Power Point Slide Show
advertisement

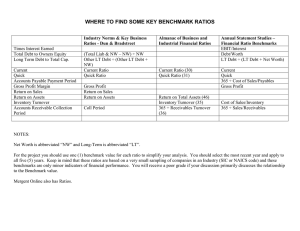
Ratio Analysis By: Joaquin Castrillo Eliezer Aldarondo at ed Current Ratio 1.38 1.89 3.77 1.94 Quick Ratio 0.81 1.11 2.33 1.16 Debt Ratio 41% 22% 10% 23% 6% 9% 15% 10% Return on Assets 13% 17% 27% 20% Return on Equity 22% 21% 29% 25% Average Collection Period 45.63 36.32 33.18 38.08 Average Days of Inventory 63.27 60.83 66.79 63.49 Return on Sales Co n so l Di vi si on id C Di vi si on B Di vi si on A Ratio Chart Ratio Comparisons 35% 30% 25% 20% Division A Division B Division C 15% 10% 5% 0% Return on Sales Return on Assets Return on Equity Liquidity Ratios Current & Quick Ratios: -There is an increase in all three ratios meaning that the company’s ability to pay short term debts increased. -Decreasing numbers in these numbers could make the company go bankrupt Long Term Solvency Ratios Debt Ratio: - This ratio is decreasing in every one of the divisions meaning that the total debt of the company is decreasing as well. -This is a positive trend for the company since we can see that the company has smaller and smaller debts to pay. Asset Management Ratios Average Collection Period: - These ratios seem to be in a decreasing trend which in our case is positive. In division A we can see that the time the company had to wait in order to get their accounts receivable was more than a month but in Division C we can see that the amount of time has decreased to approximately a month, which is a very respectable time to wait. Days Sales in Inventory: - These ratios seem to be in a stable trend which is a positive sign. This means that the amount of inventory that the company is getting is a good amount and it is being sold in a good amount of time. - High numbers of inventory might mean that the company’s products are obsolete or they are not selling the products. The End