Spanish American War Spring 2015
advertisement

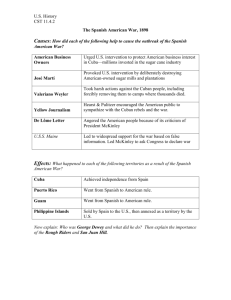
Today we are going to: • Identify the areas of United States military, economic, and political involvement and influence. • Describe how the policies and actions of the United States government impacted the affairs other countries. Spanish Empire Weakens • Spanish power was dwindling – Only a few colonies left • Phillipines, Puerto Rico, and Cuba • Resistance movement began in Cuba during 1890s. “Cuba Libre!” • Cuban patriot Jose Marti launched a war for independence from Spain in 1895. – Rebel fighters used guerilla tactics • Spanish Generals were cruel to Cubans – Concentration-style camps U.S. Chose Neutrality • By 1897, American entrepreneurs had invested millions in sugar cane plantations in Cuba – Saw Cuba as a growing market • Some supported independence for Cuba, while others wanted Spanish to take control for more stability in the sugar business “Yellow Journalists” • Yellow Journalists were publishers who exaggerated the headlines to sell papers($$). -William Randolph Hearst and Joseph Pulitzer • Pushed America to support Cuban rebels McKinley Tries Negotiations • US business interests in Cuba were threatened • McKinley threatened to recognize Cuba as an independent state • Spanish loyalists to riot in Havana, forcing McKinley to dispatch the USS The De Lome Letter (1898) • Spanish official wrote an insulting letter about McKinley – Called McKinley a “weak and stupid politician” • Hearst called it the “Worst Insult to the United States in Its History” Then the Maine Explodes! “Remember the Maine!” (1898) • USS Maine was stationed in Havana – 266 sailors killed • Yellow Journalists accuse Spain of blowing up the battleship with NO evidence! War Fever Spreads • McKinley asks for Declaration of War (April 11, 1898) • US demanded that Spain withdraw from Cuba or face US force; • Spain responded by declaring war on US Manila Bay Incident (1898) • George Dewey led ships into Manila Bay • Dewey fired on Spanish ships for no reason. – 400+ Spanish sailors died – 0 Americans Filipino Freedom! (1898) • Filipinos also want independence from Spain. – Filipino nationalists led by Emilio Aguinaldo were defeating the Spanish. • U.S. Navy defeats Spanish Navy with help from Filipino rebels. Philippines • Filipino resistance against US occupation – Emilio Aguinaldo led the resistance Philippine-American War • 3 years of brutal fighting guerrilla war • U.S. mistreatment of Filipino civilians Back in the Caribbean… War in Puerto-Rico • US Navy blockaded Cuban ports and destroyed the Spanish fleet sent to protect Cuba • 17,000 US ground forces fought • Battle of San Juan Hill The Rough Riders (1898) • Rough Riders – rugged westerners and rich easterners who volunteered to fight. • Teddy Roosevelt leads Rough Riders in two famous battles – Kettle and San Juan Hills The Treaty of Paris (1898) • Cuba = Freedom • U.S. got land for free – Guam – Puerto Rico • U.S. bought the Philippines for $20 million How did the U.S. handle these new territories? Puerto Rico • The US Military was left in charge • Foraker Act: Puerto Rico becomes US Territory – Can’t vote for President, don’t have a vote in Congress – Can have their country used as a bombing range for the U.S. military – Can go into the military – Can pay taxes Cuba • Cubans wrote their own Constitution • U.S. forced Cuba to add: – Platt Amendment 1) Cuba could not make treaties that might limit its independence or permit a foreign power to control its territory 2) The U.S. had the right to intervene in Cuba 3) Cuba could not go into debt 4) The U.S. could buy or lease land on the island for navy (Huh? Look at #1 and #4 again) Protectorate • A country who is protected diplomatically and militarily by a stronger nation • Example: after the Spanish-American War, Cuba was a protectorate of the United States