World War I – World War II 1914-1945
advertisement

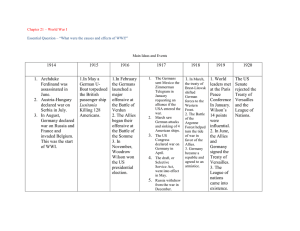
World War I – World War II 1914-1945 By Kassidy Durfee, Evan Perez, & Emily N. Presidents in this Era Woodrow Wilson – in office 1913-1921 W. G. Harding – in office 1921-1923 Democratic Party Persuaded Congress to pass the Federal Reserve Act, the Federal Trade Commission Act, the Clayton Antitrust Act, the Federal Farm Loan Act, and an income tax Republican Party Signed the Budget and Accounting Act of 1921, established the Bureau of the Budget, and created the General Accounting Office Calvin Coolidge – in office 1923-1929 Republican Party In 1924, signed the Indian Citizenship Act Presidents in this Era Herbert Hoover – in office 1929-1933 Franklin Delano Roosevelt – in office 1933-1945 Republican Party Expanded civil service coverage of Federal positions, suggested a Department of Education, and instructed the justice department to pursue gangsters on tax fraud. Thus effectively trapping Al Capone Democratic Party Served 4 terms in office, victoriously implemented the New Deal program, and pulled the US out of depression Harry S Truman – in office 1945-1953 Democratic Party Dropped both atomic bombs on Japan Platforms Election of 1912 President Taft (R) Woodrow Wilson (D) call for the strict government regulation of monopolies called for limits on campaign contributions by corporations, tariff reductions, stronger antitrust laws, banking reform, a federal income tax, a single term presidency, & the independence of Philippines Winner- Woodrow Wilson 6,296,284 in Popular vote 435 in Electoral College Election of 1916 underlined retention of the protective tariff, civil service protection, conservation of natural resources, & restrictions on immigration Theodore Roosevelt (Progressive) President Wilson (D) Charles E. Hughes (R) called for military preparedness, a ban on child labor, women's suffrage, and prison reform straightforward preparedness program & ban on child labor Winner- Woodrow Wilson 9,126,868 in Popular vote 277 in Electoral College Platforms Election of 1920 16,144,093 in Popular vote 404 in Electoral College 1923- Harding dies in office. VicePresident Calvin Coolidge takes over. reduce the tariff, income tax, farm relief with easier credit, free Philippines, strict antitrust laws, & reduce unemployment Robert de La Follette (Progressive) reducing taxes, collect foreign debts, protective tariff, opposing farm subsidies for crop prices, eighthour workday, banning child labor, & a federal anti-lynching law. John W. Davis (D) reflected the party's determination to continue Woodrow Wilson's progressive agenda at home & idealistic involvement abroad Winner- Warren G. Harding President Calvin Coolidge (R) condemned Wilson’s handling of World War I, opposed the League of Nations, advocated a higher protective tariff, & supported new immigration requirements. James M. Cox (D) Election of 1924 Warren G. Harding (R) Anti- industrial monopolies, public ownership of water resources and railroads, inheritance tax, & tax relief for farmers Winner- Calvin Coolidge 15,723,789 in Popular vote 382 in Electoral College Platforms Election of 1928 Herbert Hoover (R) promised lower taxes, a protective tariff, opposition to farm subsidies, a new farm agency, & the vigorous enforcement of Prohibition downplayed the tariff issue, support for public works projects, a federal farm program, federal aid to education, & enforcement of Prohibition Winner- Herbert Hoover Election of 1932 21,427,123 in Popular vote 444 in Electoral College President Hoover (R) called for a balanced budget, a protective tariff, & urged repeal of the 18th Amendment Franklin D. Roosevelt (D) Al Smith (D) “A new deal for the American people.” Winner- Franklin D. Roosevelt 15,723,789 in Popular vote 472 in Electoral College Platforms Election of 1936 President Roosevelt (D) “business and financial monopoly, speculation, reckless banking” no new deal, preservation of free enterprise, private competition, equality of opportunity, reemployment, & relief Winner- FDR Election of 1940 27,752,648 in Popular vote 523 in Electoral College President Roosevelt (D) Alf Landon (R) Wendell Willkie (R) still