Introduction to the Properties of Gases
advertisement

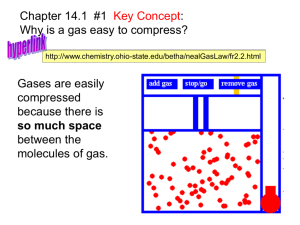
Introduction: Properties of Gases What do you know about gases? • Particle Diagrams • Ar(g), H2(g), CO2(g) • Gases take shape and volume of their container • Gases flow • Gases have low densities Properties of Gases 1. Gases have mass 2. Gases take shape & volume of their container 3. Gases are compressible 4. Gases move through each other easily “Diffusion” perfume, skunks! 5. Gases exert pressure Gases take shape of container Why don’t these balloons keep expanding until they pop? What is pressure? • Pressure = force per unit area • P = Force Area Force = mass x acceleration Would you rather have your foot stepped on by someone wearing sneakers or stilleto heels? What is air pressure? • pressure exerted on us by weight of gases above our heads (& all around our body) • at sea level: air pressure = 1 atmosphere Torricelli • discovered air pressure • invented mercury barometer in 1643 • 1st person to propose correct explanation for wind Mercury Barometer 1 To report air pressure: take short-cut & report height of Hg column at 1 atm column is: 29.92 in Hg 76 cm Hg 760 mm Hg How does the downward pressure of the Hg in the column compare to the pressure of the atmosphere? water barometer has to be 13.6 times taller than Hg barometer (DHg = 13.6 g/ml) because … DH2O = 1.0 g/ml How does air pressure at top of Mt. Whitney (14,494 ft) compare to air pressure at John Jay? It’s less What about Death Valley (86 m below sea level)? It’s greater When you drink through a straw, you reduce the pressure in the straw • Why does the liquid in the cup go up the straw? • Could you drink a soda this way on the moon? Why or why not? Units of pressure = 1 atm • 14.7 lb/in2 • 29.9 in Hg • 1.013 bars U.S. pressure gauges U.S. weather service Physics & Astronomy CHEMISTRY: 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg = 101.3 kPa SI Units What causes the pressure of a gas in a closed container? Impacts of gas molecules with walls of container Anything that ↑ # of impacts per second or force of each impact ↑ pressure Microscopic View Light molecules move faster & hit walls more often Heavy molecules hit walls with greater force These 2 effects essentially balance out **Gas pressure doesn’t depend on the identity of the gas** Pressure Depends on 1) concentration • # of gas molecules per unit volume (moles!!) and 2) temperature How fast do molecules in the air move? • Depends on mass • Light molecules are faster than heavy molecules at same temperature • Temperature = measure of average KE of particles in system Molecular Speeds at 298 K • • • • • H2 He O2 Ar Xe 1.93 X 105 cm/sec 1.36 X 105 cm/sec 4.82 X 104 cm/sec * 4.31 X 104 cm/sec 2.38 X 104 cm/sec 1080 miles per hour Pressure – Microscopic View • Gas molecules hit walls of container • Pressure depends on – Number of impacts per unit time – Force of each impact Pressure – Macroscopic View • Pressure depends on: • how many gas molecules per volume and • temperature • same amount of gas exerts different pressure at different temperatures • Tires • Bike • Car • etc Describing Gas Phase System Need 4 variables to describe gas phase system from macroscopic or lab view 1. Pressure (P) 2. Volume (V) 3. Temperature (T) 4. Amount of gas (# moles) Exit Ticket 1. List 5 common properties of all gases? 2. Draw a particle diagram substance in gas phase 3. Use picture from #2 to explain at least 2 properties of gases Bonus: At 0oC, a He atom is moving at 120 meters/sec. How fast is this in miles per hour? Show all work!