Chapter 2 Notes
advertisement

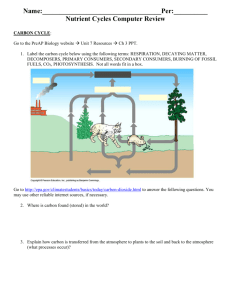
Cycles in Nature Chapter 2 Section 1 The Cycles of Matter The Cycles of Matter 1. What is matter? Anything that takes up space and has mass Used over and over again 2. How old is the matter in your body? It has been on Earth since it was formed billions of years ago Water Cycle Movement of water among oceans, atmosphere, land, and living things Water Cycle 1. Precipitation Happens when water moves from the atmosphere to land and oceans Rain, snow, sleet , and hail Water Cycle 2. Evaporation The sun’s heat causes water to change from liquid to vapor Water Cycle 3. Condensation When water vapor cools it forms a liquid that can fall back to Earth as precipitation Water Cycle 4. Ground Water A. Water that is found underground and stored in caverns or porous rock B. May stay in the ground for hundreds or thousands of years C. Provides water to soil, streams, rivers, and oceans Water Cycle 5. Transpiration A. Plants move water vapor into the atmosphere B. Plants do this by releasing water vapor through tiny openings in their leaves Water and Life A. Our body is made up of 70% water B. Water carries waste away from our body tissues C. Water helps regulate body temperature through perspiration “sweating” and evaporation This way of returning water to the environment is called- transpiration Bell Work Draw the water cycle in your science notebook or science binder Include in your drawing pictures and explanations for the process Your drawing should include Evaporation Condensation Precipitation Transpiration Groundwater Sun Tree Clouds Bell Work What process in the water cycle changes water from a liquid to water vapor (gas)? What process in the water cycle changes water from a gas to a liquid? Carbon What is GOOD about Carbon? What is BAD about Carbon? Carbon Cycle Carbon All living things need carbon because it is part of all biological molecules (fats, sugars, proteins) Carbon Cycle Movement of carbon from the environment into living things and back to the environment Carbon Cycle 1. Photosynthesis A. How carbon cycles from the environment into living things B. Plants use CO2 from the air to make sugars (or their own food) C. Animals get carbon they need from eating plants Carbon Cycle 2. Cellular Respiration A. How carbon returns to the environment from living things B. Living things break down sugar molecules to release energy C. During this process, CO2 and water are released Photosynthesis/Cellular Respiration Equations Photosynthesis (process of changing light energy into chemical energy) Sunlight+CO2+water (produces) glucose+O2 Cellular Respiration (process when cells break down food to get energy) Glucose+O2 (produces) Energy+CO2+water Bell Work Name the process in the carbon cycle where carbon is moved from the environment into living things? Hint (What process uses carbon dioxide (CO2)? Carbon Cycle 3. Decomposition A. Break down of dead material into CO2 and H2O B. When fungi and bacteria decompose organic matter, they return CO2 to the environment Carbon Cycle 4. Combustion A. Process of burning fossil fuels B. Fossil fuels-materials that are slowly formed underground from the remains of plants and animals that died million of years ago Carbon Cycle (combustion cont.) C. Carbon in coal, oil, and natural gas return to atmosphere as CO2 when these fossil fuels are burned D. Combustion provides the fuel people need to drive cars, heat homes, and make electricity E. Deforestationremoval of forests Carbon Cycle Practice Quiz Demo/Quiz How has Carbon Dioxide levels changed in the atmosphere? A. CO2 in the atmosphere has increased since the burning of more fossil fuels B. Many scientists believe that extra CO2 from fossil fuels is adding to global warming Carbon Dioxide in the Atmosphere Carbon Cycle Draw the carbon cycle in your science notebook or science binder Include in your drawing pictures and explanations for the process Your drawing should include: Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Decomposition Combustion Tree or plants Animals Fossil fuels Use of fossil fuels Deforestation Quiz Review 1. Where does most of Earth’s precipitation fall? 2. What is the process where sunlight, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water is used to make glucose? 3. What is the process where glucose is broken down for energy and carbon dioxide is released? Quiz Review 4. What are fossil fuels? Name 3 examples. 5. Name 3 ways carbon dioxide is transferred from living things into the environment? 6. What is the water cycle process where liquid water returns to the atmosphere? Quiz Review 7. What is the process called when water vapor cools? And what is formed? 8. What is deforestation? 9. What is released during decomposition? 10. Where is carbon found? Nitrogen Cycle The movement of nitrogen from the environment to living things and back again Nitrogen Cycle A. 78% of the Earth’s atmosphere is nitrogen gas (N2) B. Most organisms can not use the nitrogen in the air they breathe C. Living things need nitrogen to make proteins How do living things get nitrogen? A.Nitrogen fixation-when bacteria in the soil change nitrogen gas into a formed that can be used by plants B. Most animals get their nitrogen they need from eating plants Nitrogen Cycle D. Animal wastes return nitrogen back to the soil and plants use this nitrogen E. When plant or animals die, decomposers break down the remains and nitrogen recycles back into the soil Nitrogen Cycle How does nitrogen get from the soil back into the atmosphere? Denitrification-to take nitrogen out of the soil and change it to nitrogen gas that is released into the atmosphere Denitrifying bacteria produce nitrogen gas as a waste that is released in the atmosphere and completes the cycle Fungi How is this fungi important to the carbon cycle? Manure (animal waste) Why is this farmer spreading manure on the field? Explain the importance of this procedure in the nitrogen cycle? Bell Work 1. Why do we need nitrogen? 2. What is the process when bacteria change nitrogen into a usable form that can be used by plants? 3. What is the process when bacteria take nitrogen out of the soil and change it to a gas that is released in the atmosphere? Ammonia NH3 Question 21 Review (pages 42-43 in text book) Answer 1-3, 6-7, 9-12 14 19 24-25