Acts and Laws: 1649-1774
advertisement
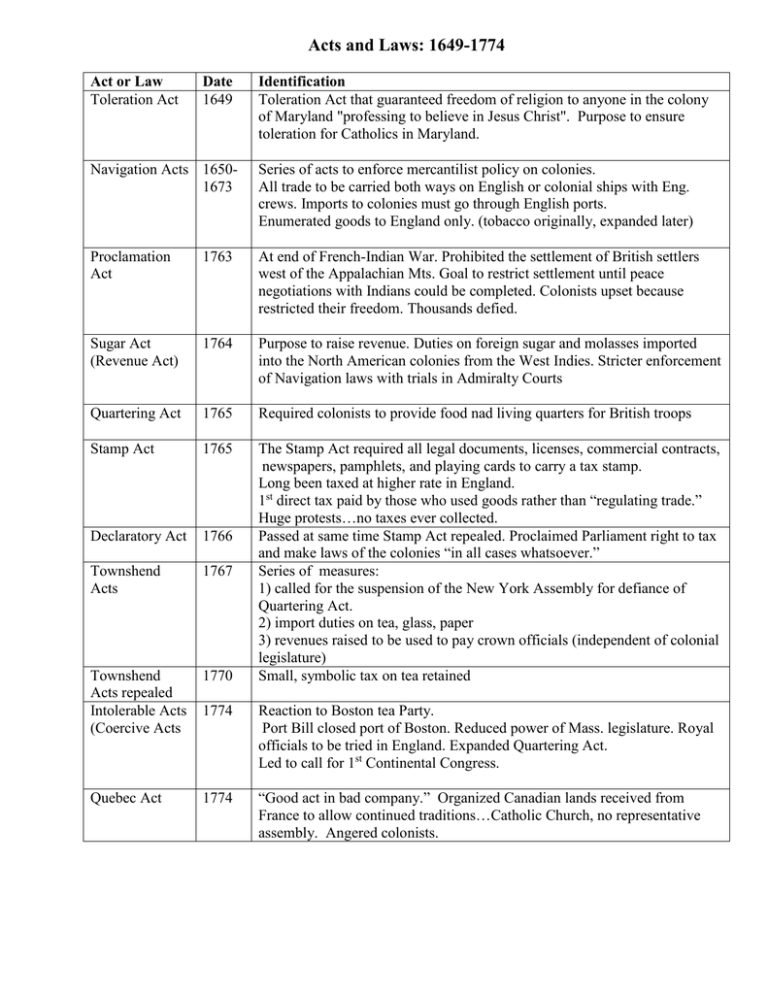
Acts and Laws: 1649-1774 Act or Law Toleration Act Date 1649 Identification Toleration Act that guaranteed freedom of religion to anyone in the colony of Maryland "professing to believe in Jesus Christ". Purpose to ensure toleration for Catholics in Maryland. Navigation Acts 16501673 Series of acts to enforce mercantilist policy on colonies. All trade to be carried both ways on English or colonial ships with Eng. crews. Imports to colonies must go through English ports. Enumerated goods to England only. (tobacco originally, expanded later) Proclamation Act 1763 At end of French-Indian War. Prohibited the settlement of British settlers west of the Appalachian Mts. Goal to restrict settlement until peace negotiations with Indians could be completed. Colonists upset because restricted their freedom. Thousands defied. Sugar Act (Revenue Act) 1764 Purpose to raise revenue. Duties on foreign sugar and molasses imported into the North American colonies from the West Indies. Stricter enforcement of Navigation laws with trials in Admiralty Courts Quartering Act 1765 Required colonists to provide food nad living quarters for British troops Stamp Act 1765 Declaratory Act 1766 Townshend Acts 1767 Townshend Acts repealed Intolerable Acts (Coercive Acts 1770 The Stamp Act required all legal documents, licenses, commercial contracts, newspapers, pamphlets, and playing cards to carry a tax stamp. Long been taxed at higher rate in England. 1st direct tax paid by those who used goods rather than “regulating trade.” Huge protests…no taxes ever collected. Passed at same time Stamp Act repealed. Proclaimed Parliament right to tax and make laws of the colonies “in all cases whatsoever.” Series of measures: 1) called for the suspension of the New York Assembly for defiance of Quartering Act. 2) import duties on tea, glass, paper 3) revenues raised to be used to pay crown officials (independent of colonial legislature) Small, symbolic tax on tea retained 1774 Reaction to Boston tea Party. Port Bill closed port of Boston. Reduced power of Mass. legislature. Royal officials to be tried in England. Expanded Quartering Act. Led to call for 1st Continental Congress. Quebec Act 1774 “Good act in bad company.” Organized Canadian lands received from France to allow continued traditions…Catholic Church, no representative assembly. Angered colonists. Acts and Laws: 1785-1850 Act or Law Land Ordinance Act of 1785: Date 1785 Northwest Ordinance Hamilton's Financial Program 1787 Alien and Sedition Acts 1798 Virginia and Kentucky Resolves 179899 Missouri Compromise 1820 Tariff of Abominations Tariff Compromise Tariff Compromise of 1850 1828 Identification Provided for surveying western territories into 6 mile-square townships before sale. Every other township was to be subdivided into 36 sections of 640 acres each. Provided for territorial status and then statehood .Outlawed slavery on the Old Northwest Proposed the funding of the national debt at face value, federal assumption of state debts, and the establishment of a national