New Imperialism
advertisement

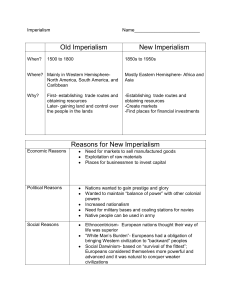
Imperialism FUN!!! Imperialism Definition Domination by one country over another country’s political, economic, and cultural life. Forms of Colonial Rule Colonies- territories owned and ruled by another country Direct – officials from Imperial Power directly control the colony Indirect – officials from the local colony rule for the Imperial Power Protectorate – a nation and its ruler are under the control of another nation Forms of Colonial Rule Sphere of Influence A region or country in which a nation holds special trading privileges Europeans – China United States – Latin America Imperialism European states such as England, France, Spain, Belgium, Portugal colonized the Americas, Asia, Africa, Southeast Asia. England had the most colonies and was the leading Imperial Power Industrial Revolution and Imperialism Industrialized countries needed raw materials such as cotton, coal, iron, oil, copper, rubber They also needed foreign markets to sell goods Control region/country first to protect investment Imperial Powers Western European Countries grew stronger. They had strong economies (industry), organized government, and powerful armies Non European civilization declined in power Middle East, India, Asia, Africa Motives for Imperialism Economic Desire to make money To expand and control foreign trade Create new markets for products and Export goods Acquire raw materials and cheap labor Compete for investments and resources Political Nation’s desire to gain power Expand territory and compete with other nations Exercise military force Gain prestige by winning colonies Boost national pride and security Motives for Imperialism Religious Desire to spread Christianity Spread Christian values and moral Educate people on European Religions Exploratory Desire to explore the “unknown” Conduct scientific research, medical searches Adventure, investigate unknown lands and cultures Motives for Imperialism Ideological Based on cultural values such as the belief in superior races (Ethnocentrism) Europeans should “civilize” other people “White Man’s Burden” Poem by, Rudyard Kipling Social Darwinism: only the strongest nations will survive Effects of Imperialism Indigenous (native populations) fought invaders with little or no weapons Colonies attempted to strengthen or reform their own traditions Growth of Nationalist movements to expel foreign imperialists