the New Deal… opposed FDR's public power policies, especially the TVA, & anti-American involvement in WW2 Winner- Franklin D. Roosevelt 27,313,945 in Popular vote 449 in Electoral College Platforms Election of 1944 President Roosevelt (D) Thomas E. Dewey (R) end the war promptly, promote world-wide stability after the war, develop Pan-American solidarity & reestablishing liberty at home Winner- FDR get through the war and continue to utilize implemented New Deal programs, equal pay for equal work regardless of sex 25,612,916 in Popular vote 432 in Electoral College April 12, 1945- Franklin D. Roosevelt dies in office. His VicePresident Harry Truman resumes the rest of the term in his place. Setting the Stage For War… In 1914 tensions in Europe were at an alltime high. Eventually WWI could not be stopped. M.A.N.I.A. (causes of world war 1) Militarism Alliances Nationalism Imperialism Assassination Causes Of WWI Militarism- the policy of building up strong military forces to prepare for war. From 1910-1914 defense expenditures increases significantly. France- 10% Britain- 13% Russia- 39% Germany- 73% The European powers modernized and equipped their armies and navies, bringing the continent closer to war. Causes Of WWI Alliances Triple Entente- Britain, France, and Russia Triple Alliance- Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy (at first anyway) Nationalism- Each European superpower had developed a firm but excessive belief in its own cultural, economic, and military supremacy. This sense of invincibility led to interesting confrontations as things heated up before the first World War. Don’t worry there will be pictures eventually, I promise. :D Causes Of WWI Imperialism- In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, colonies were both a sign of prestige and a source of great wealth. Germany, France, and Britain began competing for foreign markets and territory in Africa, which increased tension between the countries. Assassination- June 28, 1914 Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his pregnant wife Sophie are murdered by the Black Hand while visiting Sarajevo, the Bosnian capital, and participating in a parade. This was the spark that ignited the Great War or World War I. Domino Effect July 28, 1914- Austria-Hungary declares war on Serbia Germany supports Austria-Hungary Russia backs Serbia August 1- Germany declares war on Russia August 2- France pledges support for Russia August 3- Germany declares war on France On the way to France, Germany invades Belgium, which angers Great Britain. Don’t Worry, It Continues… August 4- Great Britain supports Belgium and declares war on Germany August 6- Austria-Hungary declares war on Russia and Serbia declares war on Germany August 19- US President Wilson declares the United States a neutral party in the conflict. August 23- Mons Battle First French and British coop. against Germany Retreat to the Marne River August 26- Battle of Tannenberg Russian and German conflict 90,000 killed or wounded Sides Are Taken Allied Powers Central Powers VS May the Battle(s) Begin. September 5, 1914 the First Battle of Marne begins. Trench warfare is seriously used for the first time in the war. Retreated French and British soldiers from the Mons Battle against German long range artillery First time air recon and radio interceptions were used in a major conflict France learned of German position Called for reinforcements from Paris Soldiers came in taxis and buses to get there See pictures! Major Military Actions October 19, 1914- First Battle of Ypres November 3- UK blockades Germany from North Sea February 4, 1915- Germany declares waters surrounding Great Britain a war zone. Created a submarine blockade, no merchant ship was safe February 19- Dardanelles Campaign begins April 22- Second Battle of Ypres begins Attempt to halt German advances First recorded time that Germans used poisonous gases April 25- Battle of Gallipoli begins Major Military Actions May 7, 1915- RMS Lusitania is sunk by a German u-boat. May 23- Italy declares war on Austria-Hungary September 5- Tsar Nicholas II takes intimate control of Russia’s armies February 21, 1916- Battle of Verdun begins Longest battle of