Summer Week 2 Plan
advertisement
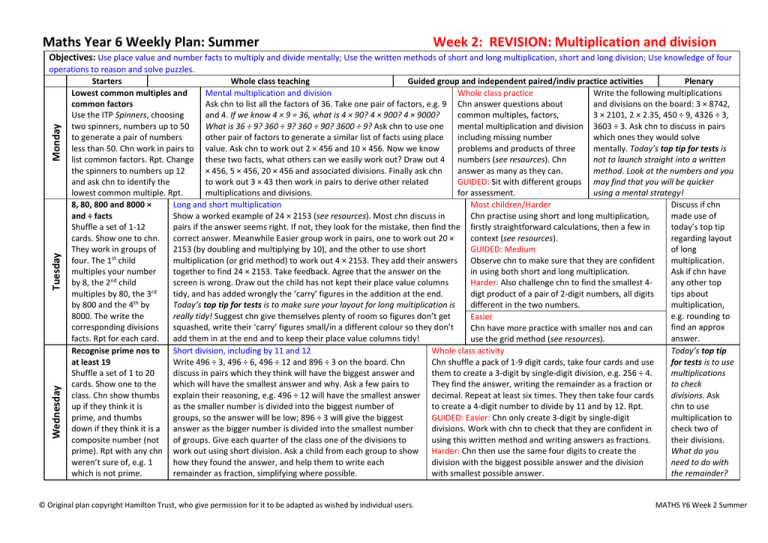
Maths Year 6 Weekly Plan: Summer Week 2: REVISION: Multiplication and division Objectives: Use place value and number facts to multiply and divide mentally; Use the written methods of short and long multiplication, short and long division; Use knowledge of four Wednesday Tuesday Monday operations to reason and solve puzzles. Starters Whole class teaching Guided group and independent paired/indiv practice activities Plenary Lowest common multiples and Mental multiplication and division Whole class practice Write the following multiplications common factors Ask chn to list all the factors of 36. Take one pair of factors, e.g. 9 Chn answer questions about and divisions on the board: 3 × 8742, Use the ITP Spinners, choosing and 4. If we know 4 × 9 = 36, what is 4 × 90? 4 × 900? 4 × 9000? common multiples, factors, 3 × 2101, 2 × 2.35, 450 ÷ 9, 4326 ÷ 3, two spinners, numbers up to 50 What is 36 ÷ 9? 360 ÷ 9? 360 ÷ 90? 3600 ÷ 9? Ask chn to use one mental multiplication and division 3603 ÷ 3. Ask chn to discuss in pairs to generate a pair of numbers other pair of factors to generate a similar list of facts using place including missing number which ones they would solve less than 50. Chn work in pairs to value. Ask chn to work out 2 × 456 and 10 × 456. Now we know problems and products of three mentally. Today’s top tip for tests is list common factors. Rpt. Change these two facts, what others can we easily work out? Draw out 4 numbers (see resources). Chn not to launch straight into a written the spinners to numbers up 12 × 456, 5 × 456, 20 × 456 and associated divisions. Finally ask chn answer as many as they can. method. Look at the numbers and you and ask chn to identify the to work out 3 × 43 then work in pairs to derive other related GUIDED: Sit with different groups may find that you will be quicker lowest common multiple. Rpt. multiplications and divisions. for assessment. using a mental strategy! 8, 80, 800 and 8000 × Long and short multiplication Most children/Harder Discuss if chn and ÷ facts Show a worked example of 24 × 2153 (see resources). Most chn discuss in Chn practise using short and long multiplication, made use of Shuffle a set of 1-12 pairs if the answer seems right. If not, they look for the mistake, then find the firstly straightforward calculations, then a few in today’s top tip cards. Show one to chn. correct answer. Meanwhile Easier group work in pairs, one to work out 20 × context (see resources). regarding layout They work in groups of 2153 (by doubling and multiplying by 10), and the other to use short GUIDED: Medium of long four. The 1st child multiplication (or grid method) to work out 4 × 2153. They add their answers Observe chn to make sure that they are confident multiplication. multiples your number together to find 24 × 2153. Take feedback. Agree that the answer on the in using both short and long multiplication. Ask if chn have by 8, the 2nd child screen is wrong. Draw out the child has not kept their place value columns Harder: Also challenge chn to find the smallest 4any other top multiples by 80, the 3rd tidy, and has added wrongly the ‘carry’ figures in the addition at the end. digt product of a pair of 2-digit numbers, all digits tips about by 800 and the 4th by Today’s top tip for tests is to make sure your layout for long multiplication is different in the two numbers. multiplication, 8000. The write the really tidy! Suggest chn give themselves plenty of room so figures don’t get e.g. rounding to Easier corresponding divisions squashed, write their ‘carry’ figures small/in a different colour so they don’t find an approx Chn have more practice with smaller nos and can facts. Rpt for each card. add them in at the end and to keep their place value columns tidy! answer. use the grid method (see resources). Recognise prime nos to Short division, including by 11 and 12 Whole class activity Today’s top tip at least 19 Write 496 ÷ 3, 496 ÷ 6, 496 ÷ 12 and 896 ÷ 3 on the board. Chn Chn shuffle a pack of 1-9 digit cards, take four cards and use for tests is to use Shuffle a set of 1 to 20 discuss in pairs which they think will have the biggest answer and them to create a 3-digit by single-digit division, e.g. 256 ÷ 4. multiplications cards. Show one to the which will have the smallest answer and why. Ask a few pairs to They find the answer, writing the remainder as a fraction or to check class. Chn show thumbs explain their reasoning, e.g. 496 ÷ 12 will have the smallest answer decimal. Repeat at least six times. They then take four cards divisions. Ask up if they think it is as the smaller number is