Chapter 39 NCLEX Questions Gastrointestinal
advertisement

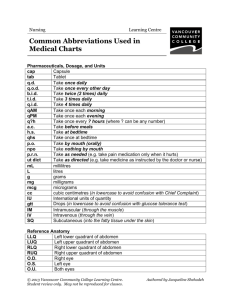
Chapter 39 NCLEX Questions Gastrointestinal 1. 1.ID: 809545608 When assessing a patient's abdomen, what would be most appropriate for the nurse to do? A. Palpate the abdomen before auscultation. B. Percuss the abdomen before auscultation. C. Auscultate the abdomen before palpation. Correct D. Perform deep palpation before light palpation. During examination of the abdomen, auscultation is done before percussion and palpation because these latter procedures may alter the bowel sounds. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 2. 2.ID: 809545631 When preparing a patient for a capsule endoscopy study, what should the nurse do? A. Ensure the patient understands the required bowel preparation. Correct B. Have the patient return to the procedure room for removal of the capsule. C. Teach the patient to maintain a clear liquid diet throughout the procedure. D. Explain to the patient that conscious sedation will be used during placement of the capsule. A capsule endoscopy study involves the patient performing a bowel prep to cleanse the bowel before swallowing the capsule. The patient will be on a clear liquid diet for 1 to 2 days before the procedure and will remain NPO for 4 to 6 hours after swallowing the capsule. The capsule is disposable and will pass naturally with the bowel movement, although the monitoring device will need to be removed. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 3. 3.ID: 809545602 Inspection of an older patient's mouth reveals the presence of white, curd-like lesions on the patient's tongue. What is the most likely etiology for this abnormal assessment finding? A. Herpesvirus B. Candida albicans Correct C. Vitamin deficiency D. Irritation from ill-fitting dentures White, curd-like lesions surrounded by erythematous mucosa are associated with oral candidiasis. Herpesvirus causes benign vesicular lesions in the mouth. Vitamin deficiencies may cause a reddened, ulcerated, swollen tongue. Irritation from ill-fitting dentures will cause friable, edematous, painful, bleeding gingivae. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 4. 4.ID: 809649624 The nurse should recognize that the liver performs which functions (select all that apply)? A. Bile storage B. Detoxification Correct C. Protein metabolism Correct D. Steroid metabolism Correct E. Red blood cell (RBC) destruction The liver performs multiple major functions that aid in the maintenance of homeostasis. These include metabolism of proteins and steroids as well as detoxification of drugs and metabolic waste products. The Kupffer cells of the liver participate in the breakdown of old RBCs. The liver produces bile, but storage occurs in the gall bladder. Awarded 0.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 5. 5.ID: 809544997 The health care team is assessing a male patient for acute pancreatitis after he presented to the emergency department with severe abdominal pain. Which laboratory value is the best diagnostic indicator of acute pancreatitis? A. Gastric pH B. Blood glucose C. Serum amylase Correct D. Serum potassium Elevated serum amylase levels indicate early pancreatic dysfunction and are used to diagnose acute pancreatitis. Serum lipase levels stay elevated longer than serum amylase in acute pancreatitis. Blood glucose, gastric pH, and potassium levels are not direct indicators of acute pancreatic dysfunction. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 6. 6.ID: 809545656 The nurse is performing a focused abdominal assessment of a patient who has been recently admitted. In order to palpate the patient's liver, where should the nurse palpate the patient's abdomen? A. Left lower quadrant B. Left upper quadrant C. Right lower quadrant D. Right upper quadrant Correct Although the left lobe of the liver is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen, the bulk of the liver is located in the right upper quadrant. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 7. 7.ID: 809545675 The patient had a car accident and was "scared to death." The patient is now reporting constipation. What affecting the gastrointestinal (GI) tract does the nurse know could be contributing to the constipation? A. The patient is too nervous to eat or drink, so there is no stool. B. The sympathetic nervous system was activated, so the GI tract was slowed. Correct C. The parasympathetic nervous system is now functioning to slow the GI tract. D. The circulation in the GI system has been increased, so less waste is removed. The constipation is most likely related to the sympathetic nervous system activation from the stress related to the accident. SNS activation can decrease peristalsis. Even without oral intake for a short time, stool will be formed. The parasympathetic system stimulates peristalsis. The circulation to the GI system is decreased with stress. