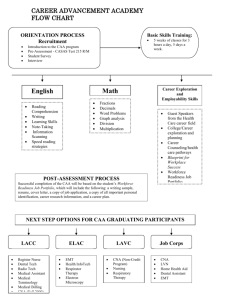
History of health care

Unit 2
Introduction
The Health Care industry employs over 10 million workers in over 200 different health careers.
Introduction
Health care has become a
2-billion-dollar-a-day business.
$2,000,000,000.00
Many different types of facilities make up this network of health care systems.
I. Types of Facilities
A. Hospitals: vary in size as well as services provided.
1. Small: serve communities
2. Large: serve larger areas & provide different services
-
-
-
-
I. Types of Facilities
A. Hospitals: fall under different income classifications :
Private or Proprietary
(for profit)
Religious
(funds by religious affiliation)
Nonprofit
(funds used for institution only)
Government
(funded by government)
I. Types of Facilities
A. Hospitals: types of hospitals:
General – treat all age groups & conditions; provides diagnostic, medical, surgical, and emergency care services; usually private
(Health Central Hospital) (Orlando General
Hospital)
I. Types of Facilities
A. Hospitals: types of hospitals:
Specialty – provide care for special conditions or age groups; private; donations
(Shriner’s Burn Center – Cincinnati)
(MD Anderson Cancer Centers)
(Arnold Palmer Hospital For Children)
(Winnie Palmer Hospital For Women)
I. Types of Facilities
A. Hospitals: types of hospitals:
Government – operated/funded by federal, state and local governments
(Veteran’s Administration “VA Hospital”)
(State Psychiatric Hospital - Chattahoochee)
I. Types of Facilities
A. Hospitals: types of hospitals:
University/College Medical
Centers – provide hospital services; research & education facility as well; can be funded privately, donations, or government sources (research)
I. Types of Facilities
A. Hospitals: types of hospitals:
University/College Medical
Centers – Examples:
University of Miami (Miami)
University of South Florida (Tampa)
Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, Maryland)
Cleveland Clinic (Ohio – School of Medicine)
I. Types of Facilities
B. Long-Term Care: provide assistance/care for elderly patients called “residents.” They can also provide care for persons with disabilities and/or chronic long-term illness.
I. Types of Facilities
B. Long-Term Care: Types:
- Nursing/Geriatric Homes : provide basic care for those who can no longer care for themselves; assist with ADL’s (activities of daily living); provide safe/secure environment; social interaction
I. Types of Facilities
B. Long-Term Care: Types:
- Extended/Skilled Care : provide skilled nursing care and rehabilitative services to prepare residents to return home or to other LTC facility
I. Types of Facilities
B. Long-Term Care: Types:
- Extended/Skilled Care : Subacute
Units: provide Services to residents who need rehabilitation to recover from major illness
(surgery, cancer, dialysis, heart disease, stroke)
-
I. Types of Facilities
B. Long-Term Care: Types:
Independent/Assisted Living : individuals who can care for themselves (ADL’s) can rent or purchase apartment in facility
(meals, housekeeping, laundry, transportation, social events, basic medical care are provided)
-
I. Types of Facilities
B. Long-Term Care: Types:
Independent/Assisted Living : most are associated with nursing homes; this allows resident to move from one facility to the other as conditions warrant
-
-
-
-
I. Types of Facilities
B. Long-Term Care:
Many career opportunities are available in long term care for health care workers.
Regulated by AHCA and OBRA
AHCA=Agency for Health Care Administration
OBRA = Omnibus Reconciliation Act of 1987
I. Types of Facilities
C. Medical Offices: can vary to only have a single doctor or a group of doctors; can be a general practice or specialty practice
-
-
-
I. Types of Facilities
C. Medical Offices: Types:
General Practice: treats all ages and all conditions
“Family Doctor”
“General Practitioner”
-
-
-
-
-
I. Types of Facilities
C. Medical Offices: Types:
Specialty Practice: specializes in one particular age group or type of treatment given
Pediatrics
Cardiology
Obstetrics
Orthopedics
I. Types of Facilities
C. Medical Offices: Offer several different opportunities for employment. Administration , nursing, bookkeeping, billing, medical coding . offices can be found in different locations to include; office buildings, standalone offices and even malls.
