Computers - Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology
advertisement

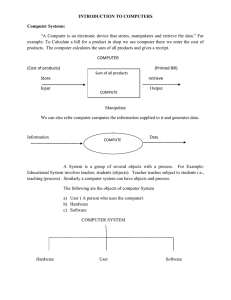
Introduction to Information Technology Executive Diploma in Information Technology About the course instructor • Maizatul Akmar Ismail • Department of Information Science Faculty of Computer Science & Information Technology, UM • 03-79676324 • maizatul@um.edu.my • Wednesday 10.00-12.00 p.m The course – 7 Sundays • Computer Hardware • Computer software • Application programs Word processing Presentation Spreadsheets • Data & information management • Computer networking • Applications of networking: Internet, Intranet Course Evaluation • • • • Final exam – 50% (Week 8) Individual Presentation – 15% Group Presentation – 15% (Due Week 7) 2 test – 20% (MCQ + structured – Week 3&6) Introduction to Computers Computer hardware Input, Output & peripheral devices History of computers Objectives • Describe the three fundamental characteristics of computers • Describe at least four areas of society in which computers are used • Identify the basic components of a computer system: input, processing, output, and storage • List some common input, output, and storage media • Distinguish data from information • Describe the significance of networking • Explain the significance of the Internet • Explain the various classifications of computers Contents • • • • • • Information Age Computer Literacy Where Computers Are Used Computer System Network Classifications of Computers Information Age • Evolving more rapidly than Industrial Age • Will continue into the current century Cornerstones of our Economy Forging a Computer-Based Society: • • • • Land Labor Capital Information Jobs Forging a Computer-Based Society: • From physical to mental • From muscle-power to brain-power A Computer in Your Future • Where used? – Bank withdrawal – Supermarket – Drive the car • Do I need a Personal Computer? – Campaign: One Home, One PC – Many more use at work • Will I use a computer in my future career? – Almost every job will involve use of a computer Computer Literacy • Awareness – Importance – Versatility – Pervasiveness in our society • Knowledge – What are computers – How do computers work – Terminology • Interaction – Use some simple computer applications Is computer literacy enough? • Need to be computer literate to manipulate a computer • Need to be computer fluent on computer concepts as a basis to build deeper knowledge • Computer fluency make one able to continue follow developments as computers continue to evolve The Nature of Computers Characteristics Results • Speed • Reliability • Storage capability • Productivity • Decision making • Cost reduction Where Computers Are Used: Graphics Graphs and charts Animated graphics Visual walk-through Where Computers Are Used: Education • Teaching and testing aid • Learning by doing • Computer-based instruction Where Computers Are Used: Retailing • Bar codes for pricing and inventory • Shipping Where Computers Are Used: Energy • Locate oil, coal, natural gas, and uranium • Monitor the power network • Meter reading Where Computers Are Used :Law Enforcement • National fingerprint files • National files on criminal • Computer modeling of DNA Where Computers Are Used: Transportation • Cars • Run rapid transit systems • Load containerships • Track railroad cars • Monitor air traffic Where Computers Are Used: Money • Record keeping • Banking by phone • Credit cards Where Computers Are Used: Agriculture • Billing • Feed combinations • Crop information • Livestock breeding and performance Where Computers Are Used: Government • Forecast weather • E-government • Process immigrants • Taxes • Registration: birth, identity, car etc. Where Computers Are Used: The Home • • • • • Educational tool Record keeping Letter writing Budgeting Drawing and editing pictures • Newsletters • Connecting with others Where Computers Are Used: Health and Medicine • Monitor patients • Electronic imaging • Diagnose illnesses • Tele-health Where Computers Are Used: Robotics • Perform jobs that are dangerous for humans • Factory work Where Computers Are Used: The Human Connection • Assist the disabled • Assist athletes by monitoring their movements Where Computers Are Used The Sciences Connectivity • Research • Simulation • Communication • Telecommuting Where Computers Are Used Training Paperwork • Airline pilots • Railroad engineers • Junk mail • Term paper • Record keeping Computers are all around! • • • • • • Grocery store Schools Libraries