Gases - My Teacher Pages
advertisement

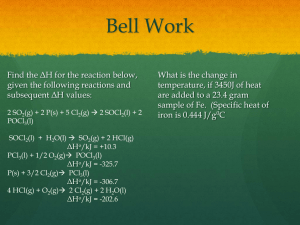
treehuggerusa.com treehugger.com Gases balloonfestivals.com Pressure The force per unit area of a surface. Units: N/cm2 N, Newton: SI unit of force As area of contact changes, force changes 500 N = 1.7 N 500 N = 83.3 N 300 cm2 cm2 6.0 cm2 cm2 Christina, Will you go to the prom with me? Steve Barometer • Used to measure the pressure of gases. barometerplanet.com Units of Pressure for Gases • Millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) • Torricelli or 1 torr = 1mm Hg • 760 mm Hg = 1 atmosphere at sea level when temp is 0oC • Pascal = pressure exerted by a force of one newton acting on an area of one square meter. Pa = N/m2 • 1.013 x 105 kPa = 1 atmosphere= 10.1N/cm2 Pressure conversion sample: Express 0.725 atm in a) mm Hg and b) kilopascals (kPa) A) 0.725 atm x 760 mm Hg = 551 mm Hg 1 atm B) 0.725 atm x 101.325 kPa = 73.5 kPa 1 atm Standard Conditions (STP) Standard Temperature is o 0 C or 273K Standard Pressure is 1 atm or 760 mm of Hg You must have done by next meeting: A list of the units of pressure (see page 364) and A list of the gas laws: Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures: PT = P1+P2+… Boyle’s: P1V1 = P2V2 T constant Charles’s: V1 = V2 P constant T1 T2 Gay-Lussac’s: P1 = P2 V constant T1 T2 Combined Gas: P1V1 = P2V2 T1 T2 Ideal Gas: PV = nRT Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases. Gas collected through water picks up water vapor, so allow inside and outside water levels in a gas collection device to stabilize and: Patm = Pgas + PH20 Dalton sample problem: Oxygen gas is collected by water displacement. The barometric pressure and the temperature during the experiment are 731.0 torr and 25.0oC. What was the partial pressure of the oxygen collected? PT = Patm = 731.0 torr PH20 = 23.8 torr (see vapor pressure of water at 25.0 oC from table in handout or book – Table A-8) PT = Patm = 731.0 torr PH20 = 23.8 torr (see vapor pressure of water at 25.0 oC from table in handout or book – Table A-8) Patm = PO2 + PH20 So PO2 = Patm – PH20 PO2 = 731.0 torr – 23.8 torr = 707.2 torr Boyle’s Law – at constant temperature, volume of a fixed gas varies inversely with the pressure. If 100.0 mL of a gas, originally at 760 torr, is compressed to a pressure of 800 torr, at a constant temperature, what would be its final volume? P1V1 = P2V2 --> V2 = P1V1 P2 V2 = 100mL(760 torr) = 95.0 mL 800 torr Charles’ Law – the volume of a fixed mass of gas at constant pressure varies directly with the Kelvin temperature. A sample of neon gas has a volume of 752 mL at 25.0oC. What will the volume at 100.0oC be if pressure is constant? V1 = V2 --> V2 = V1T2 T1 T2 T1 V2 = 752 mL (100.0oC) = 300.8 mL 25.0oC Gay-Lussac’s Law – the pressure of a fixed mass of gas at constant volume varies directly with the Kelvin temperature. At 122oC the pressure of a sample of nitrogen gas is 1.07 atm. What will the pressure be at 205oC, assuming constant volume? P1/T1 = P2/T2 --> P2 = P1T2 T1 P2 = 1.07 atm(205&273) = 1.29 atm 122+273 Gay-Lussac’s Law of combining volumes At constant temperature and pressure, the volumes of gaseous reactants and products can be expressed as ratios of small whole numbers. H2 + Cl2 --> 2HCl 1L 1L 2L H:Cl:HCl = 1:1:2 Formulas must be written correctly and chemical equation balanced. Combined Gas Law – expresses the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature of a fixed amount of a gas. PV = k T P1V1 = P2V2 --> To find V2: V2 = P1V1T2 T1 T2 P2T1 Problem: The volume of a gas is 27.5mL at 22.0oC and 0.974 atm. What will be the volume at 15.OoC and 0.993 atm? Temps to K: 22+273 = 295K and 15+273=288K The volume of a gas is 27.5mL at 22.0oC and 0.974 atm. What will be the volume at 15.OoC and 0.993 atm? V2 = P1V1T2 V1 = 27.5ml P2T1 T1 = 295K V2 = 0.974atm(27.5ml)(288K) P1 = 0.974atm 0.993atm(295K) V2 = ? V2 = 26.3 mL T2 = 288K P2 = 0.993atm Hint: in solving gas law problems, use the combined gas law and quantities that don’t change will cancel out. Avogadro’s Law – equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules. Ratios apply here also. 2H2 + O2 --> 2H2O 2molecules 1molecule 2molecules 2mol 1mol 2mol 2volumes 1volume 2volumes Standard molar volume of a gas is the volume occupied by one mole of a gas at STP. Standard molar volume = 22.4 L/mol Steve, Yes, I will go to the prom with you. Christina At STP, what is the volume of 7.08 mol of nitrogen gas? 7.08 mol (22.4L) = 158 L 1 mol A sample of gas occupies 11.9 L at STP. How many moles of the gas are present? 11.9L (1 mol) = 0.531 mol 22.4L Assuming all volume measurements are made at the same temperature and pressure, what volume of hydrogen gas is needed to react completely with 4.55 L of oxygen gas to produce water vapor? Write and balance the equation. Label known and unknown. Do unit analysis. Gas Stoichiometry – dealing with proportional relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. 2CO2(g) + O2(g) --> 2CO2(g) 2molecules 1 molecule 2 molecules 2 mol 1 mol 2 mol 2 volumes 1 volume 2 volumes Assuming all volume measurements are made at the same temperature and pressure, what volume of hydrogen gas is needed to react completely with 4.55 L of oxygen gas to produce water vapor? Write the correct chemical reaction first: 2H2 + O2 --> 2H2O Indicate known and unknown: Solve: Ideal Gas Law – the mathematical relationship among pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles of a gas. PV = nRT --> R = PV R is the ideal gas nT constant. At STP, R = 1 atm(22.414 L) = 0.0821 L atm 1 mol(273.15K) mol K R is the ideal gas constant. What pressure, in atmospheres, is exerted by 0.325 mol of hydrogen gas in a 4.08 L container at 35oC? PV = nRT --> P = nRT V T = 35 + 273 = 308K P = 0.325 mol 0.0821L atm) (308K) 4.08 L mol K P = 2.01 atm Gases spread out in a container – diffusion Gases can randomly pass through a tiny opening in a container (leak out) - effusion