I. Types of Facilities
D. Dental Offices: can vary in size; one dentist, group of dentist
(DDM=Doctor of Dental Medicine)
(DDS=Doctor of Dental Services)
Dentists’ offices can also be found in many different places to include professional office buildings, standalone offices and even malls.
I. Types of Facilities
E. Clinics: Health care facilities which can provide different types of care. Can be dental or medical or (veterinary).
I. Types of Facilities
E. Clinics: Types:
- Surgical: perform minor surgeries, also called outpatient or “oneday” clinics; patient is sent home same day after surgery
I. Types of Facilities
E. Clinics: Types:
- Urgent Care: provide first aid or emergency care to ill or injured patients; not equipped to treat critically ill patients
I. Types of Facilities
E. Clinics: Types:
- Rehabilitation: offer physical occupational, speech therapies for patients after injury or illness
I. Types of Facilities
E. Clinics: Types:
- Specialty: offer care for patients with specific diseases (diabetes, cancer), disorders (stroke) or injuries (head injury)
I. Types of Facilities
E. Clinics: Types:
- Outpatient: offer procedures to patients who are then not admitted to the hospital – go home. Different than surgical clinics in that procedures are not only surgeries
(endoscopy, colonoscopy)
I. Types of Facilities
E. Clinics: Types:
- Health Department: may offer treatment for pediatric patients; sexually transmitted diseases; respiratory diseases; immunizations and other services
(pharmacy)
I. Types of Facilities
E. Clinics: Types:
- Medical Center: Usually located in colleges and universities; often offer FREE medical care and treatment to provide learning experiences for medical students.
I. Types of Facilities
F. Optical Centers: can be individually owned by ophthalmologist (M.D. or D.O.) or optometrist (O.D.); or part of large chain of stores
(Lens Crafters,
Pearle Vision, etc.)
I. Types of Facilities
G. Emergency Care Services: provide care for victims of accidents or sudden illness by highly trained medical professionals
-
-
-
-
-
I. Types of Facilities
G. Emergency Care Services:
Types:
Private ambulance services
Rescue squads (Fire Dept.)
Emergency/Urgent Care Clinics
Emergency Rooms
Aircraft (helicopters/airplanes)
-
-
-
I. Types of Facilities
H. Laboratories: can be part of larger facility, such as hospital, clinic or college/university, or can be stand-alone
Pathologist
Laboratory technicians
Phlebotomist
-
-
-
-
I. Types of Facilities
I. Home Health Care: provide care in patient’s home
Nursing care
Personal care
Therapy
Homemaking
I. Types of Facilities
J. Hospice: care for patients who have less than 6 months to live as a result of a medical condition
Care can occur in the patient’s home or in Hospice care centers
The family of the patient is ALSO cared for.
-
-
-
-
I. Types of Facilities
K. Mental Health: Types:
Counseling centers
Psychiatric clinics
Chemical abuse
Physical abuse
-
-
-
-
I. Types of Facilities
L. Genetic Counseling:
Prenatal (before birth) tests
Checking for abnormalities & birth defects
Identify all medical options
Assist parents in coping with genetic disorders of child
I. Types of Facilities
M. Rehabilitation: can be located in hospitals, clinics or be standalone entity; the goal of rehabilitation is to have the patient reach their maximum potential, given their specific medical condition.
I. Types of Facilities
N. Health Maintenance
Organizations (HMO’s): provide total health care directed toward preventative health care; some
HMO’s are run by large corporations with many employees (lowers costs)
I. Types of Facilities
O. Industrial Health Care
Centers: found in large companies; provide healthcare for employees of the company; focus on accident prevention and safety
I. Types of Facilities
P. School Health Services: found in many schools and colleges; many different levels of services provided
II. Government Agencies
Government Agencies: are financially supported by taxes.
National and international organizations exist around the world which monitor health and health care-related issues.
