File

Modern Biology
Chapter 18
Section 4 Notes
Ecosystem Recycling
Biogeochemical Cycles- substances passing between the living and nonliving worlds—being recycled and reused
I. The Water Cycle
A. Crucial to life
1. cells—70-90% water
2. chemical reactions occur in water
B. Water everywhere
1. bodies of water—lakes, rivers, streams
2. atmosphere—water vapor
3. groundwater—underground water
C. Water cycle
1. is movement of water
2. 3 processes in water cycle a. evaporation
1. adds water as vapor to atmosphere
2. heat causes water to evaporate b. transpiration
1. water evaporates from the leaves of plants c. precipitation
1. water leaves atmosphere when it becomes saturated
2. rain, snow, sleet, hail, fog
3. animals contribute to water cycle a. breathing
b. sweating c. excreting
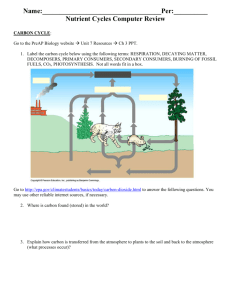
II. The Carbon Cycle
A. Photosynthesis
1. autotrophs use CO
B. Cellular Respiration
2 with water and light E to make carbs
1. auto and heterotrophs use oxygen to break down carbs
2. byproducts of cellular resp. are CO
2
and water
C. Decomposers
1. release CO
2
into atmosphere when break down organic compounds
l
III. Nitrogen Cycle
A. Needed for life
1. needed to make proteins and nucleic acids
B. Atmosphere
1. Nitrogen gas in atmosphere
C. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria
2. not usable form for organisms a. organisms need nitrogen in form of nitrate b. converting nitrogen gas to nitrate is called nitrogen fixation
1. live in soil and on roots of legumes
2. plants feed bacteria carbohydrates-----bacterial make nitrogen usable to plants (as nitrates)
3. there is also some nitrates released into soil
IV. Phosphorus Cycle
A. Needed for life
1. to form bones, teeth, DNA, RNA
B. Plants
1. get P from soil and water
C. Animals
1. get P by eating other organisms
D. P cycle
1. P dissolves in water and soil from rocks
2. plants absorb P in roots
3. when organisms die and decompose, P goes back into soil