Chapter 6

Chapter 6
Performing Basic Vehicle
Maneuvers
Steering
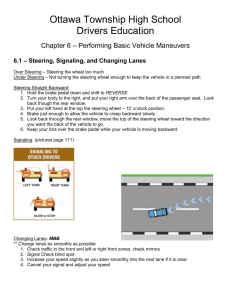
Over Steering
The driver turns the steering wheel too much
Under Steering
The driver did not turn the wheel enough
Steering
Two Methods Used for Steering
Hand Over Hand Steering
Push-Pull Method
Steering in Reverse
When steering in reverse, always turn your steering wheel in the direction that you want the back of your car to go.
Always look behind you and not just in your mirrors
Turnabouts
A turnabout is used for turning your car to go in the opposite direction.
Turnabouts should rarely be used
Types of Turnabouts
Midblock U-Turn
Back into driveway on right side
Pull into driveway on left side
Pull into driveway on rightside
Three-point turnabout
Changing Lanes
Steps to follow while changing lanes:
Check traffic in the front and left-front zones. Check rear zones through the rearview mirrors
Signal and make a blind-spot check over your left shoulder to see if any vehicle is about to pass you
Changing Lanes
Check traffic ahead
Increase your speed slightly as you steer smoothly into the next lane if it is clear
Cancel your signal and adjust your speed
Making Turns
Check all around your car (6 zones)
Be in the lane closest to turn about a block before turn
Obey all traffic signs, regulations, signals, and roadway markings
Remember to yield to oncoming traffic and that pedestrians have the right of way
The last place you should always look is the direction that you’re turning.
Making Turns
It is recommended to slowdown to about
10 mph when making a turn.
Always brake gradually for your turns
Steering and Speed Control is vital when making a proper turn.
Always turn into the closet lane available to you.
Backing Left and Right
Check traffic (6 zones)
Use hand over hand method
If you want to back to the right, steer to the right
If you want to back to the left, steer to the left
Types of Parking
Angle - To park your vehicle diagonally to the curb
Perpendicular - To park your vehicle at a right angle to the curb
Parallel - To park your vehicle parallel to the curb
Parking
When you leave any type of parking space, you must yield to all traffic
Always signal when entering into a parking space
A person’s Reference Point, Standard
Reference Point, and Personal
Reference Point can be used for parking
Up and Down Hill Parking
Uphill with a curb - Street
Uphill without a curb - Grass
Downhill with a curb - Grass
Downhill without a curb - Grass
Always make sure you know the direction of your tires when leaving a parking spot
Always use your Parking Brake on a hill
Hand Signals
These signals are most often used by motorcyclists and bicyclists
Left – Left Arm Straight Out
Right – Left Arm Bent at 90 degrees up
Stop – Left Arm Bent at 90 degrees down
Key Vocab
Reference Point
A part of the outside/inside of he vehicle as viewed from the driver seat, that relates to some part of the roadway.
Push-Pull Steering
Pushing the steering wheel up with one hand and down with the other.
Key Vocab
Parallel – Difficult parking maneuver that is done along side a curb and backing into a stall
Rear Zone – The zone behind you that you want to make sure is clear before backing up
Key Things to Remember
You should be in the lane closest to the center lane to begin a left turn on a two-way street.
A standard reference point might be a hood ornament.
Only use your left foot to push down on the
Clutch Pedal
Look Ahead, Plan Ahead, Stay Back!!!