The Odyssey - Plain Local Schools
advertisement

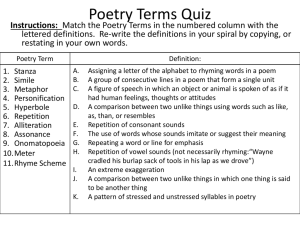
The Odyssey Literary Terms: Please copy those that are NOT labeled review. Alliteration (Review) Repetition of initial consonant sounds Example: “Where shall a man find sweetness to surpass?” Allusion (Review) A figure of speech that refers to a wellknown story, event, person, or object in order to make a comparison in the readers' minds. Archetype A character, symbol, or behavioral pattern that is basically a universal template for a character that is copied throughout all forms of storytelling. Example: The Hero Example: The Mother Figure Example: The Wise Old Man Assonance (Review) Repetition of vowel sounds Example: “before/ Odysseus’ door, the threshold to his court” Example: Grab Bag Caesura (Review) A pause or sudden break in a line of poetry Catalogs/Genealogies Verse that presents a list; usually of people, objects, or abstract qualities. Example: Character list at the beginning of an epic poem Consonance (Review) Repetition of consonant sounds NOT limited to the beginning of words. Example: River and Ever Elegy/ Elegiac Mood A mournful, melancholic or plaintive poem, especially a funeral song or a lament for the dead. End Rhyme (Review) Rhyming words that appear at the ends of two or more lines of poetry Example: “Nor till the ground, though grain . . .” Ripen in heaven’s rain . . .” Enjambment (Review) Running over of a sentence or a thought from one line to another Epic Hero The main character in an epic poem-typically one who embodies the values of his or her culture. Epic Poem A long, narrative poem that is usually about heroic deeds and events that are significant to the culture of the poet. Epic Simile Also called Homeric simile, an extended simile often running to several lines, used typically in epic poetry to intensify the heroic stature of the subject and to serve as decoration. Epithet A byname, or a descriptive term , accompanying or occurring in place of a name and having entered common usage. It can be described as a glorified nickname. Example: “Alexander the Great” Example: “Slayer of Argos” Hyperbole (Review) Exaggerations effect. to create emphasis or Example: I tried 1,000 times Imagery (Review) The use of vivid language that appeals to the senses “The Cyclops’ rams were handsome, fat, with heavy fleeces, a dark violet” In Medias Res Latin: in the middle of the narrative. *Many epics start this way. Invocation The act of invoking or calling upon some agent for assistance A prayer asking God for help An appeal for inspiration and guidance from a Muse or deity at the beginning of a poem Internal Rhyme (Review) Rhyme between a word within a line and another either at the end of the same line or within another line. Myth A traditional story, especially one concerning the early history of a people or explaining some natural or social phenomenon, and typically involving supernatural beings or events. Onomatopoeia Words for sounds. Example: hiss Oral Tradition Information passed down through the generations by word of mouth that is not written down. This includes historical and cultural traditions, literature and law. Personification (Review) A figure of speech in which an animal, object, force of nature, or idea is given human characteristics Example: “Death sat there” Point of View (Review) Vantage point from which the story is told Example: Some of the Odyssey is 1st person point of view, from the perspective of Odysseus Rhapsodes/Bards Refers to a classic Greek performer of epic poetry. Associated with the oral tradition Rhyme (Review) Repetition of identical sounds Rhyming Couplet (Review) Two consecutive lines that rhyme Slant Rhyme (Review) Sounds that are similar but not identical Example: again/them Speaker (Review) The voice in a piece of writing that is assumed by the writer. Syllable A unit of pronunciation. Theme (Review) The main idea or lesson in a literary work. *Should be a phrase or sentence– NOT ONE WORD! Tone (Review) Attitude of a writer toward a subject or an audience. * Tone is sometimes confused with mood. T he author’s feelings O N E M y feelings O O D







![English poetic terms[1].](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009640365_1-09d91eea13bb5c84d21798e29d4b36a3-300x300.png)