New Imperialism - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

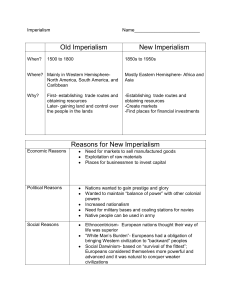
IMPERIALISM: domination by one country over another country’s political, economic, and cultural life. Similar to your scramble for furniture, European imperialists scrambled and competed for territory in Africa in the late 19th century (1800s) Became caught up in a competitive race to claim furniture You claimed furniture without knowing how it would really benefit you Industrialized groups had more advantages and the other groups tried to catch up We discussed the fairness of the game European colonial powers became caught up in a competitive race to claim African land Colonial powers claimed land they had little knowledge about Industrialized nations had a head start in acquiring colonies and the other countries tried to catch up The colonial powers met at the Berlin Conference in 18841885 to divide up African territory fairly. Imperialism The “New” Imperialism… 1700s – 1800s different from earlier explorers in 1500s – 1600s (like in North & South America) New imperialists wanted to have significant influence over the lives of the colonized peoples Imperialism Definition Domination by one country over another country’s political, economic, and cultural life. Industrial Revolution and Imperialism Industrialized countries needed raw materials such as cotton, coal, iron, oil, copper, rubber They also needed foreign markets to sell goods Needed to control a region/country to protect raw materials & markets Imperial Powers They had strong economies (industry), organized governments, and powerful armies Older civilizations declined in power Middle East, India, Asia, Africa Western European Countries grew stronger. European states such as England, France, Spain, Belgium, Portugal colonized the Americas, Asia, Africa, Southeast Asia. England had the most colonies and was the leading Imperial Power (why?) Forms of Colonial Rule Colonies- territory or country ruled by a foreign power Protectorate – a country that keeps its own government, but under the control of another nation Sphere of Influence – a territory in which an outside power claims exclusive trading privileges Forms of Management Direct Control Foreign officials brought in to rule No self-rule Used by French & most European nations Indirect Control Local government officials used Limited self-rule Used by the United States & Britain Motives for Imperialism Economic Desire to make money To expand and control foreign trade Create new markets for products Acquire raw materials and cheap labor Religious Educate & convert people to Christianity Political Nation’s desire to gain power & security Expand territory and compete with other nations Gain prestige & nationalism by winning colonies Exploratory Desire to explore the “unknown” – seeking adventure Conduct scientific research, medical searches Ideological Based on cultural values such as the belief in superior races Europeans should “civilize” other people (“White Man’s Burden”) Social Darwinism: only the strongest nations will survive