Histology notes Kidney functional unit: nephron (1
advertisement

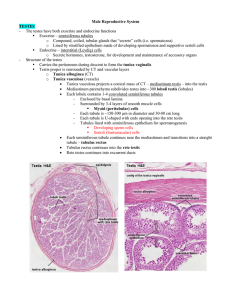
Histology notes Kidney - - - functional unit: nephron (1-4 mio) o cortical nephrons o juxtamedullary nephrons nephron consists of: o renal corpuscle o prox. Conv. Tubule o thin & thick limbs of Henle loop o distal conv. Tubule o collecting tubules & ducts renal corpuscle o glomerolus Afferent arteriole o Bowmans’ capsule Parietal layer –simple squamous epithelium Visceral layer – Podocytes o Between parietal & visceral layer: Urinary space Vascular & urinary pole Podocytes: Primary process Secondary process filtration slits: 25 mm Proximal convoluted tubule: - Simple Cuboidal or low columnar epithelium Numberous mitochondria Brush Border In cross section of tubule o Only a few cells (3-5) o No cell boundaries visible – basolateral interdigitations Henles loop: - - - - Two types of nephrons: o Cortical o Juxtamedullary General structure: o Thick descending part o Thin descending part o Thin ascending part o Thick ascending part o Simple squamous epithelium Cortical nephron: o Short thin descending part o No thin ascending part Juxtamedullary nephron: o Short thick descending part o Long thick ascending &descending part !both! o Thick ascending part Distal convoluted tubule: CELL BORDERS VISIBLE! - Simple Cuboidal epithelium No brush border No apical canaliculi Smaller cells – more cells seen in cross section At the vascular pole of nephron: o Macula densa (tall columnar cells) Liberation of: 1.) Renin 2.) Angiotensinogen 3.) Angiotensin I 4.) Angiotensin II Collecting tubules & ducts: Collecting tubules - cuboidal ep. (cortical) - collumnar ep. (medullary) - Cells stain weaker than usual renal cells Inter cellular limits clearly visible Ep. Responsive to Argentine, Vasopressin, ADH Juxtaglomerular Apparatus: 1) Juxtaglomerular cells a. Tunica media of afferent arteriole specialized cells 2) Macula densa of distal convoluted tubule 3) Extraglomerular mesangial cells –LACIS cells Function: Blood pressure regulation due to production of Renin Bladder & Urinary Passage Consists of: - Calyces Urethers Urinary Bladder Urethra General structure: - Transtional epithelium (Uroepithelium) Lamina propria of CT & vessels Muscle layer o o Circular: Calyces Renal pelvis Urethers Longitudinal: Bladder Internal longitudinal layer Middle circular layer External longitudinal layer Urethra: Male: ~ 20 cm Intramural part Uroepithelium Prostatic part Membranous part Stratified columnar epithelium Spongious part Fossa navicularis: stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium Little glands in the spongious part of the male urethra are mucous glands Female: ~ 40 cm Intramural part: Uroepithelium Membranous part: Stratified squamous epithelium Male Reproductive System: Seminiferous tubules: - - - Spermatozoids are produced in those Pathway: o Convoluted seminiferous tubules o Straight seminiferous tubules o Rete testis o Ductuli efferentes o Epididymic duct General structure: o Germinal / seminiferous epithelium Sertoli Cells Spermatogenic lineage o Basal lamina o Fibrous connective tissue Innermost layer of basal lamina: o Flattened Myoid cells (smooth muscle characteristics) Spermatogenesis: - Process in which Spermatozoids are created Spermatogonium Type A Spermatogenia Stem cells Type B Spermatogonia differentiate Primary Spermatocytes (4n) Slow 1st meiotic division Secondary Spermatocytes (2n) Fast 2nd meiotic division Spermatids (1n haploid) Spermiogenesis: - - - - Process in which Speematids are made into Spermatozoa Divided into 3 phases: o Golgi o Achrosomal o Maturation Golgi: o Proachrosomal granules o Achrosomal granule o Achrosomal vesicle o Centriole movement Achrosomal: o Achrosomal vesicle covers anterior half of nucleus: Achrosome o Forming of: Flagellum Middle Piece o Achrosome: Hydrolytic enzymes responsible for achrosomal reaction in fertilization & therefore get access to oocyte Maturation o Residual body formation o Residual cytoplasm is removed by Sertolli cells in late Spermatids Sertolli Cells: - Structure: o Elongated pyramidal cells o Bases lie on basal lamina o Apical ends extend into lumen of seminiferous tubules o - Adjacent Sertolli cells connected by: Tight junctions (Blood testis barrier) Gap junctions (cycle of seminiferous epithelium) Function: o Support of Spermatozoa (nutrients) o Maturation phase of Spermiogenesis o Secretion of: ABP (androgen binding protein) Inhibin o Production of: Anti-Müllerian-hormone (AMH) o Inhibit Z (growth factor B family o BLOOD-TESTIS-BARRIER Leydig cells: - steroid secreting cells: o Testosterone o Dihydrotestosterone Factors influencing testicular function: Hypothalamus FSH/ CH-RH Inhibin (-) Activin (+) Negative feedback of Androgen Ant. Pituitary gland LH + Leedig Cells Testosterone (Androgen) Blood vessel FSH + Sertolli Cells ABP in seminiferous tubule Intratesticular genital ducts: - - - - Composed of: o Tubuli recti o Rete testis o Ductuli efferentes Tubuli recti: o Loss of spermatogenic cells o Cuboidal epithelium Rete testis: o Thickening of tunica albuginea o Cuboidal epithelium Ductuli efferentes: o 10 – 20 only o Ciliated & uncillated cuboidal epithelium Excretory genital ducts: - - - Composed of: o Ductus Epididymis o Vas deferens o Urethra Ductus Epididymis: o Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia o Basal lamina o Smooth muscle cells Ductus deferens : o Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia o Lamina propria o Muscular layer: Inner longitudinal Middle circular Outer longitudinal Accessory genital glands: - - - Composed of: o Seminal vesicle o Prostate o Bulbourethral glands Seminal vesicles: o Pseudostratified columnar epithelium o Highly tortuous glands / tubes o Produces yellowish fluid: high in fructose Prostate: o Tubuloalveolar glands o Ducts empty into urethra at colliculus seminalis o Has 3 zones & 3 gland types o - Penis Pseudostratified columnar epithelium Bulbourethral glands o Proximal to membranous part of urethra o Tubuloalveolar glands o Simple cuboidal epithelium