Meiosis
advertisement

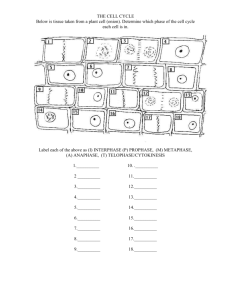
Meiosis Males – only occurs in the testicles. Females – only occurs in the ovaries. Formation of four cells that are NOT genetically identical with only half the chromosome number as the parent cell. Vocabulary Haploid – half the regular number of chromosomes Diploid – Regular number of chromosomes Tetrads – Homologous pairs side by side Homologous pairs – Same size chromosomes that contain genes for the same trait. Humans have 23 homologous pairs. Crossing over – Occurs between homologous chromosomes. Pieces of the homologous chromosomes sometimes cross over and exchange segments. Law of Segregation (1st law) – Pairs of alleles separate in meiosis and each gamete receives one allele of a pair. Law of Independent Assortment (2nd law)– Homologous chromosomes line up independently from other homologous chromosomes during metaphase 1. Meiosis 1 Prophase 1 – Duplicated chromatin condenses. Each chromosome consists of sister chromatids. Crossing over can occur in the latter part of this stage. Metaphase 1 – Homologous chromosomes align in the middle of the cell Anaphase 1 – Homologous pairs separate with sister chromatids remaining together. Telophase 1 – Two daughter cells are formed with each daughter cell containing only one chromosome of the homologous pair. Meiosis 2 Prophase 2 – DNA does not replicate. Metaphase 2 – Chromosomes align in the middle of the cell Anaphase 2 – Sister chromatids are pulled apart at the centromere by the centrioles. Telophase 2 – Cell division is complete. Four haploid daughter cells are obtained. Meiosis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CMXjBgLjjxo Comparison of Meiosis and Mitosis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i9WDSfaPW00 Connect the words Phenotype Recessive Gene Dominant Heterozygous Allele Homozygous Genotype Fundamentals of Genetics Gene – Segment of DNA that codes for a particular trait. Ex: eye color Allele – One of the number of different forms of the same gene for a specific trait. Ex: blue eyes and brown eyes. In general, for every one gene there are two alleles. Dominant – Referring to an allele that masks the presence of the recessive allele for the same gene. Usually noted with a capital letter. Ex: B. Recessive – Referring to an allele that is masked by the presence of the dominant allele. Usually noted with a lower case letter. Ex. b. Homozygous – Referring to an allele pair in which the two alleles code for the same thing. Ex: BB or bb. Heterozygous – Referring to an allele pair in which the two alleles do not code for the same thing. Ex: Bb. Genotype – The genetic makeup of an organism. Ex: BB, Bb or bb. Phenotype – The physical appearance of an organism that is determined by the individual’s genotype. Ex: blue eyes, brown hair, dimples, etc. Punnett square – a model used to establish the probabilities of the results (offspring) of a genetic cross. Genotypic ratio – The probable ratio of genotypes for the offspring. Phenotype ratio – The probable ratio of phenotypes for the offspring.