Ch. 21 Shoulder Injuries
advertisement

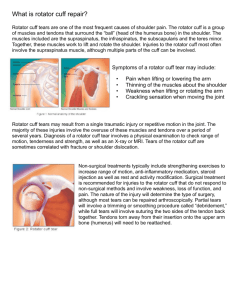
Ch. 21 Shoulder Injuries Impingement Syndrome Space between humeral head below and acromion above becomes narrowed The structures that live in that space becomes impinged ◦ Joint capsule ◦ Tendons of rotator cuff ◦ bursa Impingement Syndrome Most common in overhead athletes S/S: pain over GH area, weakness with abduction, decreased IR Treatment: fix technique, strengthen rotator cuff, taping Special Tests ◦ Hawkins-Kennedy ◦ Neer’s Rotator Cuff Tear Can occur in young and old people Usually a traumatic injury in young Partial thickness vs full thickness tears Common overuse injury in overhead athletes Rotator Cuff Tear Partial tears will have pain with normal ROM Complete tears will usually be unable to move the arm normally Diagnosis with MRI Special Tests ◦ Drop Arm ◦ Empty Can Biceps Tendonitis Irritation of the tendon in the bicipital groove Caused by repetitive overhead motion Treatment: NSAIDs, rest, ice, ultrasound Biceps Tendon Rupture Usually occurs with a ‘pop’ during vigorous activity S/S: bruising, Popeye muscle Treat conservatively or surgical Clavicular Fracture Most common at the distal third Usually from contact with equipment, player, or ground Usually an obvious deformity present Treatment includes sling, clavicle harness, ice, NSAIDs Shoulder Dislocation Most common is anterior Occurs when arm is abducted and a force causes external rotation Will notice a flat deltoid Place in sling and refer to doctor Usually treated conservatively Glenoid Labrum Injuries Glenoid labrum holds the humeral head in place on the glenoid fossa Tear occurs with trauma or repetitive stress Baseball pitchers are susceptible to labral changes Glenoid Labrum Injuries S/S: pain, catching, popping, decrease ROM Treatment conservatively with rotator cuff strengthening Surgery to trim off flap Special Test ◦ Clunk Test Multidirectional Instability Shoulder slips out of socket easily Usually bilateral Strengthening program should solve problem Special Test ◦ Sulcus Sign ◦ Anterior Apprehension ◦ Feagin’s Acromioclavicular Separation AC sprain occurs when athlete falls on tip of shoulder S/S: pain, decreased ROM, elevation of clavicle Treat with immobilization, ROM exercises Brachial Plexus Injury Known as a stinger or burner Brachial plexus is a group of nerves that innervate the arm MOI is head and neck forced to one side therefore stretching the brachial plexus on the other side Brachial Plexus Injury S/S: pain from neck down to the arm, pins and needles sensation, weakness in arm Can last for several minutes to several hours Symptoms must resolve before return to play