Unit 4 - msnall
advertisement

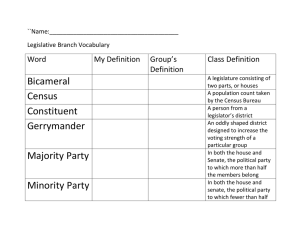
Unit 4 Spring 2015 The Legislative Branch 114th US Congress January 3, 2015 – January 3, 2017 Table of Contents Legislative Branch-Vocab • Constitution: written plan of government • Federal: level of government that controls the United States • Term Length: number of years for 1 term • Term Limit: number of terms allowed to serve • Bicameral: 2 house legislature Table of Contents The Supremacy Clause • Supremacy Clause: Article 6 in the US Constitution, making the Constitution the highest law in the land The U.S. Constitution Federal Laws State Constitutions State Statutes (Laws) County/City Ordinances Table of Contents • Full Faith and Credit Clause-each state must respect the laws, records and judicial proceedings of other states. Legislative Branch-Vocab • seniority system: system where more experienced people are given special privileges. • impeach: officially accusing an elected official of a crime • constituent: people being represented in a legislature (the voters) Table of Contents Legislative Branch-Vocab • Ex post facto: “after the fact;” charging someone for a legal action that is later made illegal • Habeas corpus: the right to be informed of your crime before a judge • Bill of attainder: a law that takes away one’s right to a trial by jury Table of Contents Legislative Branch (p.7 chart) • Gov’t Body: Congress • Main Role: creates the laws • Powers ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Establish courts Approve treaties Declare war Coin money Impeach & remove President Approve Pres. Appointments Levy taxes Table of Contents The (114th) U.S. Congress (legislative branch) (top of p. 3) • U.S. Senate ▫ Total in Congress = 100 senators ▫ How many per state = 2 per state • House of Representatives ▫ Total in Congress = 435 house members ▫ How many per state = depends on state population Table of Contents Table of Contents U.S. Senate Democrats-44 Republicans-54 Independents-2 (both caucusing with Democrats) North Carolina’s Senators • Richard Burr (R) • Tom Tillis(R) Table of Contents U.S. House of Representatives Democrats-188 Republicans-245 Vacant - 2 Rocky River District Representative Districts Your Possible House Representative Alma Adams(D) Table of Contents Your Possible House Representative Richard Hudson (R) District 8 Your House Representative Robert Pittenger (R) Table of Contents Who’s in charge here!?! Leaders of Congress Table of Contents Speaker of the House • Leading officer of the HoR. • Chosen by the majority party (party with the most members) John Boehner(R) is the current Speaker of the House Table of Contents President of the Senate • The Vice President serves as head of Senate • Tie-breaking vote • Vice President Joe Biden Table of Contents President Pro Tempore • Temporary leader of the Senate (Vice President is usually doing something else) • Orrin Hatch(R) is the current President Pro Tem Table of Contents Senate Majority Leader • Sets the legislative agenda for the Senate • Mitch McConnell(R) is the current Senate Majority Leader Table of Contents Table of Contents Expressed/Enumerated Powers • Powers written in the Constitution • Examples ▫ Power to… Lay & collect taxes raise and support armies Table of Contents Implied/Unemumerated Powers • Powers not written in the Constitution • Examples ▫ “lay & collect” implies… Creating the IRS ▫ “Raise and support armies” implies… Drafting citizens if necessary Table of Contents Necessary & Proper Clause a.k.a. “The Elastic Clause” • “The Congress shall have Power - To make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers, and all other Powers vested by this Constitution in the Government of the United States, or in any Department or Officer thereof.” ▫ Article I, Section 8, Clause 18 • It allows Congress to create implied powers when necessary, which stretches its overall power. Table of Contents Closure • How is the idea of limited government promoted in the United States Constitution? • What limits does the U.S. Constitution place on the powers of Congress? • Is it necessary to treat all people the same in order to ensure justice and equality? Warm up – 10/8/13 • Please copy the charts on page p. 181 to the back of your notes packet. 32 33 Pigeonhole • Step #2 & #5 • When a committee or sub-committee puts a Bill aside until it is forgotten about (dies) 34 Filibuster • • Step #6 When a senator tries to prevent a vote by talking as long as possible during the debate The Longest Filibusters 1.) 24 hours, 18 minutes: Strom Thurmond, civil rights bill, 1957. 2.) 23:30: Alfonse D'Amato, military bill, 1986. 3.) 22:26: Wayne Morse, Tidelands oil bill, 1953. Only 12 hours https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=60d_Sc0AIKc https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E1_9nSzG_hk 36 Cloture • Step #6 • When 60 Senators vote to stop (clot) a filibuster 37 Conference Committee • Step #7 • When members of the HoR and Senate compromise on differences in a Bill before it goes to the President. 38 Veto • Step #8 • When the President rejects a Bill 39 Pocket Veto • Step #8 • When the President puts a Bill aside for 10 days and it does not become a law if Congress has adjourned • After 10 days if Congress is still in session, the bill becomes a law. 40 Override Veto • Step #9 • If President Vetoes or Pocket Vetoes a Bill, The Senate and HoR can override the President if 2/3 of each house agrees. The Legislative Process (Textbook Edition) • http://www.centeroncongress.org/e-learningmodule-the-dynamic-legislative-process Warm Up • On the board! • Happy Friday!!!! 