Warm up:
advertisement

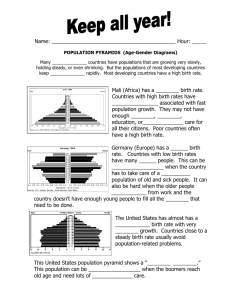
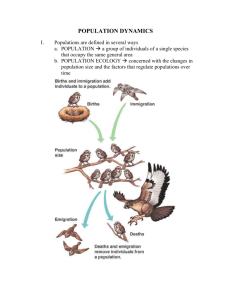
Warm up: Describe your perfect civilization. Include a description of landforms, population and natural resources. Objectives We will be able to analyze population pyramids and use maps and other data to describe countries/regions and describe current date trends and predict future trends. We will be able to define push/pull factors and explain how ESPN push/pull factors and physical geography affect where and how people migrate. Where do people settle? Both physical and human factors affect where people settle, even today. Three-quarters of the world’s population now live on less than 5% of Earth’s surface. Most of the world’s population is concentrated in five areas, with more than half in the first two: 1. East Asia, including China, Korea, Japan and Taiwan 2. South Asia, with India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka 3. Southeast Asia 4. Europe 5. North America Physical Factors • Populations tend to cluster around seaports and water sources • 2/3 of world population live within 500 miles of an ocean • 8/10 cities are on or near earthquake faults • Population is sparse near dry, wet, cold or mountainous areas • People like: low-lying lands, fertile soil and mild climates Human Factors • Populations need to establish capital cities and transportation routes • As technology improves, people are able to explore and settle in new locations (despite unfavorable physical factors) • Economic activities bring people to new areas – Ex. Gold, diamonds, oil, etc. Two types of population maps 1.Dot Population Maps 2.Population Density Maps Dot Population Maps • Use dot to indicate where major towns and cities are located • A key will indicate how many people a dot represents 1. Where do you see the largest populations? 2. What physical factors are these populations near? Population Density Maps • Use patterns or colors to show how many people live in a given area • The key will indicate what the patterns or colors represent 1. Where do you see the largest populations? 2. What physical factors are these populations near? How is this information gathered? http://www.prb.org/Journalists/Webcasts/2012 /distilled-demographics-population-data.aspx Patterns Throughout history, cities have exhibited variations in their size and distribution. Cities began undergoing changes as they matured. Often the business district was located in the city’s center, surrounded by residential neighborhoods. As newcomers from the countryside moved to the center, wealthier residents often began to move to the city’s outskirts. Patterns In more recent times, suburbs have developed outside cities. Often, these suburbs come to form satellite cities around the older city center. As the population increases further, these cites may merge into a single metropolitan region. Patterns In less developed countries, people often arrive from the countryside without education or resources. These newcomers may settle in squatter settlements or shanty town, usually found outside the city. A shanty town is a slum settlement where poor people live in dwellings made from scrap materials—such as plywood, corrugated metal and plastic sheets. Suburbs An outlying district of a city, esp. a residential one. Metropolitan Region A region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories, sharing industry, infrastructure and housing Squatter Settlements/Shanty Towns A slum settlement (sometimes illegal or unauthorized) of impoverished people who live in improvised dwellings made from scrap materials: often plywood, corrugated metal and sheets of plastic In Brasil, they are called flavelas. Approximately 8% of India’s population lives in the slums. Population Pyramids • Show a break down of populations • This can be done by age, sex or other grouping • Demographers study characteristics of human populations and where people settle Iran, 2010 Case Study: Iran Use the following information to make your own population pyramid. Ages Males Females Birth to 9 2600 2550 10 to 19 1900 1700 20 to 29 1300 1200 30 to 39 900 800 40 to 49 600 600 50 to 59 450 400 60 to 69 300 200 70 to 79 100 90 80+ 20 10 Case Study: Iran 1. When do the sexes even out? How could this be explained? 2. What factors could contribute to the drop in population in the 20s? 3. What policies could improve these statistics? At what ages would they be beneficial? Pages 78 - 82 • Define: birthrate, mortality rate, fertility rate, rate of natural increase, push/pull factors • In Latin America, which city has the highest density? In Africa? In the U.S.? In East Asia? • Why might Korea be more densely populated than China, which is in the same region? • In South Asia, which city has the lowest density? In Europe? In Russia and the Republics?