Class Slides
advertisement

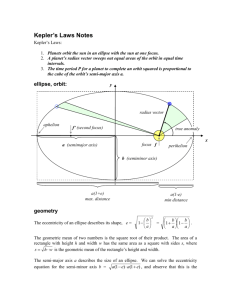
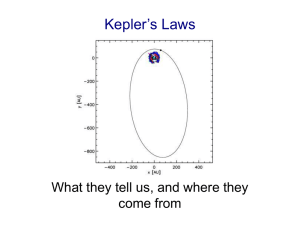
Reminders • Homework 1 (Introduction to Mastering Astronomy) is due TODAY at 5 pm. • Only 8 people have registered for Mastering Astronomy. All information needed is on class website: http://www.ifa.hawaii.edu/users/clhung/Astro 110.html • Homework 2 (Scales in Astronomy) is due Tuesday at 5 pm. New Discoveries: Higgs Boson! • The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world’s largest and highestenergy particle accelerator • Located near Geneva, Switzerland • Running since 2010 Main goal: Search for the Higgs Boson! But, other discoveries are sure to be made. Video link at: http://www.phdcomics.com/comics.php?f=1489 July 4, 2012 What does it mean? • Confirms the current theoretical model of physics • Our predictions were right! • Need to do more tests to determine that it really is the Higgs Boson. • Next up: Search for more particles! Planetary Motions Geocentric Models of the Solar System • “Geo” = Earth • Primary model of solar system from Ancient Greeks (like Aristotle) until 1600 AD • Explains rise and setting of sun, constellations, and some planets • BUT, could not explain retrograde motion of Mars, Jupiter & Saturn. Retrograde Motion Ptolemaic Model Heliocentric Model • Nicolaus Copernicus developed the first heliocentric (sun centered) model in 1543. • Explains general motion of planets (including retrograde motion), rising & setting sun • Problems – planets orbited in circles with uniform speed - wasn’t actually any more accurate than Ptolemaic system. Kepler’s Theory of the Solar System • In 1605 AD, Johannes Kepler perfected the heliocentric model by introducing elliptical orbits. • Very accurately predicts rising & setting sun, moon, and motion of planets & stars. • Kepler used the orbit of Mars (measured by his boss Tycho Brahe) – He hit upon the idea of an ellipse after 40 (!) failed attempts to calculate the orbit of Mars. What is an ellipse? An ellipse looks like an elongated circle. Eccentricity = Amount of flattening Class Action! Eccentricity, e •how squashed or out of round the ellipse is •a number ranging from 0 for a circle to 1 for a straight line e = 0.02 e = 0.7 e = 0.09 Kepler’s 1st Law The planets, including Earth, revolve around the sun in elliptical orbits. The sun is at one focus of the ellipse, the other is empty. What is the shape of Earth’s orbit around the Sun? Earth, e = 0.016 Kepler’s 2nd Law The line joining a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times as the planet travels around the ellipse. It takes as much time to go from A to B as from C to D Planets move faster closer to the sun Speed Note: If you drive at higher speeds, you will cover a larger distance in the same amount of time. OR: If you drive at higher speeds, you will cover the same distance in less time. Class Action! If you cover 100 miles in 7 hours, then your speed would be (a) Greater than 11 mph (b) Less than 11 mph (c) Equal to 11 mph Kepler’s 2nd Law The line joining a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times as the planet travels around the ellipse. Class Action! Class Action! Class Action! Lecture Tutorial • Break up into groups of 2-3 – NO MORE THAN 3 • In your group, work through the following: – Kepler’s 2nd Law (pages 21-24) – Discuss the answers – don’t be silent! • I will be roaming around if you need help… • If your group finishes, check your answers with another group & begin Newton’s Law & Gravity (pages 29-31) Class Action! Kepler’s second law says “a line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal amounts of time.” Which of the following statements means nearly the same thing? A) Planets move fastest when they are moving toward the Sun. B) Planets move equal distances throughout their orbit of the Sun. C) Planets move slowest when they are moving away from the Sun. D) Planets travel farther in a given time when they are closer to the Sun. E) Planets move the same speed at all points during their orbit of the Sun. Summary Kepler’s 1st Law: The orbits of planets are ellipses with the sun at one focus Kepler’s 2nd Law: A line drawn from a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. A planet must move rapidly when it is close to the sun and more slowly when it is far from the sun.