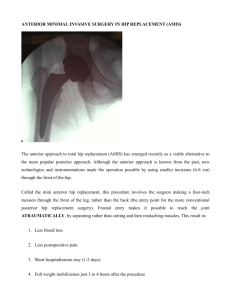
THE HIP JOINT

THE HIP JOINT
Muscles of the Hip
Gluteus Maximus
O: lower posterior iliac crest and posterior surface of the sacrum
I: gluteal tuberosity (upper, posterior aspect of the femur) &
I.T. band
Actions:
Extension of the hip
External rotation of the hip
Lower fibers (below the center of motion) assist in adduction
Extension
Gluteus Maximus
Produces hip extension beyond 15 degrees; not used extensively during walking
Strongly used during running, hopping, skipping, and jumping
Best isolated with the knee flexed to reduce hip extension from the hamstrings
40 degrees
Gluteus Medius
O: outer surface of the ilium just below the crest
I: greater trochanter
Actions:
Abduction of the hip
Anterior fibers:
Internal rotation,
Posterior fibers:
External rotation.
Gluteus Minimus
O: outer surface of the ilium beneath the gluteus medius
I: greater trochanter of the femur
Actions
Abduction of the hip
Internal rotation
Gluteus Medius and Minimus
During walking these muscles abduct (or hold up) the free leg, preventing it from sagging.
Both are important in transferring weight from one leg to the other (e.g. running, hopping, skipping, etc.)
Their effectiveness decreases with age.
Biceps Femoris
Lateral side
Origin:
1.) Long head - ischial tuberosity;
2.) Short head - lower half of the linea aspera
Insertion: Head of the fibula
Action:
Extension of hip
External rotation of the hip
(and knee)
(Flexion of knee)
Biceps Femoris
One of the hamstring muscles (semitendinosus and semimembranosus)
A two-joint muscle which is a powerful hip extensor unless the knees are flexed
Isolated during leg curls with some external rotation of the hip and knee. This “lines up” the origin and insertion.
Semitendinosus
Medial side; superficial
Origin: Ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Medial surface of proximal end of the tibia
Action:
Extension of the hip
Internal rotation of the hip (and knee)
Flexion of the knee
Semimembranosus
Medial side, deeper than semitendonosus
Origin: Ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Medial surface of the tibia
Action:
Extension of the hip
Internal rotation of the hip (and knee)
Flexion of the knee
Semitendinosus &
Semimembranosus
Two-joint muscles
Used in ordinary walking for hip extension
Best exercised with knee flexion exercises (leg curls) with the hip and knee internally rotated
Help to medially stabilize knee
Tensor Fasciae Latae
O: iliac crest
I: iliotibial (I.T.) band
Actions:
Flexion of the hip
Internal rotation
Abduction of the hip
Tensor Fasciae Latae
Prevents external rotation at the hip is flexed
Stretching
Strengthening
Tensor Fascia
Latae
(Anterior View)
Iliopsoas
Origins:
iliac fossa vertebral bodies of the last thorasic and lumbar vertebrae
I: lesser trochanter of the femur
Actions:
Flexion of the hip
External rotation
Iliopsoas
Strong hip flexor muscle
Raises legs off the floor from the supine position.
Pulls anteriorly on the lower lumbar vertebrae
May aggravate lower back problems
Abdominal muscles can prevent lumbar strain
Used during complete situps and straight leg sit-ups.
Stretching this muscle requires hyper-extension of the hip.
Pectineous
O: pubic crest or ramus
I: below the linea aspera
Actions
Flexion
Adduction
Internal rotation
Tensor Fasciae Latae
Pectineus
Adductor Brevis
Origin: Inferior ramus of pubis
Insertion: Pectineal line (linea aspera)
Actions:
Adduction
External rotation
Adductor Longus
Below the adductor brevis
O: front of the pubis just below its crest
I: middle third of the linea aspera
Actions:
Adduction
Flexion
Adductor Magnus
Located posterior to the longus
O: edge of the pubic crest and ischial tuberosity
I: linea aspera
Actions:
Adduction
External rotation
Gracilis
O: pubic crest
I: medial condyle of tibia
Actions:
Adduction at the hip
Internal rotation
[Flexion at the knee]
Adductor Muscles
Adductor Brevis
Adductor Longus
Adductor Magnus
Gracilis
Not heavily used in ordinary movements
Horse back riding, the breaststroke kick in swimming
Sartorius
Origin: Anterior-superior spine of the ilium
Insertion: Anterior medial condyle of the tibia (behind the medial condyle)
Action:
Flexion of hip
External rotation of the hip
[Flexion of the knee]
Sartorius
Longest muscle in the body
It is a two-joint muscle; hip flexion and knee flexion
It is weak when both actions take place at the same time.