WWI, lasted until December 18th May 4- Germany makes Sussex Pledge May 31- Battle of Jutland Betrayed Central Powers and joined Allies Full scale military naval battle July 1- Battle of Somme First time tanks are introduced to battle Major Military Actions January 19, 1917- Germany sends Zimmerman telegram to Mexico March- Germany violates pledge to suspend Unrestricted Submarine Warfare April 2- President Wilson goes before Congress to request a declaration of war. April 6, 1917- United States of America declares war on Germany July 30- Third Battle of Ypres begins November 7- Bolsheviks overthrow Russian government in revolution December 17- Armstice between Russia and Central Powers goes into effect More of Them…. January 8, 1918- President Wilson issues his 14 Points March 21- Germany launches it’s Spring Offensive April 21- Baron Manfred von Richthofen (Red Baron) is shot down July 15- Second Battle of Marne begins November 9- Kaiser Wilhelm II abdicates and flees Germany November 11- Germany signs armstice June 28, 1919- Treaty of Versailles is signed. WWI is over Treaties Treaty of Versailles Treaty of St. Germain Treaty between allies and Hungary. Greatly reduced Hungary’s atomic might Treaty of Neuilly Ended the war with Austria and dismantled Austrian Empire Treaty of Trianon Demilitarized Germany, Germany had to take full responsibility for the war, many territories were taken from Germany and distributed, and the League of Nations was established to keep the peace Bulgaria was to pay $100 million in reparations and demilitarized to an army of 20,000 men only. They also gave up a few territories Treaty of Serves Peace treaty with the Ottoman Empire. Thought to be extremely harsh. the Allies were given the power to control their finances, Armenia was established, & the Kingdom of Hejaz was recognized Technology From the War Machine Gun Poison Gases Tanks Submarines Airplanes Gas Masks Longer Range Artillery Effects of WW1 World War 2 Prosperity of USA Dismantling of Europe’s monarchies German resentment New super weapons (for the time) US recognized entirely as a global power Women’s liberation Global Trade increase The Roaring Twenties Post-war, the economy of the United States soared partially due to inflation. Women’s skirts became shorter and morals became looser. Gang activity ran ramped. Bootleggers in Chicago and New York. Jazz and dancing characterized the age. Parties and illegal drinking were heavy Speakeasies and Flappers Cinema and Radio CARS!! AIRPLANES!! AL CAPONE!! Publications The Great Gatsby- F. Scott Fitzgerald Winnie-the-Pooh- A.A. Milne All Quiet on the Western Front- Erich Maria Remarque The Sun Also Rises- Ernest Hemingway This Side of Paradise- F. Scott Fitzgerald The Hobbitt- J.R.R. Tolkien Gone With the WindOf Mice and Men- John Steinbeck The Grapes of Wrath- John Steinbeck Harlem Renissance African-American literary and artistic cultural Revolution in 1921. The first black recording house opened in 1921. African Americans had their own musicals in 1921. In 1923, the Harlem Globetrotters were created. Langston Hughes Zora Neale Hurston Rise of jazz. The Dirty Thirties The Great Depression Causes Stock Market Crash Over speculation Bank Failures Reduction of Consumers Economic Policy with Europe Drought World War 2 Causes Hitler & dictators Treaty of Versailles Failure of Appeasement Failure of the League of Nations Highlights March 1935- Germany begins rearmament March 1936- German troops re-occupy the Rhineland March 1938- German forces annex Austria September- Germany annexes Sudetenland and signs the Munich Agreement with Britain and France. March 1939- Germany annexes all of Czechoslovakia August- Germany and Russia sign a 10 non-aggression pack September- Germans begin attacking Poland Britain and France declare war on Germany So does Canada Russian Armies invade poland WW2 Highlights March 1940- Soviet Union conclude a peace girl Treaty April- German Troops invade Denmark May- Main Dutch Army surrenders to Germany. Belgium surrenders June- Norway surrenders to Germany. Italy declares war on Britain and France. France surrenders to Germany July- Battle of Britain begins WW2 Highlights September 1940- War in