Disorders Worksheet

WS – Spinal cord Info & Brain disorders
Name: ___________________
A. Alzheimer’s disease F. encephalitis L. meningitis
B. ataxia
C. cerebral edema
D. cerebral palsy
E. Cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
G. hemiplegia
H. Huntington’s chorea
I. hydrocephalus
J. ischemia
K. kernicterus
M. multiple sclerosis
N. Parkinson’s disease
O. Transient Ischemic
Attack (TIA)
_____ Ima Sue Ellen is being given corticosteroids to reduce a swelling involving the membranes covering the brain.
_____ Mr. Pot A. Tohead’s MRI shows a blockage of the cerebral aqueduct resulting in a fluid buildup within the brain. If the situation is not rectified, the pressure on the brain tissue may cause permanent brain damage or even death.
_____ Mrs. Ura Kidin visited her doctor after experiencing some numbness & temporary paralysis.
The doctor stated that she had a “pre-stroke” - temporary episodes of reversible cerebral ischemia
– what is the term for this?
_____ Swelling of the brain tissue due to a fluid buildup from trauma or infection is known as __.
_____ Shay Kin is in her mid 40s and has just begun to have muscle control problems. You check her antibody levels and determine that it is a demyelinating disorder that is believed to be autoimmune in nature. What is the name of this disorder?
_____ A lumbar puncture can be used to draw out spinal fluid to check for infection. If the infection is within the membranes lining the spinal cord, it is termed spinal ___.
_____ If Mrs. Ura Kidi n’s MRI identifies a blood clot in a cerebral artery, this puts her at great risk for a _____, commonly called a stroke
_____ Mr. Simmons is an aged patient that is having trouble naming things, determining what time period of history he is in, and other difficulties. You diagnose ___________ which is a progressively degenerative disease of the brain ultimately results in dementia.
_____ Lefty Lookinback had a stroke which resulted in paralysis of the right side of body due to brain injury. This paralysis is called ____.
_____ A trauma to the head (or any other part of the body) can damage blood vessels causing deprivation of blood supply to tissue resulting in deficient oxygen and nutrient delivery to cells. This deprivation & possible tissue death is known as ___.
_____ Problems during pregnancy or labor & delivery that cause a lack of oxygen to the baby can cause ____.
_____ Mrs. Butter crust noticed that her newborn son Amarillo’s skin was slightly yellow. She suspected Jaundice and went to get treatment so the baby wouldn’t get worse and develop ______.
_____ Klum See fell down the stairs and hit the posterior inferior portion of his skull. While he was conscious, his uncoordinated, wavering motions led his friend, Smar Tee, to surmise that he had bruised his cerebellum causing ____.
_____ While working in the nursing home, you meet a patient in his 60s with tremors, stiff facial expressions, and very slow movements. You read the chart and notice that he is being treated with the drug L-dopa, a synthetic form of dopamine. This will help his symptoms since the disease is caused by the degeneration of dopamine releasing neurons in his brain.
_____ In your clinic, you see a woman in her mid 40s who exhibits wild, jerky motions of her arms and legs. She tells you that her father showed the same signs in his 40s and died in his early 60s. She has been treated with drugs that block dopamine to help calm her symptoms. You realize that she has ____.
Short Answer:
I. Which compound in appropriate amounts helps prevent spina bifida? _______________
II. What is the difference between flaccid and spastic paralysis?
Motion
Flaccid Spastic
Muscle health
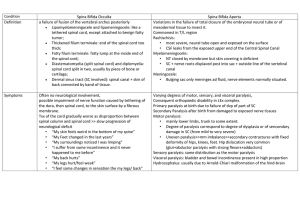
III. Matching for spina bifida.
_____1. No external manifestations
_____2. Cyst contains meninges, CSF, portions of spinal cord and nerve roots
_____3. Fluid filled cyst protrudes from spin
_____4. Cyst contains meninges & CSF
A. Cystic
B. Myelomeningocele
C. Meningocele
D. Occulta
IV. List the features of the spinal cord. a. Approximately ___________ long and extends from _________________________ to
__________________________ and is about the size of your ______________ for most of its length. b. Meningeal coverings extend to the level of __________________ c. Spinal Tap: i. What is the purpose of a lumbar (or spinal) tap? ii. Why is this procedure done at the level of L4 or L5? iii. Why must the patient remain lying down for 6-12 hours after this procedure (be specific as to why)?