43 The 9 steps of how a Bill becomes a Law • Step #1 • Bill introduced into the HoR • Step #2 • Bill goes to committee & subcommittee • Step #3 • Debate and voted on in the HoR 44 The 9 steps of how a Bill becomes a Law • Step #4 • Bill introduced into the Senate • Step #5 • Bill goes to committee • Step #6 • Debate and voted on in the Senate 45 The 9 steps of how a Bill becomes a Law • Step #7 • Conference Committee • Step #8 • Presidential Action ▫ Sign ▫ Veto ▫ Pocket Veto • Step #9 • Override Veto 46 The Bill Flow Chart: Introduction in the House of Reps. Sent to Committee/ SubCommittee Debate & Vote in the HoR Sent to the Senate and Introduced Senate Committee Debate & vote Senate Floor Vote Conference Committee Sent to the President: Signs = Law Veto No Law Veto Override: 2/3 Vote in Congress = Law The Legislative Process • What really happens! • http://www.centeroncongress.org/e-learningmodule-the-dynamic-legislative-process Your Task • Congratulations 1stRRHS Congress is now in session! • Your task is to create a law within your committee that will improve RRHS (even if you do not agree) • Each committee will be given a topic • Based on your topic you must come up with a committee name • Together you and your committee must be able to rally support from all of Congress before it is sent to Ms. Nall (class president) for approval or veto. • You will have 2 minutes to debrief us on your bill proposal (make sure you sell it!) • You must also be able to answer questions other congressmen may have. They can ask you a total of 4 questions about your Bill. • You will have 20 minutes to prepare! Tasks of the Committee • Facilitator/Committee Leader – ▫ ▫ Your job is to lead the discussion on the reading assigned to your group. Make sure each of the discussion questions for your reading is discussed and ensure that every voice is heard (including your own.) Make sure the group stays focused on the task assigned. While ensuring everyone else participates in the discussion, you should also provide your thoughts. Make sure you listen to your other group members and add on to their ideas whenever possible. Pose any of your own questions that come to mind as well. • Recorder/ Writer of the Bill▫ ▫ Your job is to take notes during the discussion your group has regarding the reading assigned to you. Make sure you write down a final answer to each discussion question. You will assist the Presenter in preparing his/her notes for the summary he/she provides to the other groups as well. You should also participate in the discussion by providing your thoughts to the questions posed regarding the reading assigned to your group. Make sure you listen to your other group members and add on to their ideas whenever possible. Pose any of your own questions that come to mind as well. • Task Manager/Rules Committee Member ▫ ▫ Your job is to monitor the time as your group works and to provide time warnings (i.e. “10 minutes left,” “5 minutes left,” etc.) to your group. Make sure that your group equally divides its time among the questions and tasks, while ensuring all aspects of the assignment are completed before time is up. If any supplies are needed, you are responsible for getting them and ensuring they are returned. Also, assist the Facilitator in ensuring everyone in the group participates and stays on track. You should also participate in the discussion by providing your thoughts to the questions posed regarding the reading assigned to your group. Make sure you listen to your other group members and add on to their ideas whenever possible. Pose any of your own questions that come to mind as well. • Presenter /Bill Introducer ▫ Your job is to summarize your group’s discussion for the remainder of class once time is up. Make sure you do this in a way that teaches the other groups about the reading assigned to your group. Be prepared to speak in a clear, concise manner. The Recorder can help you in preparing and writing the summary to be presented. ▫ You should also participate in the discussion by providing your thoughts to the questions posed regarding the reading assigned to your group. Make sure you listen to your other group members and add on to their ideas whenever possible. Pose any of your own questions that come to mind as well. Q & A-er /Researcher ▫ Your job is to keep track of any questions that your group members pose throughout the discussion. Whenever possible, assist in finding the answers to these questions. (For example, you may need to look up a word in the dictionary, or consult your text book for further information on a topic.) If the group needs the teacher’s assistance, you are responsible for communicating the group’s questions or needs to the teacher. Also, after the Presenter summarizes your group’s reading and discussion with the remainder of class, you are responsible for answering any clarifying questions other groups may have of your group. ▫ You should also participate in the discussion by providing your thoughts to the questions posed regarding the reading assigned to your group. Make sure you listen to your other group members and add on to their ideas whenever possible. Pose any of your own questions that come to mind as well. Presentations of Bills • Rules for Congressional Meeting ▫ No one should interrupt the Congressman who has the floor. (There should always be order) ▫ You have two minutes to present your Bill. ▫ There will be no more than 4 questions asked of the Congressmen before we vote. ▫ Before you can ask a question you must be recognized by the chair to speak. ▫ We are the House of Representative so therefore there can be no Filibuster! Written Discussion • Had you already decided on your position on each legislation before hearing the arguments? Why? Provide an example. • Did your vote change after hearing the argument from the congressmen or after they were asked questions? Why? Provide an example for clarification. • Did peer pressure affect your vote in any way? • What other factors may sway a Congressman’s vote? • Did you consider the impact of the bills on the entire school and the people you represent before you voted? Provide an example for clarification. • Do you think you understand the textbook description of the lawmaking process? Explain your answer. Warm Up: •What do I see? (evidence right there in the image) •What do I wonder? (question, ponder about evidence) What can I infer? (interpret, conclude, think based on what evidence – not how you know this prior knowledge) Discussion • What message is the artist trying to convey? • What message is the cartoon implying regarding the powers of the President? • Does the President make his or her own rules? Explain. • In what ways does the structure of our government prevent the President from “making his/her own rules” or abusing his power? (Think about the Principles of the US Constitution) • Where can you find what powers the President officially has, as granted by the US Constitution? The Executive Branch Table of Contents Two Truths and A Lie • The President gets paid to throw large parties. • The President can declare war if America's national security is threatened. • The President has the power to appoint ambassadors. Two Truths and A Lie • The President has the right to withhold certain information from Congress if he thinks it would endanger America. • No president has ever made it to the highest office without being elected to either the presidency or the vice‐presidency • The President is allowed to campaign for other candidates of his same party running for office Two Truths and A Lie • The power of the vice‐presidency has been increasing since the early 1990s. • The president is one of the highest paid members of American society. • There has been one president who has been elected to more than two terms. Executive Branch (p.7 chart) • Gov’t Body: President • Main Role: Carry out (enforce) the law • Powers: ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Approve or veto laws Appoint judges Make treaties Pardon, reprieve, commute Direct military Create Executive orders Table of Contents How is the President Chosen? • The President is officially elected by the Electoral College which is guided by the people’s vote. • The V.P. is elected along with the candidate who won the electoral vote. Table of Contents President—The Perks • World-wide celebrity status • Salary: $400,000/year, ▫ even when retired they receive a pension ($199,700) • Air force One • Golf cart One • Camp David Retreat Table of Contents Judicial Powers p. 6 • Pardon: Forgive a convicted criminal of his/her crimes • Commute: Reduce the sentence of a convicted criminal • Reprieve: Delay the sentence of a convicted criminal. Table of Contents Roles of the President Table of Contents Chief Diplomat • The president decides what American diplomats and ambassadors shall say to foreign governments. With the help of advisers, the president makes the foreign policy of the United States. Examples: Entertaining Japanese diplomats in the White House, Traveling to London to meet with British leaders Table of Contents Commander-in-Chief • Leader of the US armed forces, All military generals (Chiefs of Staff) and admirals take their orders from the President Ex: Sending troops into battle. Table of Contents Judicial Leader • Appoints federal judges, can pardon, reprieve or commute a criminal Table of Contents Legislative Leader • Only Congress has the actual power to make laws. But the Constitution gives the president power to influence Congress in its lawmaking. Presidents may urge Congress to pass new laws or veto bills that they do not favor. Examples: Making a speech to Congress (State of the Union Address) and Signing a bill of Congress Table of Contents Chief Executive • The president is "boss" for millions of government workers in the Executive Branch, deciding how the laws of the United States are to be enforced and choosing officials and advisers to help run the Executive Branch. Examples: Appointing someone to serve as head of the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), Holding a Cabinet meeting to discuss government business, and Reading reports about problems of the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) Table of Contents Head (Chief) of State (on the side) • Acts as a celebrity figure, makes public appearances • This role requires a president to be an inspiring example for the American people. Examples: Attending Funerals, Awarding medals to the winners of college scholarships, and Greeting visitors to the White House. Table of Contents Party Leader (on the side) • In this role, the president helps members of his political party get elected or appointed to office. The president campaigns for those members who have supported his policies. At the end of a term the president may campaign for reelection. Example: Traveling to California to speak at a rally for a party nominee to the U.S. Senate. The President’s Helping Hands The Cabinet (some of it anyway) Table of Contents President’s Cabinet • One