Soviet Takeover of Eastern Europe File
advertisement

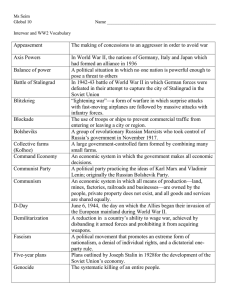
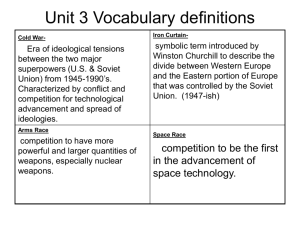
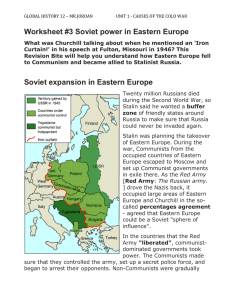
The creation of the Communist ‘bloc’ • Title: Stalin’s takeover of Eastern Europe • Answer the following question: 1. What reasons did Stalin have for expanding Soviet influence into Eastern Europe? • The Soviet Union physically transported and relocated east European industry to the Soviet Union • In eastern European Axis countries, such as Romania and Hungary, this policy was considered as reparations (a principle accepted by Western powers) • Other Eastern Bloc states were required to provide coal, industrial equipment, technology, and other resources to reconstruct the Soviet Union • The initial problem in countries occupied by the Red Army in 1944–45 was how to transform occupation into long-term control • Because communists were small minorities in all countries but Czechoslovakia, they were initially instructed to form coalitions in their respective countries • Soviet takeover of control at the outset generally followed a process: 1. a general coalition of left-wing, antifascist forces; 2. a reorganized 'coalition' in which the communists would have the upper hand and neutralize those in other parties who were not willing to accept communist supremacy; 3. complete communist domination, frequently exercised in a new party formed by the fusion of communist and other leftist groups. SocialDemocrats Communists Communists Other Parties Communists LiberalSocialists Coalition of Left-Wing parties Re-organized ‘coalition’ Full Communist takeover • Answer the following questions: 2. Why did the communist parties of Eastern Europe take orders from the Kremlin? 3. Construct your own flow diagram to show how the communist parties took power in the Eastern European countries. • Quite a significant proportion of the 'partisan movement' that fought to defeat fascist forces during the war, were politically communistoriented • The Soviets, therefore, were to an extent able to 'ride the wave' of respect and admiration these partisans had earned amongst the populations of these countries by the time the war had ended. • Answer the following question: 4. Why might the populations of Eastern European countries have accepted the takeover of their communist minorities? • It was only in the Socialist Republic of Yugoslavia that former partisans (under Tito) entered their new government independently of Soviet influence • Tito insisted on specifically not being a puppet regime • Led to the Tito-Stalin split and other moves towards an "independent socialism" that quickly made SR Yugoslavia unique within the context of overall Eastern Bloc politics. Explain how the Soviet Union took control of Eastern Europe stage by stage. What reasons motivated Stalin to pursue the USSRs interests at the end of the Second World War?