VBScript16
advertisement

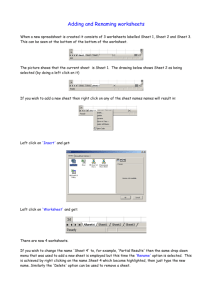
VBScript Session 16 1 Last time we’ve learned Regulars Expressions. Methods and properties. How to use the object and his collections. How to create complex patterns. 2 Subjects for session 16 Microsoft Excel Object Model. Workbooks and Worksheets Ranges and Cells. Worksheet Functions. 3 Microsoft Excel Object Model 4 Microsoft Excel Object Model 5 Workbooks Use the Workbooks property of the “Excel.Application” object to return the Workbooks collection. Dim objAppXL Set objAppXL = CreateObject(“Excel.Application”) objAppXL.Visible = False With objAppXL.Workbooks .Add ‘--- Create an new empty workbook. .Open “bugs.xls” ‘--- Open an existing workbook. .Close ‘--- Close all open workbook. End With objAppXL.Quit Set objAppXL = Nothing 6 Workbooks Use the Workbooks collection with an index or a name to reference a workbook. ‘--- Set focus on the firstopened/created workbook. objAppXL.Workbooks(1).Activate ‘--- Set focus on the bugs.xls workbook. objAppXL.Workbooks(“bugs.xls”).Activate You can also use the ActivateWorkbook property. ‘--- Set focus on the firstopened/created workbook. objAppXL.Workbooks(1).Activate objAppXL.ActiveWorkbook.Author = “Dani V.” 7 Workbooks Use the Workbook – Example objAppXL.Workbooks.Open “\\zeppo\FT_QA\bugs.xls” objAppXL.Workbooks.SaveAs “C:\bugs_local.xls” objAppXL.ActiveWorkbook.Close objAppXL.Workbooks.Add.Activate objAppXL.ActiveWorkbook.Subject = “sales 2004” 8 WorkSheets Use the Worksheets property of the workbook collection to return the Worksheets collection. ‘--- Show the number of worksheets in the workbook. MsgBox objAppXL.ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets.Count 9 WorkSheets Use the Worksheets collection with an index or a name to reference a worksheet. ‘--- Activate, print and save the first worksheet objAppXL.ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(1).Activate objAppXL.ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(1).PrintOut objAppXL.ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(1).SaveAs “x.xls” ‘--- Delete, the “Sheet 3” worksheet objAppXL.ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(“Sheet3”).Delete You can also use application object’s ActivateWorksheet property ‘--- Set focus on the first opened/created workbook objAppXL.ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(1).Activate objAppXL.ActiveWorksheet.PrintOut 10 Worksheets Use the Worksheet – Example Dim objWshXL Set objWshXL = objAppXL.ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(1) ‘--- Perform a calculation. objWshXL.Range(“A1:A3”) = “1” objWshXL.Range(“A4”) = “=Sum(A1:A3)” objWshXL. PrintOut 11 Ranges and Cells You may want to reference cells or a range of cells for doing something such entering a formula or changing the format. A Range can be also a single cell. Example ‘--- Show the number of worksheets in the workbook. objWshXL.Range(“A1:A3”).Font.Bold = True 12 Ranges and Cells Range(“A1”) Range(“A1:B5”) Range(“C5:D9,G9:H16”) Range(“A:A”) Range(“1:1”) Range(“A:C”) Range(“1:5”) Range(“1:1,3:3,8:8”) Range(“A:A,C:C,F:F”) Cell A1. Cells A1 thorough B5. A multiple area selection. Column A. Row 1. Column A thorough C. Rows 1 thorough 5. Rows 1,3, and 8. Columns A,C, and 13 Ranges and Cells Referencing cells: ‘--- Show the number of worksheets in the workbook. objWshXL.Cells(6,1) = “10” objWshXL.Range(“A6”) = “10” Dim i For i = 1 to 20 objWshXL.Cells(i,3) = i Next 14 Ranges and Cells Referencing cells: ‘--- Show the number of worksheets in the workbook. objWshXL.Cells(6,1) = “10” objWshXL.Range(“A6”) = “10” Dim i For i = 1 to 20 objWshXL.Cells(i,3) = i Next 15 Ranges and Cells Referencing rows and columns: Rows(1) Rows Columns(1) Columns(“A”) Columns Row one. All the rows on the worksheet. Column one. Column one. All the columns in the worksheet. Example ‘--- Setting the fone of first row to be bold. objWshXL.Rows(1).Font.Bold = True 16 Ranges and Cells Referencing a named range: ‘--- Font all range cells red color. objWshXL.Range(“salaries”).Font.Color = RGB(255,0,0) Referencing all cells: ‘--- Clear all worksheet’s cells. objWshXL.Cells.ClearContents 17 Ranges and Cells Looping through a range of cells: ‘--- Go over all cells in a range. For Each c In objWshXL.Range(“A1:D10”).Cells if Abs(c.Value) = 0.01 Then c.Value = 0 Next Selecting cells: objWshXL.Range(“A1”).Select objWshXL.ActiveCell = “Hello” objWshXL.Range(“A1”) = “Hello” 18 Ranges and Cells Useful methos and properties Methods Activate CheckSpelling Clear ClearContent ClearFormats Copy Cut Paste Delete Replace Select Sort Properties Cells Columns Rows Font Formula Style Value 19 Ranges and Cells Used as a container for Microsoft Excel worksheet functions that can be called from VBScript. Example: ‘--- Find the minimum value within a range. Dim theRange, minVal Set theRange = objWshXL.Range(“A1:C10”) minVal = objAppXL.WorksheetFunction.Min(theRange) MsgBox “The minimum is: “ & minVal 20 Ranges and Cells Useful worksheets functions Methods Count Max Min Sum And Or Power Round StDev Average Pi And Many More 21 Make sure to visit us Tutorials Articles Proikects And much more www.AdvancedQTP.com 22