Pedi Med Administration
advertisement
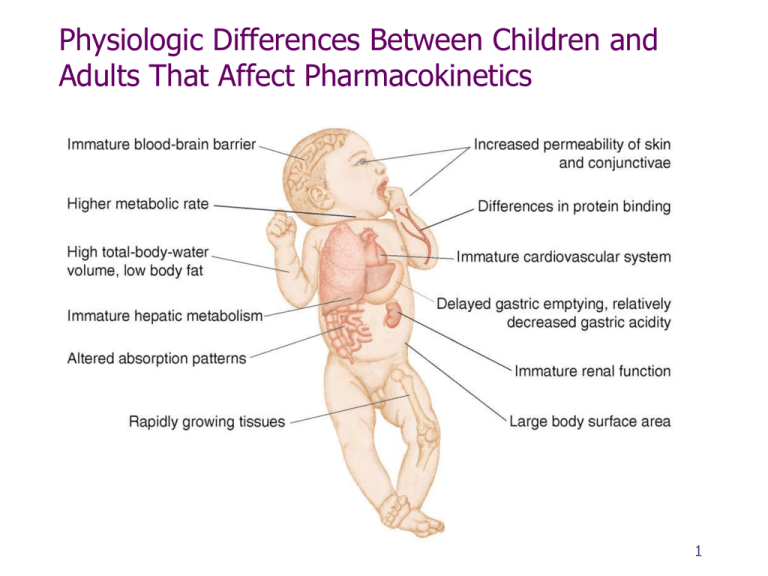
Physiologic Differences Between Children and Adults That Affect Pharmacokinetics Fig. 38-1, p. 993 1 Giving Medications: what’s the same? Safety & accuracy 6 Rights Understand expected action and side effects Signs of toxicity, adverse reactions 2 Extra Considerations for Children Safe volume (IM) Po often liquid Dosage by body weight Check dosage with reference Mg/kg/dose or mg/kg/day? Check calculations with another nurse 3 Example 1. Order: Augmentin 200 mg po q. 12 hrs Child: 9.5 kg Available: suspension 125 mg/5 mL Range (drug book) 25-45 mg/kg/day Is dose within range? How many ml is required to give the ordered dose? 4 Principles of Medication Administration in Children Consider growth and development principles. Honesty and praise help to gain trust and cooperation. Restraint may be necessary. Provide rewards for good behavior and for trying. Dosages by body wt 5 Safety Considerations Children unpredictable Get help with restraining Extra needle Parent/caregiver involvement Be quick, skillful Never give injection to a sleeping child 6 Must Know: 1 Kg = 2.2 lbs 1 Kg = 1,000 gm 1 Gm = 1,000 mg Kg = lbs 2.2 Kg x 2.2 = lbs 7 Strategies for Medicating Children Infants Restrain cuddle, comfort. Toddlers Use play minimize restraint give praise stickers as rewards. 8F Strategies for Medicating Children Pre-school, early school-age Provide choices, explanations Distraction Support Adolescents Explain Allow participation in decisions praise cooperation provide outlet for frustrations. 9 Methods of Administering Medications to Children Oral NG, GT, JT Rectal Topical Otic (ear) Ophthalmic (eye) IV Intraosseous IM, SQ 10 Giving oral meds 11 Gastric or NG Meds Stop feeding (as appropriate) Flush with (sterile) water – 5-25 mL Administer med Flush Always flush when stopping feeding 12 Ear drops 13 Intramuscular Sites in Children table 38-1 Fig. 38-UF01a, p. 999 14 Intramuscular Sites in Children Fig. 38-UF01b, p. 999 M 15 IM 16 Procedure for Pediatric IM Look at procedure in syllabus 17