -Threatening, Horror -Nonchalant -Indifferent NEUTRAL - Detached Authoritative Straightforward: Matter-of-fact: Disinterested: Formal vs. Informal • When we write essays (or send emails to teachers) are tone must CONSISTENTLY be Formal… • What’s the difference between formal and informal tones? Informal Language— WORDS TO AVOID •Casual Speaking st nd •1 /2 Person Pronouns: •Examples: •I, me, my, you, your, our, we Contractions Words that are a combination of two words. Examples: can't, doesn't, that's, they're, it’s, etc. ALL contractions need to be separated Examples: Cannot, does not, that is, they are, it is, etc. To create a FORMAL tone— WORDS TO USE Write in the 3rd Person Avoid using words like “You” or “Your” or “I” Instead, use the following words as substitutes Examples: "An individual..." or "A person..." or "People," and "One." Avoid Basic Adjectives in Formal Writing • Instead of using basic adjectives that you might use when you are speaking with someone you are very comfortable with--like a friend--instead use words that are academic and enhance the formal tone of your paper. Example 1 Informal: •I think that it's really bad that students have to do so much homework all the time. Example 1 Formal: Many people, specifically students, feel that it is unfair that they receive a surplus of homework each day. Example 2 Informal: When you look at bacteria through a microscope, it might seem like nothing, but its effects are really bad if you're exposed to it directly. Example 2 Formal: If an individual observes bacteria through a microscope, one might find that it appears harmless. However, individuals exposed to bacteria have a higher likelihood of contracting the harmful effects, such as an illness. Practice • Use the worksheet to practice using consistent tones. Formal vs Informal • With your partner write two letters. The first will be a letter to your teacher and the second will be one to a friend. Your topic for the prompt is: Homework. (Do you like or dislike it? Is it useful? Should it be banned?) Homework • Read A Party Down At the Square. Remember to annotate by asking questions and making connections with the text Wednesday, September 23, 2015 • Complete the Apostrophe Do Now Homework • Write 10 sentences using the Sentence Types. Label the parts of sentence. If not labeled correctly, you will be in LaSalle! • Remember to use your Cheat Sheet! Objectives • SWBAT Justify the theme(s) of A Party Down At the Square using evidence from the text. Theme Analysis • Complete the worksheet. Timed Writing • You will have 40 minutes to complete the following prompt: How does the narrator’s tone contribute to Ellison’s purpose for writing A Party Down At the Square? Be sure to include 2 compound sentences, 2 complex sentences, and two compound-complex sentences. (Highlight them) Thursday, September 24, 2015 • SSR (20 minutes) Objective • SWBAT study Grammar skills with peers in stations. Grammar Stations • Station 1: Sentence Types • Station 2: Semicolons • Station 3: Apostrophes and Irregular Plural Nouns • Station 4: Tone/Consistent Word Choice You will spend 12-13 minutes at each station; I will display the timer and prompt you when to move to a different station. You must attend each station. Homework • Study for tomorrow’s CCRS Midterm Friday, September 25, 2015 Homework: Read and annotate The Yellow Wallpaper. Write 5 questions you have about the text. (Must use the starter phrase I wonder…) • Clear your desk and prepare for Midterm. ASSMNT Grade: 40 points Homework • Read and annotate The Yellow Wallpaper. Write 5 questions you have about the text. (Must use the starter phrase I wonder…)