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 8. 8.ID: 809545667 A 90-year-old healthy man is suffering from dysphagia. The nurse explains what age-related change of the GI tract is the most likely cause of his difficulty? A. Xerostomia Correct B. Esophageal cancer C. Decreased taste buds D. Thinner abdominal wall Xerostomia, decreased volume of saliva, leads to dry oral mucosa and dysphagia. Esophageal cancer is not an agerelated change. Decreased taste buds and a thinner abdominal wall do not contribute to difficulty swallowing. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 9. 9.ID: 809545673 A patient had a stomach resection for stomach cancer. The nurse should teach the patient about the loss of the hormone that stimulates gastric acid secretion and motility and maintains lower esophageal sphincter tone. Which hormone will be decreased with a gastric resection? A. Gastrin Correct B. Secretin C. Cholecystokinin D. Gastric inhibitory peptide Gastrin is the hormone activated in the stomach (and duodenal mucosa) by stomach distention that stimulates gastric acid secretion and motility and maintains lower esophageal sphincter tone. Secretin inhibits gastric motility and acid secretion and stimulates pancreatic bicarbonate secretion. Cholecystokinin allows increased flow of bile into the duodenum and release of pancreatic digestive enzymes. Gastric inhibitory peptide inhibits gastric acid secretion and motility. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 10. 10.ID: 809545677 The patient tells the nurse she had a history of abdominal pain, so she had a surgery to make an opening into the common bile duct to remove stones. The nurse knows that this surgery is called a A. colectomy B. cholecystectomy C. choledocholithotomy Correct D. choledochojejunostomy A choledocholithotomy is an opening into the common bile duct for the removal of stones. A colectomy is the removal of the colon. The cholecystectomy is the removal of the gallbladder. The choledochojejunostomy is an opening between the common bile duct and the jejunum. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 11. 11.ID: 809545671 The ED nurse has inspected, auscultated, and palpated the abdomen with no obvious abnormalities, except pain. When the nurse palpates the abdomen for rebound tenderness, there is severe pain. The nurse should know that this could indicate what problem? A. Hepatic cirrhosis B. Hypersplenomegaly C. Gall bladder distention D. Peritoneal inflammation Correct When palpating for rebound tenderness, the problem area of the abdomen will produce pain and severe muscle spasm when there is peritoneal inflammation. Hepatic cirrhosis, hypersplenomegaly, and gall bladder distention do not manifest with rebound tenderness. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 12. 12.ID: 809545619 A patient who is scheduled for surgery with general anesthesia in 1 hour is observed with a moist, but empty water glass in his hand. Which assessment finding may indicate that the patient drank a glass of water? A. Flat abdomen without movement upon inspection B. Tenderness at left upper quadrant upon palpation C. Easily heard, loud gurgling in the right upper quadrant Correct D. High-pitched, hollow sounds in the left upper quadrant If the patient drank water on an empty stomach, gurgling can be assessed without a stethoscope or assessed with auscultation. High-pitched, hollow sounds are tympanic and indicate an empty cavity. A flat abdomen and tenderness do not indicate that the patient drank a glass of water. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 13. 13.ID: 809545669 When caring for the patient with heart failure, the nurse knows that which gastrointestinal process is most dependent on cardiac output and may affect the patient's nutritional status? A. Ingestion B. Digestion C. Absorption Correct D. Elimination Substances that interface with the absorptive surfaces of the GI tract (primarily in the small intestine) diffuse across the intestinal membranes into intestinal capillaries and are then carried to other parts of the body for use in energy production. The cardiac output provides the blood flow for this absorption of nutrients to occur. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points.