divided into the biggest number of to create a 4-digit number to divide by 11 and by 12. Rpt. chn to use prime, and thumbs groups, so the answer will be low; 896 ÷ 3 will give the biggest GUIDED: Easier: Chn only create 3-digit by single-digit multiplication to down if they think it is a answer as the bigger number is divided into the smallest number divisions. Work with chn to check that they are confident in check two of composite number (not of groups. Give each quarter of the class one of the divisions to using this written method and writing answers as fractions. their divisions. prime). Rpt with any chn work out using short division. Ask a child from each group to show Harder: Chn then use the same four digits to create the What do you weren’t sure of, e.g. 1 how they found the answer, and help them to write each division with the biggest possible answer and the division need to do with which is not prime. remainder as fraction, simplifying where possible. with smallest possible answer. the remainder? © Original plan copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. MATHS Y6 Week 2 Summer Friday Thursday Maths Year 6 Weekly Plan: Summer Week 2: REVISION: Multiplication and division Starters Square nos to 144 Chn work in pairs to shuffle a set of 1 to 12 cards, and place face down. When you say go, they turn over each card, one at a time, and square the number on the card. Can they get through the whole pack in under 2 minutes? Rpt. Find a mean Ask chn to find the mean (average) of the following tree heights: 6m, 4m, 5m, 8m, and 7m. Challenge chn to work in pairs to write other groups of 5 heights with the same mean. Whole class teaching Guided group and independent paired/indiv practice activities Plenary Use long division to divide 3-digit and 4-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers Most children/Harder Ask chn if Martin the florist is making up bunches of 15 roses. He has 1250 roses in stock. How many bunches can he Chn practise using long they found make? Ask children what calculation is needed to work out the answer. Discuss how we can use long division, firstly today’s top division to work out 1250 ÷ 15, and remind children that it is helpful to make a list of multiples of the straightforward calculations, tip (make a divisor, the number we are dividing by, to help. Record ‘List multiples of the divisor when working out long then in context (see list of division’ as today’s top tip for tests. Ask chn from the Easier group to help you to list multiples of 15 on the resources). multiples of board, and then ask for a volunteer from Medium/Harder groups to model using long division. The answer GUIDED: Medium the divisor to to the calculation is 83 r 5, but what is the answer to the question? If he found 10 more roses, how many Observe a group to make sure help) helpful. bunches could Martin make then? Remind chn that when working out a division to solve a word problem, that they are confident in Did any make we often have to think what to do with the remainder, e.g. whether to round the answer down, up, or using long division. use of write it as a fraction or decimal. Repeat with: A 9m price of ribbon is divided into 24 equal lengths to tie yesterday’s Easier round bunches. What is the exact length of each piece? Discuss the problem together, drawing out that it Chn use the list of multiples of top-tip? will be useful to think of 9m as 900cm, and to estimate the answer by thinking how many 25s are in 900. 15 to divide as many numbers Together list multiples of 24 and use to work out the long division 900 ÷ 24, to give an answer of 37 r12. between 150 and 1000 as How can we write this as an exact length in centimetres? Agree that 3712/24 is 73 ½, i.e. 37.5cm. they can. Use four operations to reason and solve puzzles Whole class activity Write 7 □ 5 = 45 □ 10 on the Write the following puzzle on the board: Anna chooses two numbers, adds them together, and Chn solve puzzles like board. What operations need then divides by 2. Her answer is 19. One of the numbers she chose was 14. What was the other Anna’s mystery number to go on each side to make number? Ask chn to discuss this in pairs, and then take feedback on how this puzzle could be puzzle, multiplication this statement true? Rpt with solved. Draw out using inverse operations, i.e. multiplying 19 by 2 to give 38, then subtracting 14 arithmagons and addition 36 □ 3 = 4 □ 3 and 45 □ 24 = to give 24. Let’s check this works. Add 14 and 24. Now divide your answer by 2. Do you get 19? grids (see resources). 