DNA Replication Making New DNA Molecules
advertisement

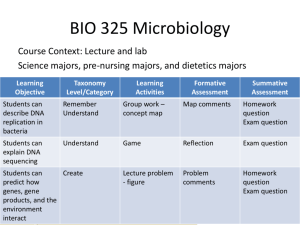
Do Now 1. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? - Sugar (deoxyribose), phosphate, nitrogen base 2. Adenine (A) bonds with ____________ - Thymine (T) 3. Guanine (G) bonds with ____________ - Cytosine (C) Objective: Describe DNA replication. Explain the importance of DNA replication. Model DNA replication. DNA Replication Making New DNA Molecules Objective: Describe DNA replication. Explain the importance of DNA replication. Model DNA replication. Overview of DNA Replication • DNA replication is the process by which the cell copies its DNA. – Happens in the S phase (synthesis) of cell cycle. • The double helix separates, and each strand serves as a template on which a new strand is built. • Each new piece of DNA has one old strand and one new strand. Step 1: Separation of the Strands • In order for the DNA to replicate, the two strands need to be separated. – This happens easily because the hydrogen bonds holding them together are weak. • An enzyme called helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds and separates the strands. Step 2: Building New DNA • A second enzyme called DNA polymerase attaches to the DNA strands to attach complementary nucleotides. • The DNA polymerase joins the nucleotides by covalent bonds in the backbone and hydrogen bonds between the 2 strands. Animation animation 2 Objective: Describe DNA replication. Explain the importance of DNA replication. Model DNA replication. •http://207.207.4.198/pub/flash/24/24.html Objective: Describe DNA replication. Explain the importance of DNA replication. Model DNA replication. Step 3: Proofreading • DNA replication is very accurate, with only about one error in 10,000 paired nucleotides. • Mutations are mistakes or changes to the DNA. – Some of them can be fixed, and some cannot. – Some can have serious effects, and some do not affect the cell at all. • Enzymes proofread and repair many of the mutations that can occur. – This reduces the error rate to about 1 in every 1 billion base pairs. End Result of Replication • Replication results in the creation of two identical molecules of DNA. • The process is described as being semi-conservative. – “semi” = half – “conserve” = to save – Replication is semiconservative, because each new molecule is made of one old strand of DNA and one newly created strand. Activity time! • Now you are going to take your DNA model from yesterday and simulate replication. • You need your model, scissors, glue and colored pencils, using same colors as yesterday! Sugars – Red Adenine - Purple Phosphates – Black Thymine - Pink Guanine – Green Cytosine – Blue • Listen to the instructions as they are given!!