tissues - School Stuff 10
advertisement

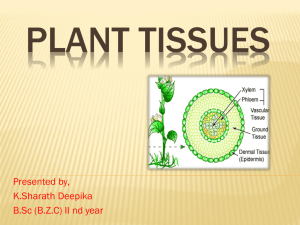
TISSUES Q1. Define the term ‘tissue’. Ans. Tissue is a group of related cells that have a common origin and perform a common function. Q2. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them. Ans. There are four types of elements which together make up the xylem tissue: a) Tracheids b) Vessels c) Xylem parenchyma d) Xylem fibres Q3. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants. Ans. Simple tissue 1. It is formed of only one type of cells Complex tissues 1. It is formed of more than one type of cells. 2. All the cells perform the same function 2. The different cells perform different part of a function. 3. They form primary structure of the plant 3. They form transport system of the plant. Q4. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma.(write the following answer in a tabular form) Parenchyma: The cell wall is thin. Cell wall is smooth. The cell wall is formed of cellulose. Collenchyma: The cell wall is thickened at corners. The cell wall is unevenly thickened. The cell wall is made of pectocellulose (pectin & cellulose) Sclerenchyma: The cell wall is thickened. The cell wall is uniformly thickened. The cell wall is cellulosic but thickening is lignified. Q5. What are the functions of stomata? Ans. Functions of stomata: Stomata are sites where exchange of gases occurs between the plant and the external environment. Major part of transpiration occurs through stomata. They regulate both gaseous exchange and transpiration. Q6. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present. Ans. Parenchyma occurs in almost all non-woody parts of the plant such as cortex, pith, medullary rays of stem, cortex and pith of roots, leaves, flowers , pith of fruits etc. Q7. What is the role of epidermis in plants. Ans. Epidermis acts as protective tissue in plants and protects underlying tissues. Epidermis helps in absorption, secretion, excretion, gaseous exchange and transpiration. It protects the entry of pathogens. Q8. How does the cork act as a protective tissue? Ans. Cells of cork are dead and completely arranged without intercellular spaces. They also have a chemical called suberin in their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water. TO BE DONE ON THE BLANK SIDE OF THE NOTE BOOK: 1. FLOW CHART ON PLANT TISSUES (given in running notes) 2. DIAGRAM – LOCATION OF MERISTEMATIC TISSUES IN PLANT BODY (Pg.69) 3. DIAGRAM – VARIOUS TYPES OF SIMPLE TISSUES – L.S & T.S (Pg.- 71) 4. DIAGRAM – GUARD CELLS AND EPIDERMAL CELLS (Pg. 72) _______________________________________________________________ -