Covalent Bonds
advertisement

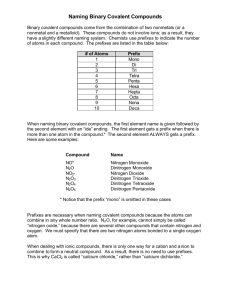
Day 14 – Covalent bonds Sci 10 Chemistry Covalent Bonds Non-metal + non-metal A compound without any metals?!???! What happens when 2 nonmetals react? Remember: Metals want to give away their electrons and nonmetals want to accept them. • A compound made of only nonmetals (Hydrogen counts as a non-metal) is called a covalent or molecular compound. Atoms in molecular compounds don’t want to lose their electrons SO … • electrons are shared amoung multiple atoms to have full valence shells Animation: http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp02/02020.html H and Cl Hydrogen and chlorine are both gases and nonmetals (even though hydrogen is found in Group 1 (the alkali metals)). Neither H nor Cl want to give up their electrons to form an ionic sompound so they share them instead, forming a covalent bond (which gives us a covalent compound) H now has 2e- in its valence shell and Cl has 8, so they are both full. The line between H and Cl indicates there are 2e- shared between the 2 atoms. This form is called a Lewis Dot Diagram. HOBrFINCl’s The following elements exist in a diatomic form (2 atoms are always bonded together). These diatomic molecules only exist in pairs of atoms. Draw Lewis Diagrams for H2, O2, Br2, F2, I2, N2 and Cl2 Triple bond Double bond Molecular compounds Give the structural formula (Lewis diagram with lines representing shared electrons) for the molecular compound that will form from the following pairs of elements: 1. bromine + iodine 2. nitrogen + chlorine 3. carbon + fluorine 4. sulfur + bromine Answers Structural formula Br Cl I N Cl F F C F F Br S Br Cl Practice Draw Lewis structures for the following compounds: H2O, CO2, NH3, SCl2, CH4, C2H6, P4, CBr4, CH2Cl2 P4 et S8: Elemental shapes (Chem 11) • No need to memorize this but just to show you that certain atoms bond to others forming specific angles. The compounds that are formed with have specific shapes. Practice . . . again Show the bond formation between each of the following pairs of elements by drawing Lewis diagrams. Indicate if the compound formed is ionic or covalent. Try to write the formula for the compound. a) K and Se f) C and Cl b) Br and Cl g) C and O c) Sr and Br h) N and I d) B and H i) Ca and N e) Al and S j) Al and Br Naming Covalent Compounds 1. Is it a covalent compound (non-metal + non-metal)? If yes, 2. Name the element that is furthest left on the periodic table first. Use a prefix if there is more than one atom of this element. 3. Name the second element. Use a prefix to indicate the # of atoms (even if there is only 1) and add the ending –ide. Prefixes # of atoms Prefix 1 mono(only use when naming the 2nd element i.e. names of covalent compounds never start with mono-…) 2 di- 3 tri- 4 tetra- 5 penta- 6 hexa- 7 hepta- 8 octa- 9 nona- 10 deca- Examples and practice • NO = nitrogen monoxide • N2O = dinitrogen monoxide • Name NO2 – nitrogen dioxide • Name CO – carbon monoxide Try It! Name the following molecular compounds: 1. PI3 phosphorus triiodide 2. SO2 sulfur dioxide 3. SO3 sulfur trioxide 4. S2F10 disulfur decafluoride 5. CCl4 carbon tetrachloride 6. N 2 O5 dinitrogen pentoxide Name to formula • Look at the prefixes to write the formula • Ex: phosphorus pentachloride • PCl5 Find the formula • nitrogen tribromide – NBr3 • nitrogen dioxide – NO2 • sulfur pentoxide – SO5 Naming diatomic molecules • For the HOFBrINCl elements, they always exist in pairs of atoms as gases • To name them, just use the name of the element – H2 (g) = hydrogen – O2 (g) = oxygen – N2 (g) = nitrogen To do • Day 14 Covalent Practice