Chapter 15
advertisement

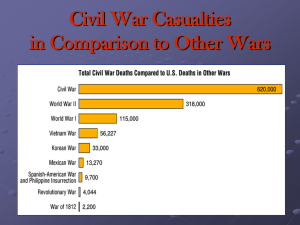
The Civil War, 1861-1865 Fort Sumter, SC Advantages North South Larger population Defensive war Loyal Navy More troops/supplies – shorter distances Strong economy, industry Difficult to blockade East coast Controlled-banking capital Experienced military leaders Logistical support Demand for cotton brings financial aid Well-established central government Mobilizing for War Both sides unprepared Conscription acts April 1862: Confederacy Finance Union Federal spending up 15% War bonds Paper money “greenbacks” Legal Tender Act 1862 $150 million National Banking Act 1863 Confederacy Political leadership Union Lincoln’s personality and leadership succeed Overcomes initial problems with respect and Democrats Confederacy Jefferson Davis strong leader, with enemies Lack of political unity States vs Davis First Years of a Long War: 1861-1862 1st Battle of Bull Run July 1861 Union troops attacked Confederate troops in VA Union close to victory but Stonewall Jackson saves the day for Confederates Ends illusion of a short war Promoted rebel myth Union Strategy Devised by Gen. Winfield Scott Use U.S. navy to blockade coast Divide Confederacy into two using Mississippi River Take Richmond Peninsula Campaign George B. McClellan Wanted long period of training for troops Invaded VA March 1862 Stopped by General Robert E. Lee Retreated back over Potomac 2nd Battle of Bull Run Lincoln replaces McClellan General Lee takes advantage Drew Union into a trap and attacked Union forced to withdraw Antietam Lee invades Maryland (Union territory) Wanted official British recognition McClellan in charge again for Union Union intercepted Lee’s plans Bloodiest single day of combat in war Lee retreated, McClellan does not pursue Claimed as a Union victory Emancipation Proclamation Fredericksburg McClellan replaced with Gen. Burnside Recklessly attacked Lee in VA Dec 1862 Union suffered heavy losses Big Changes Presidential Powers Revolutionized finance Secured borders by suspending habeas corpus in MD, 1861 Ex Parte Merryman 1861 Chief justice Roger Tanney declares Lincoln’s actions unconstitutional Doesn’t stop Lincoln “Modern” War Railroads Telegraphs Mass-produced weapons Joint army-navy tactics Iron-plated warships Rifled guns, artillery Trench warfare War continues Monitor vs. Merrimac North needed to effectively blockade Southern ports March 1862 Confederate ironclad ship Merrimac could sink Union wooden ships easily Union built Ironclad called Monitor Five-hour duel, ended in draw Prevented Confederacy from truly challenging Union blockade Revolutionize future modern warfare General Grant in the West Union’s campaign for control of Mississippi under Gen. Ulysses S. Grant Had stunning victories Early 1862 Fort Henry and Fort Donelson on Cumberland River Took 14,000 Confed. prisoners Opened up Mississippi to Union attack Shiloh Confederates surprise Grant Union holds ground Confederates forced to retreat April 1862 David Farragut captures New Orleans Virginia (Merrimac) vs. Monitor Foreign Affairs Trent Affair 1861 Confederate diplomats on a British ship the Trent Union stopped ship and took diplomat prisoners Britain threatened war Lincoln gave in to British demands Confederate Raiders South purchased war ships from Britain Mainly commerce raiders South tried to buy Laird Rams from British, but blocked by U.S. minister to Britain Charles Francis Adams Failure of Cotton Diplomacy European intervention a lost cause Europe quickly found cotton from other sources Reasons Britain did not recognize Confederacy Antietam Emancipation Proclamation New Goal of the War Confiscation Act 1861 Did not free slaves, put in army Enemy property freed 2nd Confiscation Act 1862 Now “free” blacks Could be soldiers Emancipation Proclamation Sept 1862, after Union victory at Antietam Enacted January 1, 1863 No practical impact, political Enacted by Lincoln, not congress Changes war Union Triumphs 1863-1865 Turning Point Vicksburg Union controlled Mississippi by Spring 1863 Confederates surrendered the city after heavy bombardment Union controlled full length of river, cut off west Gettysburg Lee invaded MD and PA Wanted to capture a major northern city July 1, 1863 surprised Union Bloodiest battle of the war Lee forced to retreat to VA Grant in Command Lincoln finally had a General 1864 made Commander of Union Approach to “outlast” Lee War of attrition Foreshadowed Trench Warfare Sherman’s March Chief instrument of Grant’s strategy Led 100,000 men from Chattanooga, Tennessee on campaign of deliberate destruction from Tenn, through Georgia and South Carolina Took Atlanta September 1864 Broke the will of the Confederacy Election of 1864 Democrat