Bank Mail Malls We interact with computers everyday! What computers can’t do yet? Complex human activities Computer System People Software Hardware People • Computer programmer – person who writes programs • Users or End-users – make use of the computer’s capabilities Software • Programs • Set of instructions that directs the hardware to do a required task and produce the desired results Hardware: Basic Components of a Computer Computer • A machine that can be programmed to accept data (input), process it into useful information (output), and store it away (in secondary storage device) for safekeeping or later reuse • Process is directed by software but performed by the hardware Function of Computer System Data handling I P O S Input Process Output Storage Processing: Batch vs. Interactive • 2 types of information processing – Batch processing – Interactive processing : Real time Input devices • Accept data or commands and convert them to electronic form • Getting data into the computer – Typing on a keyboard – Pointing with a mouse – Scanning with a wand reader or bar-code reader – Terminal Can you think of any other input devices? Output devices • Convert from electronic form to some other form • May display the processed results • Usable information Monitor or screen Printer • • • • • • • Black and white • Color Text Numbers Symbols Art Photographs Video The Processor Central Processing Unit (CPU) • Converts data to useful information • Interpret and execute instructions • Communicate with input, output and storage Two Types of Storage • Secondary storage long-term storage • Primary storage or memory temporary storage Memory / Primary Storage • Temporary storage • Holds input to be processed • Holds results of processing • Contains the programs to control the computer and manipulate input into output • Volatile Secondary Storage • Long-term storage • Non-volatile Secondary Storage Examples • Magnetic disks – read and written by magnetic disk drive – Hard disk – Diskette • Optical disks – read and written by optical disk drives – CD-ROM – DVD-ROM • Magnetic tape – read and written by magnetic tape drives – Primarily used for back-up Computer System • Computer – CPU – Memory • Peripheral equipment – Connected to the computer by a cable – Input, output, storage Computer Network • Definition – A system that uses communications equipment to connect computers and their resources. • Types – Local area network (LAN) – connects computers in close proximity – Metropolitan are network (MAN) – connect computers between buildings in the same geographic area – Wide are network (WAN) – connects computers over great distances Home Connectivity • Connect home PC to other computers • Use modem to convert signals between electronic (computer) and analog (voice) formats Internet • • • • Collection of networks No ownership No central source for services available No comprehensive index of what information is available Connects Everyone! Individuals Businesses Organizations Libraries Research labs Government Getting Connected • User’s computer must connect to a server • Server must communicate using TCP/IP • The user can purchase access to a server from an ISP (Internet Service Provider) Internet – What Can You Do? • WWW – World Wide Web • FTP – File Transfer Protocol • E-mail • UseNet • IRC – Internet Relay Chat • Bulletin Boards World Wide Web • Browser – program that allows the user to move around and explore the Internet • Use the mouse to point and click on text and graphics • Web page • Web site • Home page Classifications of Computers • Use the computer that fits your needs • Based upon – Size – Speed – Cost – Portability – Number of simultaneous users supported – Available software – Typical use Personal Computers • Other names – PC – Microcomputer – Home computer • Categories – Low-end functional – Fully powered – Workstations – Net computer or net box (Web TV) • Desktop Models Notebook Computers • Portable – Lightweight – Fits in a briefcase – Battery operated • Laptop – Larger – Heavier • More expensive that desktop models Handheld Computers • Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) – Scheduling – Addresses – Handwritten input – May offer wireless e-mail and fax • Pocket – More power than PDA – Runs basic productivity software Other Types of Computers Mainframes – – – – – High speed More expensive Used to process large amounts of data quickly Support multiple users Does server tasks Supercomputers – Fastest speed – Most expensive QUESTIONS?