Africa begins. Japan signs the Tripartite, joining forces with Germany and Italy April 1941- Yugoslavia & Greece surrender to Germany June- Germany launches a massive attack on the Soviet Union December 8, 1941- Pearl Harbor December 9, 1941- USA is in the war WW2 Highlights January 1942- Wannsee Conference is held February- Japanese land in Singapore May- Japanese forces capture the Philippines. Battle of Coral Sea. June- Battle at Midway September- German forces begin the battle for Stalingrad November- Operation Torch. February 1943- German army surrenders at Stalingrad WW2 Highlights….Again August- Allied forces recapture Sicily November- Hitler issues a directive warning of Allies landing in western Europe. Battle of Berlin begins. March 1944- Allies win Battle of Berlin. June- D-Day. AM forces recapture Rome July-September- tons of small places are liberated! October- US returns to the Philippines December- ‘Battle of the Bulge’ Last Time I Promise March 1945- Allies bomb Tokyo killing 85,000 April 30, 1945- Adolf Hitler and his wife commit suicide in an underground bunker May- Soviets complete the capture of Berlin August- Atomic Bombs are dropped on Nagasaki and Hiroshima in Japan September- Japan signs official surrender Foreign Policy One major factor of United States and Germany having tensions was Germany’s unrestricted warfare. Events such as the sinking of unarmed vessel ships Ex: The sinking of the RMS Lusitania Another major factor that led to the US joining the war was the Zimmerman Telegram, a telegram written by German Foreign Minister Arthur Zimmerman to the German Ambassador in Mexico City, proposing an alliance against U.S. This along with the submarine attacks led to the public opinion sway from neutrality to war. Even before declaring war, the United States helped the allies with supplies on merchant ships. The United States declared war on April 17, 1917. Foreign Policy After WW1 After WW1, Wilson developed the League of Nations and his Fourteen Points in order to make sure that this Great War never happened again. Fourteen Points is rejected and United States leaves meetings. Treaty of Versailles put huge financial punishments on Central Powers, mainly Germany This inevitably lead to World War 2. Foreign Policy on WW2 After news of Germany’s aggression, Roosevelt started to take steps in order to prepare the U.S. for war. The United States remained neutral but helped out Britain with acts such as the Lend Lease Act, giving Britain old battleships for naval bases in North and South America U.S. passed the Neutrality Acts of 1935, 1936, 1937, & 1939 All neutrality was gone after the attack on Pearl Harbor. FDR went to Congress the next day December 8, 1941 and asked for a declaration of war. Major Supreme Court Decisions Korematsu v. United States 1944 After the bombing of Pearl Harbor, the United States feared an attack in the US by Americans of Japanese descent might help the enemy, so the government put them into internment camps. Fred Korematsu challenged this saying that the government didn’t have the power to issue relocation orders and he was being discriminated because of his race. The court decided with the government because the need to protect the country was a greater priority than individual rights of the Japanese and the Japanese Americans. Major Supreme Court Decisions Takao Ozawa v. United States Filed for United States citizenship under the Naturalization Act of 1906, wanted Japanese to be classified as white. The court ruled him ineligible for naturalization. Japanese were members of an “unassailable race” , lacking provisions in any Naturalization act. Major Supreme Court Decisions De Jonge v. Oregon 1937 A case that held that the fourteenth amendment due process clause applies to freedom of assembly Amendments 18th Amendment- 1919 19th Amendment- 1920 Prohibits denying someone the right to vote based on sex. Gave women the right to vote 20th Amendment- 1933 Made the production, transport, and sale of alcohol illegal Changed the date of when the terms of President, Vice-President, and Senators end/begin 21st Amendment- 1933 Repealed the 18th Amendment and only amendment to ever repeal a previously existing one