Esters Finished Version ppt
advertisement

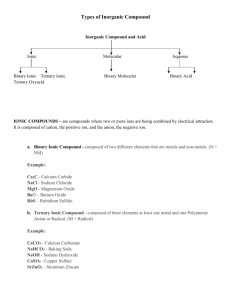
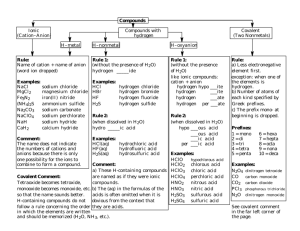
Esters Kaitlyn Picavet, Natalie Williamson, Sidney Wittman, Vivian Ly General Structure O || R – C – O – R’ • The general formula of an ester is written as RCOOR’ Where RCO = carboxylic acid And where OR’= alcohol Nomenclature • Esters are made up of 2 alkyl groups and 2 oxygen atoms. • The alkyl groups and oxygen come from the carboxylic acid and alcohol used in esterification (the formation of esters). Ethanol + Butanoic Acid Ethyl Butanoate + Water Alcohol Carboxylic Acid Ester The name follows the pattern ____yl ____oate • The first blank comes from the alcohol -drop the -anol -add -yl ie) ethanol would be ethyl. • The second blank comes from the carboxylic acid -drop the -oic -add -oate ie) butanoic acid would become butanoate • (drawings on white board) Drawing Rules • Drawing esters combines drawing Alcohols and drawing Carboxylic Acids. O OH Butanoic Acid + OH Ethanol O + H-OH O Ethyl Butanoate • The alkyl with the –oate is double bonded to an oxygen atom. The alkyl with the –yl has an oxygen atom incorporated in it. Physical and Chemical Properties • • • • Low polarity Not as polar as alcohols Dipole-Dipole, London dispersion In Hydrogen bond, esters can only act as Hydrogen acceptors, not donors • Unsaturated fats/oils always have at least one C=C double bond • Similar boiling points to ketones and Aldehydes • As chain length increases, solubility in water decreases • Solid form: Fat • Liquid form: Oil • Fats have a higher boiling point Uses • Esters are known for the odours of fruits, flowers, cosmetics and perfumes. • Esters are also used in fats and oils. • Synthetic esters are added as flavourings to processed foods. • They are good compounds for polar organic compounds like; printing ink and cement. Examples • Apple- methyl butanoate CH3CH2CH2COOCH3 • Banana- 3-methylbutyl ethanoate CH3 | CH3COOCH2CH2CHCH3 • Cherry- ethyl benzoate C6H5COOC2H5 • Pineapple- ethyl butanoate CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3 • Rum- ethyl methanoate CH3CH22CH2CH2CH2CH2COOCH2CH3 Reactions: Esterification • Neutralization/condensation reaction heat carboxylic acid + alcohol ----------> ester + water catalyst organic base O organic salt O || heat || – OH + R–OH --------> RC–O–R + HOH catalyst RC Reactions: Hydrolysis • Ester treated with acid or base: reversal of esterification occurs (split into acid & alcohol) • Products: sodium salt of acid + alcohol O O || || RC–O–R + NaOH- ------> RC–O- + Na+ + R–OH ester base acid alcohol Reactions: Saponification • Fats and oils are esters of long-chain acids: • When heated with a strong base, saponification occurs & produces soap. References AUS-e-TUTE. (n.d.) Chemistry Tutorial: Esters and Esterification. Retrieved from the Web 29/09/11. http://www.ausetute.com.au/esters.html Clark, J. (2004). Introducing Esters. Retrieved from the Web 22/09/11. http://www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/esters/background.html Kimble, M.G. (2008). Esterification Reactions. Retrieved from the Web 29/09/11. http://www.ipfw.edu/chem/112/kimble/5-Synthesis%20of%20Esters.pdf Snelling, C.R. (2002). Synthesis of an Ester: Fischer Esterification. Retrieved from the Web 29/09/11. http://www2.volstate.edu/msd/CHE/242/Labs/Ester.htm van Kessel, H., Jenkins, F., Davies, L., Plumb, D., Di Giuseppe, M., Lantz, O., & Tompkins, D. (2003). Nelson Chemistry 12. Toronto: Nelson Thomson Canada Limited.