-
-
-
II. Government Agencies
A. World Health Organization
(WHO): international agency sponsored by the United Nations
Statistics & info about diseases
Publishes health info
Investigates/addresses serious health threats around the world
II. Government Agencies
B. U.S. Dept. of Health and Human
Services (USDHHS): national agency
- Deals with health problems within the United States
II. Government Agencies
C. National Institutes of Health
(NIH): national agency
- Division of USDHHS involved in research of diseases
II. Government Agencies
D. Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention (CDC): national agency
- Division of USDHHS concerned with causes, spread, and control of diseases in populations
II. Government Agencies
E. Food and Drug Administration
(FDA): national agency
- Responsible for regulating food and drug products sold to the public
II. Government Agencies
F. Agency For Health Care Policy and Research (AHCPR): national agency established in 1990
- Responsible for researching the quality of health care delivered and identify standards of treatment for health care facilities
II. Government Agencies
G. Occupational Safety and Health
Administration (OSHA): national agency
- Establishes & enforces standards that protect workers from job related injuries and illnesses
-
-
-
-
II. Government Agencies
H. Health Departments: national agency; falls under USDHHS
Community based
Gather statistics, trends
Prevention education
Immunizations
III. Health Insurance Plans
In order to pay for costs associated with health care most people rely on health insurance plans.
There are THOUSANDS of insurance plans , but most work under same basic idea: You pay premium to insurance company and insurance covers costs.
III. Health Insurance Plans
The amount of payment and type of services covered by the insurance company you have may vary. Not all insurances are the same and no two insurance plans are alike . Some cover more, some cover less than others.
III. Health Insurance Plans
Terms to know:
Deductible: amount paid by patient for medical services before policy begins to pay
Example: $500 out-of-pocket before insurance pays anything
III. Health Insurance Plans
Terms to know:
Co-insurance: expenses for medical care are shared between the patient and the insurance company
Example: 80/20 plan: insurance pays 80%, you pay remaining 20%
III. Health Insurance Plans
Terms to know:
Co-payment: also known as “copay” this is the amount of $ you pay for a particular service regardless of total cost of service
Example: $25 per visit; whether for a physical or more serious illness
III. Health Insurance Plans
A. Medicare: government programs that provides health care for individuals over the age
of 65 and for any person who has been disabled for at least two years
III. Health Insurance Plans
A. Medicare: Types:
- Part A: covers hospital services and care provided by an extended care facility, or home health care agency after hospitalization
-
-
-
III. Health Insurance Plans
A. Medicare: Types:
Part B: covers doctor’s visits, outpatient treatments, therapy and other health care
A deductible is paid for Medicare
Part B
Part B only pays 80%
-
-
-
III. Health Insurance Plans
B. Medicaid: medical assistance program operated by individual states. Persons covered by this program vary from state to state.
Low income
Children who qualify
Physically disabled or blind
III. Health Insurance Plans
B. Medicaid: provides inpatient and outpatient hospital services, physician’s medical and surgical care, lab, x-ray, well-baby and well-child care, including immunizations
III. Health Insurance Plans
C. Worker’s Compensation: provides treatment for workers injured on the job. Funded by employers and each individual state
III. Health Insurance Plans
D. TRICARE: U.S. Government health insurance program.
Provides care for all active duty personnel and their families, survivors of military personnel, and retired members of the military
IV. Organizational Structure
All health care facilities must have an organizational structure . This is the line of authority, or chain of command within a facility. This organizational structure of a facility should indicate areas of responsibility.
IV. Organizational Structure
The higher you are on the organizational structure of an institution or facility, the more responsibility you will have.
IV. Organizational Structure
Superintendent
Asst. Superintendent
School Principal
Asst. Principal Asst. Principal Asst. Principal
Teacher Teacher Teacher Teacher Teacher Teacher
Student Student Student Student Student Student Student Student Student Student Student Student
IV. Organizational Structure
Hospital
Administrator
Chief Nursing
Officer
Nurse Manager
RN RN RN
LPN LPN LPN
CNA CNA CNA CNA CNA CNA
LPN LPN LPN
CNA CNA CNA CNA CNA CNAt
IV. Organizational Structure
CNA CNA CNA CNA CNA CNA CNA CNA CNA CNA CNA CNA
LPN LPN LPN LPN LPN LPN
RN RN RN
Nurse Manager
Chief Nursing
Officer
Hospital
Administrator