bank. Extensive program for federal stimulation of industrial development, through subsidies and tax incentives. Funding of these programs would come from an excise tax (whiskey) and from tariffs on imports. The Alien Act raised new hurdles in the path of immigrants trying to obtain citizenship (to become a citizen you had to live in the country for 14 years not 5). The Sedition Act widened the powers of the Adams administration to muzzle its newspaper critics. Madison and Jefferson came up with these resolves ( in response to Alien and Sedition Acts) which were presented to the Virginia and Kentucky legislatures respectively. They proposed that John Locke's "compact theory" be applied, which would empower the state bodies to "nullify" federal laws within those states. The issue died since the resolves were only adopted in Kentucky and Virginia Henry Clay proposal, the Missouri Compromise stated that the Louisiana Purchase would be divided among the latitude 36 degrees 30', the north for non-slave states and the south for slave states. Missouri would become a slave state, Maine as a free state, thus balancing the representation in the Senate. Increased tariff to levels deemed intolerable by the South 1832 1833 South Carolina reacted by nullifying tariff. Clay compromise. Accompanied by Force Bill, which SC nullified 1850 Compromise over admission of states from the Mexican Cession. California free state, the slave trade was abolished in Washington D. C., the Fugitive Slave Act was passed, and the territories of New Mexico and Utah were established on the basis of popular sovereignty which would allow the people in the territory to decide the issue of whether the territory should be slave or free. 1790 Progressive Era Legislation 1890 1901 1902 1903 1905 1906 1911 1912 1913 1914 1916 1919 1920 Sherman Antitrust – Outlaw monopolies – restraint trade (not effective) New York Tenement House Law – housing code for safety and sanitation Newlands Reclamation Act – federal irrigation Elkins Act – outlaw rebates U.S. Forest Service – manage water and timber Hepburn Act – strengthen ICC – permission to raise rates Pure Food and Drug Act Meat Inspection Act New York State Factory Commission (result of Triangle fire) Illinois grants aid to dependent children Mass. estab. min wage for women and children 16th Amendment – federal income tax authorized 17th Amendment – direct election of senators Underwood Tariff – lowered tariff, levied income tax Dept. of Labor estab. Federal Reserve Act – established federal to regulate banks and currency Federal Trade Commission – oversee business activities Harrison Act – regulated distribution and use of narcotics Smith-Lever Act – county agent system; grants to estab agricultural extension program Clayton Antitrust Act – weak Keating-Own Act – Indirectly prohibited child labor ( prohibited taking children across state lines for work) National Park Service Seamen’s Act – rights of merchant marines Federal Farm Loan Act – low interest rural loans 18th Amendment – prohibition 19th Amendment – Woman suffrage Women’s Bureau established within Department of Labor