Rectus Femoris
Two joint muscle; most superficial
Origin: anterior-inferior iliac spine of the ilium
Insertion: top of the patella and patellar ligament to the tibial tuberosity
Actions:
Flexion of the hip [Extension of the knee]
Rectus Femoris
A two-joint muscle: hip flexion and knee extension
Powerful knee extension when the hip is extended but weaker when the hip is flexed.
The gluteus maximus and the hamstring muscles will extend the hip making the rectus femoris stronger during knee extension
Hip Rotator Muscles
ANTERIOR
Obturator Externus
Anterior
Hip Rotator
Muscles
POSTERIOR
Piriformis
Gemellus superior
Obturator internus
Gemellus inferior
Quadratus femoris
Posterior
Hip Rotator Muscles
Posterior
Posterior
Hip Rotator Muscles
Posterior Anterior
Six Hip Rotator Muscles
Common action is External Rotation
Powerful external rotation of the hip is required to throw a baseball, swing a bat or golf club.
The sciatic nerve passes just inferior to the piriformis therefore a tight piriformis muscle my contribute to compression on the sciatic nerve.
Review
Name the action at her hip
Abduction
Name the action at his right hip
Flexion
Name the actions at her hip
Extension, Abduction &
External Rotation
Name the two action at his right hip
Extension and External
Rotation
Name the action at his hip
Flexion
Name the actions at his hip
Flexion and External Rotation and Abduction
Name the actions at his hip
Flexion and Adduction
The Femur
1 =
2 =
3 =
4 =
5 =
6 =
7 =
Head
Neck
Greater trochanter
Lesser trochanter
Linea Aspera
Medial condyle
Lateral condyle
1.
2.
5.
4.
3.
6.
7.
Anterior
1 = iliac crest
2 = anterior spine
3 = greater trochanter
1.
2.
4 = lesser trochanter
5 = ischial tuberosity
3.
6 = pubis crest
4.
5.
6.
Name the sections of the pelvis
1.
Ilium
2.
Pubis
3.
Ischium
Posterior
1 =
2 =
3 =
4 =
5 = iliac crest greater trochanter ischial tuberosity lesser trochanter linea aspera
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Name the muscle
Actions: extension of the thigh at the hip lateral rotation of the thigh lower fibers (below the center of motion) assist adduction upper fibers (above the center of motion) assist in abduction
Gluteus Maximus
Name the muscle
Actions
adduction of the thigh at the hip
aids in flexion
Adductor Brevis
Name the muscle
Actions
abduction of the thigh medial rotation flexion
Gluteus Minimus
Name the muscle
Actions:
adduction of the thigh assists in flexion of the thigh at the hip
Adductor Longus
Name the muscle
Actions:
abduction of the thigh
anterior fibers: flexion and medial rotation,
posterior fibers: extension and lateral rotation.
Gluetus Medius
Name the muscle
Actions:
adduction at the hip
medial rotation
[flexion at the knee]
Gracilis
Name the muscle
Actions:
flexion of the thigh at the hip slight adduction flexion of the spine
Iliopsoas
Name the muscle
Actions
flexion of the hip
adduction
Pectineus
Name the muscle
Actions:
flexion of the thigh at the hip
medial rotation
abduction of the thigh, medial rotation (weak)
Tensor Fasciae Latae
Name the muscle
Actions:
adduction of the thigh at the hip
flexion (anterior fibers)
extension (posterior fibers)
Adductor Magnus
What is the most anterior hip rotator muscle?
Obturator Externus
What is the common action of these muscles?
Piriformis
Gemellus superior
Obturator internus
Gemellus inferior
Quadratus femoris
External Rotation
Name the muscle
Deep muscle
Action:
Extension of the hip
Flexion of the knee
Internal rotation of the hip (and knee)
Semimembranosus
Name the muscle
Superficial muscle
Action:
Extension of the hip
Flexion of the knee
Internal rotation of the hip
(and knee)
Semitendonosis
Name the muscle
Action:
Flexion of hip
External rotation of the hip
Sartorius
[Flexion of the knee]
Name the muscle
Actions:
Flexion of the hip
[Extension of the knee]
Rectus Femoris
Name the muscle
Action:
Extension of hip
Flexion of knee
Lateral rotation of the hip (and knee)
Biceps Femoris
Name the muscle
Gluteus Medius
Name the muscles
Pectineus
Adductor Brevis
Adductor Longus
Adductor Magnus
Gracilis
Name the landmarks
Iliac crest
Anterior spine
1
Name the landmarks
1.
2.
3.
Acetabulum
Sciatic notch
Ischial tuberosity
2
3
Name the muscles
1.
2.
Tensor fasciae latae
Sartorius
1
2
1. Name the muscle
Gluteus Maximus
2. Name the landmark
Iliac Crest
3. Name the structure
Iliotibial band