Cell Structures and Their Function
advertisement
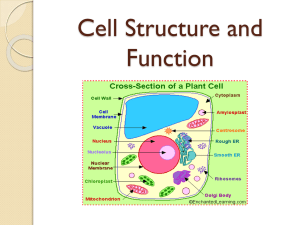
Functions of the Cell Basic unit of life Protection and support Movement Communication Cell Metabolism and energy release Inheritance Cell Structure Organelles: “little organs” within the cells that carry out the basic functions. Organelles lie in the cytoplasm of the cell, which is located between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Cell Membrane Cell/Plasma Membrane: Is the outermost component of the cell, which functions as a barrier between the extracellular substance (outside) and the intracellular substance (inside) Make up of the Cell Membrane Fluid Mosaic Model: Model used to show the structure and function of the cell membrane Structure of the cell membrane: Phospholipids (double Layered) Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Proteins Membrane Channels Carrier Molecules Receptor Molecules Nucleus All cell have a nucleus at some point in their life Nucleus: Stores hereditary information in DNA. Also site where RNA is copied from DNA. Nucleus Parts of the Nucleus 1.) Nuclear Envelope- double membrane, outer most layer 2.) Chromatin/Chromosomes- located inside nuclear envelope. 3.) Nuclear pores- Openings in the nuclear envelope, responsible for allowing RNA to pass through. 4.) Nucleolus- Place where ribosomes are made. Ribosomes Ribosomes: Organelles where proteins are produced and synthesized Rough and Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum: Transport system; canals and channels that connect membrane to nucleus and to organelles within the cell Rough ER: Contains ribosomes (manufactures proteins) Smooth ER: lacks ribosomes (Lipid synthesis) Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus: Collects, modifies, packages, and distributes proteins and lipids produced by the ER. Mitochondria Mitochondria: “Power house”, Major site where adenosine triphosphate (ATP) “energy” is produced. Do you think your muscle cells have a lot or a little mitochondria? Lysosomes Lysosomes: “Waste Management”, Contains enzymes that digest proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, DNA, RNA, old organelles, and viruses that get into the cell. Cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton- is a network of long protein strands that give a cell its shape and size. Two major components that make up the cytoskeleton 1.) Microfilaments 2.) Microtubules Microfilaments- Threads of protein called actin. Microtubules-Hollow tubes extend outwards from nucleus. When a cell divides, bundles of microtubules come together to form spindle fibers, which aid in moving chromosomes Cillia, Flagella, and Microvilli Structure: Cillia, microvilli and Flagella Function: Movement through cell environment. Cilia- Short tiny hair like structures. Flagella- Long hair like structures Microvilli- Increase surface area Label This Cell