Containment
advertisement
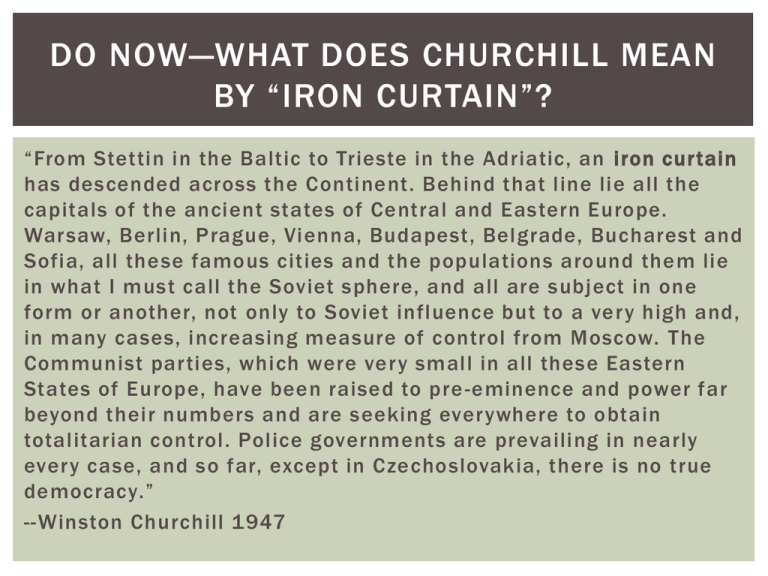
DO NOW—WHAT DOES CHURCHILL MEAN BY “IRON CURTAIN”? “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia, all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are subject in one form or another, not only to Soviet influence but to a very high and, in many cases, increasing measure of control from Moscow. The Communist parties, which were very small in all these Eastern States of Europe, have been raised to pre -eminence and power far beyond their numbers and are seeking everywhere to obtain totalitarian control. Police governments are prevailing in nearly every case, and so far, except in Czechoslovakia, there is no true democracy.” --Winston Churchill 1947 THE COLD WAR 1945-1991 2 superpowers emerge after World War II United States Soviet Union (Russia/USSR) The struggle between them was known as the Cold War Political, military and economic battle between the U.S. and Soviet Union Capitalism/Democracy vs. Communism Natural Resources Markets CONTAINMENT The U.S. establishes a new foreign policy during the Cold War Containment The U.S. wanted to limit the spread of communism to where it already existed (Soviet Union and Eastern Europe) Map of Europe during Cold War WHAT’S THE PURPOSE OF CONTAINMENT? The U.S. does not always support democratic governments — often it supports dictatorships who are anti -Communist Nationalist China (Chiang kai-Shek) Chile (Augusto Pinochet) Iran (Shah Pahlavi) Vietnam (Ngo Dinh Diem) Cuba (Fulgencio Batista) Also, the Cold War can be seen as a form of imperialism The US and Soviets were competing for new markets as well as sources of raw materials DO NOW How is the policy of containment a change from the traditional version of U.S. foreign policy? THE UNITED NATIONS In 1945 the United Nations was founded after being suggested by Franklin Roosevelt Its predecessor was the League of Nations The purpose was to settle disputes peacefully Unlike the League of Nations, most nations, including the US, joined the UN MARSHALL PLAN While Eastern Europe is under the influence of the Soviet Union, Western Europe is struggling after the end of WWII The U.S. fears Western Europe may turn to communism if their economies don’t improve The U.S. gave economic aid to Western Europe to help them return to prosperity TRUMAN DOCTRINE Greece and Turkey were two countries along the Iron Curtain in danger of falling to communism President Harry Truman said the U.S. will arm people fighting communism COLD WAR CONFLICT 1948—The Berlin Airlift Berlin (Germany’s capital) had been divided at the end of WWII It was located in East Germany (Communist) BERLIN AIRLIFT The U.S. was allowed to supply West Berlin by the Soviet Union after WWII 1948—Stalin blockades the road to Berlin The U.S. is forced to supply Berlin by air The purpose was to avoid a war over Berlin (maybe WWIII???) BERLIN WALL 1961—the Communists build a wall around East Berlin Economic conditions in E. Berlin were bad compared to W. Berlin It was intended to keep E. Berliners from leaving to W. Berlin But, it became a symbol of the Cold War between the U.S. and Soviets Also symbolic of the closed society that the Communist system was THE BERLIN WALL FELL IN 1989, THE SYMBOLIC END OF THE COLD WAR CLOSING How did the U.S. try to limit the spread of communism in Europe from the late 1940s to the early 1960s?