challenger General George McClellan Platform: Called for peaceful settlement of war Lincoln Republican nominee VP: Andrew Johnson from Tennessee Lincoln crushed electoral vote, but popular vote much closer End of the War Appomattox Confederate government tried to negotiate for peace Lincoln would not accept Lee forced to surrender April 9, 1865 at courthouse Lincoln’s Assassination Urged South to be treated benevolently in 2nd inaugural address April 14th, 1865 John Wilkes Booth shoots Lincoln Loss of Lincoln’s leadership mourned Impact of War Political Change Electoral College Functioned throughout war New factions created Republicans Radicals Moderates Democrats Peace Copperheads The Draft Both Union and Confederacy forced to draft Substitutes allowed Draft riots NYC July 1863 Irish attacked Blacks and wealthy whites Civil Liberties Suspension of Habeas Corps Ex Parte Milligan 1866 Political dominance of the North With Union victory new definition of the federal Union Nullification and Secession no longer issues Supremacy of Federal government over states solidified Abolition gave new meaning to concept of democracy Advanced cause of democracy Inspired countries around the world Impact of the War North Economic Republicans favor growth Financing the War Borrowed $2.6 billion through sale of government bonds Raised tariffs Tariffs 1862, 1864 Instituted first income tax Issued $430 million in paper currency called Greenbacks National Banking System created in 1863 Modernizing the North Manufacturing increases Pacific Railroad Act 1862 Authorized Transcontinental Railroad Homestead Act 1862 Promoted settlement of Great Plains offering 160 acres of free land Had to live on for 5 years Morrill Land Grant Act 1862 Encouraged states to use sale of federal land grants t maintain agricultural and technical colleges Problems Modernizing benefitted the rich Prices increase Excise taxes, inflation Wages behind cost of living Social Changes Blacks Became Union soldiers 54th regiment 1/10th army Freedman’s Bureau 1865 Equal pay, rights Sea Island Experiment Reconstruction Experiment Gideon’s Band 13th Education the key Amendment 1865 Four million “freed” Women Nursing field open to women Took on responsibilities of men Medicine United States Sanitary commission Battlefront nursing corps Dorthea Dix Clara Barton Geneva Convention Miasm theory Better sanitation Civilian 620,000 dead Economic Cost $15 billions in war costs and property loss Southern economy ruined Greenbacks national currency National banking replaces state banks Political States right’s argument disappear Characteristics of US democracy and capitalism economy strengthened Business Large-scale business organization Impact of the War Railroad corporations Northern industry prospered Political Cartoon Practice Marching Through Georgia* (Henry Clay Work) Bring the good old bugle boys, we'll sing another song. Sing it with a spirit that will start the world along Sing it as we used to sing it fifty thousand strong, While we were marching through Georgia. cho: Hurrah! Hurrah! We bring the Jubilee! Hurrah! Hurrah! The flag that makes you free, So we sang the chorus from Atlanta to the sea, While we were marching through Georgia! How the darkeys shouted when they heard the joyful sound! How the turkeys gobbled that our commissary found! How the sweet potatoes even started from the ground While we were marching through Georgia. Yes, and there were Union men who wept with joyful tears, When they saw the honored flag they had not seen for years! Hardly could they be restrained from breaking forth in cheers, While we were marching through Georgia. "Sherman's dashing Yankee boys will never reach the coast!" So the saucy rebels said, and 'twas a handsome boast, Had they not forgot, alas, to reckon with the host While we were marching through Georgia. So we made a throroughfare for Freedom and her train Sixty miles in latitude, three hundred to the main; Treason fled before us for resistance was in vain While we were marching through Georgia. Primary Source Practice Group Questions What was the immediate cause of the Civil War? Had there been a background of agitation for the principles victorious during the Civil War? Were personalities involved on either side whose strengths and weaknesses may have helped determine the outcome of the struggle? Were any new and potent ideas stimulating the loyalty of a considerable number of people? How did the economic groups line up on the issue? Were religious forces active? Did any new technological developments influence the Civil War? Can the events be partially explained by weakened or strengthened institutions? Was the physical environment itself a factor in the situation?