7 □ 3. Ask chn to work in Yes! Repeat with: Anna chose two whole numbers. They had a product of 18 and a difference of 7. GUIDED: Harder pairs to make up their own What were her numbers? Chn discuss how to go about this and feedback, e.g. list factor pairs of 18 Chn solve every other one, equalities, involving at least and look for ones with a difference of 7. That’s 9 and 2. Display the arithmagon (see resources). then investigate the one multiplication or Explain that numbers written on neighbouring vertices are multiplied together to give the minimum number of cells division. Share some with the numbers written on the sides. What number is a factor of both 18 and 12? Write 2 at the top. If 2 which need to be complete class. Today’s top tip is to goes here, what goes on the bottom left vertex? And the bottom right. Ah, that doesn’t work. in order to solve an addition check your answer works in What other numbers go into both 18 and 12? Try these and complete the arithmagon. Show one grid. missing number problems. of the addition grid on the activity sheet. Explain how the outside numbers are added to give the inside numbers. Ask chn to discuss how the missing numbers might be found. © Original plan copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. MATHS Y6 Week 2 Summer Maths Year 6 Weekly Plan: Summer Week 2: REVISION: Multiplication and division Resources ITP Spinners (see resources) Monday: Whole class practice (see resources) Large set of 1-12 cards Tuesday: Example of an error in long multiplication, 24 × 2153 (see resources) Tuesday: Multiplication practice (versions for Most children/Harder group and for Easier group) (see resources) Large set of 1 to 20 cards 1-12 cards IWB 2 minute timer Thursday: Long division Activity sheet (see resources) Friday: Solving number puzzles Activity sheet (see resources) Abacus Year 6 Textbooks 1, 2 and 3 A choice of Abacus Textbook Pages for Alternative/Additional Practice Day Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Mixed calculation practice Group Easier Most children Easier Most children Harder Most children/Harder Page Textbook 2, page 51 Textbook 2, pages 51 and 53 Textbook 3, page 29 Textbook 2, pages 32 and 33; Textbook 3, pages 30, 32 and 34 Textbook 2, page 33; Textbook 3, pages 31, 33 and 34 Textbook 3, page 35 Easier Most children Harder Most children Textbook 2, page 88 Textbook 2, page 89; Textbook 3, pages 38 and 41 Textbook 2, page 90; Textbook 3, page 39 Textbook 1, page 102, Textbook 2, page 101; Textbook 3, page 77 The links to the websites and the contents of the web pages associated with such links specified on this list (hereafter collectively referred to as the ‘Links’) have been checked by Hamilton Trust (being the operating name of the registered charity, William Rowan Hamilton Trust) and to the best of Hamilton Trust’s knowledge, are correct and accurate at the time of publication. Notwithstanding the foregoing or any other terms and conditions on the Hamilton Trust website, you acknowledge that Hamilton Trust has no control over such Links and indeed, the owners of such Links may have removed such Links, changed such Links and/or contents associated with such Links. Therefore, it is your sole responsibility to verify any of the Links which you wish you use. Hamilton Trust excludes all responsibility and liability for any loss or damage arising from the use of any Links. © Original plan copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. MATHS Y6 Week 2 Summer Maths Year 6 Weekly Plan: Summer Week 2: REVISION: Multiplication and division Outcomes Monday Tuesday 1. Use place value and number facts to multiply and divide mentally. 1. Use short and long multiplication to multiply 3-digt and 4-digit numbers by 1-digit and 2-digit numbers. Outcomes for most children Wednesday 1. Use short division to divide 3digit and 4-digit numbers by singledigit numbers and 11 and 12. Thursday 1. Use long division 3-digit and 4digit numbers by 2-digit numbers. Friday 1. Use knowledge of operations and reasoning to solve number puzzles. Default (outcomes for children not on statements but not able to reach the outcomes for most children) 1. Use place value and number facts to multiply and divide mentally. 1. Use short multiplication to multiply 3-digt numbers by 1-digit and the grid method to multiply by 2-digit numbers. 1. Use short division to divide 3digit numbers by single-digit numbers. 1. Use multiples of the divisor to support using long division 3-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers. 1. Use knowledge of operations and reasoning to solve number puzzles. Only record names of children who struggled or exceeded these outcomes © Original plan copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. MATHS Y6 Week 2 Summer