Carbon Cycle
advertisement
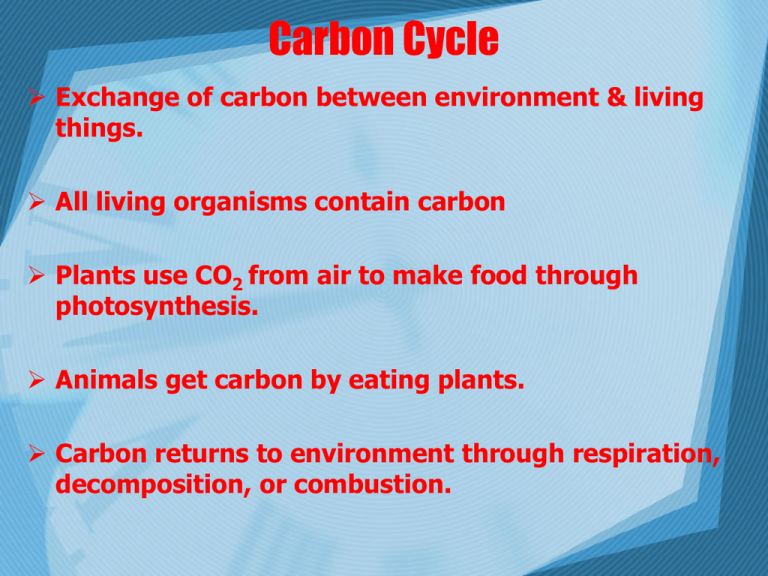
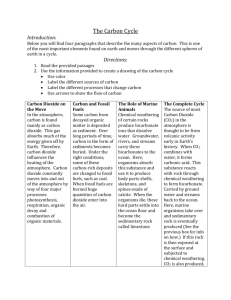
Carbon Cycle Exchange of carbon between environment & living things. All living organisms contain carbon Plants use CO2 from air to make food through photosynthesis. Animals get carbon by eating plants. Carbon returns to environment through respiration, decomposition, or combustion. Carbon Cycle Carbon Pools Pool Atmosphere Terrestrial Plants Soil Organic matter Ocean Fossil Fuel Deposits Marine Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks Amount in Billions of Met ric Tons 578 (as of 1700) - 766 (a s of 1999) 540 to 610 1500 to 1600 38,000 to 40,000 4000 66,000,000 to 100,000,000 Carbon is stored on our planet in the following major pools: • as organic molecules in living and dead organisms found in the biosphere; • as the gas carbon dioxide in the atmosphere; • as organic matter in soils; • in the lithosphere as fossil fuels and sedimentary rock deposits such as limestone, dolomite and chalk; • in the oceans as dissolved atmospheric carbon dioxide and as calcium carbonate shells in marine organisms. 2/12 Global Carbon Cycle Carbon is exchanged between the active pools due to various processes such as photosynthesis and cellular respiration between the land and the atmosphere, and diffusion between the ocean and the atmosphere. 3/12 Plants & The Carbon Cycle • Plants take in carbon dioxide and convert it to sugar which can be stored until used for energy. • This process is called photosynthesis. • Photosynthesis= Energy (sun)+ Water+ Carbon dioxide Glucose+ Oxygen Plants & The Carbon Cycle • Plants release small amounts of carbon dioxide as a waste product when they convert their stored sugar to chemical energy (ATP). • Plants need ATP for growth & reproduction. • This process is called cellular respiration. Cellular Respiration: C6H12O6 + O2 - CO2 + H2O + energy Animals & The Carbon Cycle • Animals eat carbon contained in animal and plant tissues and release carbon dioxide as a waste product. • This process is cellular respiration. Cellular Respiration: C6H12O6 + O2 - CO2 + H2O + energy Decay & The Carbon Cycle: • Decomposers release the carbon from dead plant and animal tissues back into the atmosphere. Fossil Fuels & The Carbon Cycle: • Over millions of years fossil fuels may form from the buried remains of plants and animals. Fossil Fuels & The Carbon Cycle: • This carbon reenters the atmosphere during combustion (burning). The Oceans & The Carbon Cycle: • Dissolved carbon dioxide in sea water becomes deposited as calcium carbonate shells. The Oceans & The Carbon Cycle: • Over millions of years, these shells form sedimentary rock. • Ocean deposits are the biggest sink of carbon on the planet. • The Rock Cycle ultimately releases carbon stored in sedimentary rock. Explore Carbon Cycle • Use the diagram from the website to examine the elements of the carbon cycle.