of the principal purposes of the Cabinet (drawn from Article II, Section 2 of the Constitution) is to advise the President on any subject he may require relating to the duties of their respective offices. • The Cabinet includes the Vice President and the heads of the 15 executive departments Table of Contents Secretary of State John Kerry • Advises the President on Foreign relations, negotiates treaties, represents U.S. • Assists the Presidents when acting as Chief Diplomat Table of Contents Secretary of Defense Aston Carter • Oversees the branches of the military, carries out the President’s war plans • Assists the Pres. when acting as Commanderin-Chief Table of Contents Secretary of Justice (Attorney General) Eric Holder • Gives legal advice to Pres & represents US in court • Assists the Pres. when acting as Judicial Leader Table of Contents Legislative Leaders • Review! • Speaker of the House • Vice President • President Pro Tempore Chief Executive • Review • All Cabinet Members! • All Secretaries Secretary of Treasury Jacob Lew • Advises Pres. on the economy and oversees the gov’ts revenue and expenditures • Must sign Federal Reserve notes before they can become legal tender. • Assists the Pres. when acting as economic leader Table of Contents Presidential Line of Succession (25th Amendment) • President • Vice President • Speaker of the House • Senate President Pro Tempore • Secretaries (in order of year created) • State Governors (in order of state pop.) Table of Contents Class Work • Congratulations! You have just been elected the President of the United States of America. Given what you have learned regarding the powers granted to the president, you must deal with the following situations in an appropriate manner, making good use of your power and justifying your right to handle these situations by noting what role gives you the power to make such a choice. • Remember, the roles of the President include: Chief Executive, Chief Diplomat, Commander in Chief, Legislative Leader, Head of State, Economic Leader, and Party Leader. Homework – Separate Sheet of Paper Happy Friday!!! Please pass up your homework then get started on your warm up! • Warm Up – READ!!! • Purpose: ERT – Everyone Reads to… ▫ Find out more about the roles and responsibilities of the president ▫ Figure out the difficulties of each role and responsibility • Silently read and annotate the text for 10 minutes ▫ “How do I annotate the text?” you may ask. Simply follow these directions and you will be on your way… • Evidence: As you read, underline information that helps you answer the above ERT questions • Question: Write on the side of the reading, the questions you have as you read and the points that make you think "oh that's like..."or "I wonder...“ (connections to prior and background knowledge) Discussion • Discuss your thoughts about the things you highlighted and the questions you had with your shoulder partner. • Why did you underline the things you did? Why did YOU think they were important? Unit 3 Test Data Analysis • As you are correcting your Unit 3 Exam for each question I want you to explain why you missed the question. • Some examples could include ▫ I failed to read the question thoroughly ▫ I did not know the content – did not study that section ▫ I did not understand the word (?) which caused me to not understand the question. • You have 20 minutes to complete • When you are finished please work on the Current Events activity. Post Test • When you are finished please work on the Current Events activity. Warm Up Warm Up: •What do I see? (evidence right there in the image) •What do I wonder? (question, ponder about evidence) What can I infer? (interpret, conclude, think based on what evidence – not how you know this prior knowledge) Unit 4 Exam •Thursday 3/19 Notes Time Comparing the Executives The President of the US The Governor of North Carolina VS. Governor • At least 30 • 5 years citizen • 4 Years • 2 Consecutive terms vs. President • At least 35 AGE CITIZENSHIP • Natural Born citizen TERM LENGTH • 4 Years TERM LIMIT • 2 terms Governor • • • • • • vs. Legislative Leader Judicial Leader ROLES Chief Executive Chief of State Party Leader Commander-in-Chief • Line-item veto VETO POWER President • • • • • • • Legislative Leader Judicial Leader Chief Executive Chief of State Party Leader Commander-in-Chief Chief Diplomat • Veto (All or nothing) The Judicial Branch Table of Contents Judicial Branch p. 7 • Gov’t Body: US Supreme Court • Main Role: Interpret the law • Powers: ▫ Can declare laws of Congress and acts of the President unconstitutional; judicial review Table of Contents The Federal Court System US Supreme Court-hears cases on appeal that deal with the Constitution US Court of Appealshears cases that are appealed from the District Court on legal errors. US District Court-hears cases for the first time, place of the original trial Table of Contents Becoming a Federal Judge Appointed by the President Approved by the Senate Table of Contents Original Jurisdiction • The authority to hear a case for the first time • Courts with original jurisdiction ▫ US District Court ▫ US Supreme Court-(only if a foreign official commits a crime or if a state sues another state) Table of Contents Appellate Jurisdiction • The authority to review a lower court’s decision (after the trial has been held) • Courts with appellate jurisdiction ▫ US Court of Appeals-must hear all appeals ▫ US Supreme Court-chooses the appeals it wants to hear (writ of certiorari) Table of Contents Jurisdictions Quiz Table of Contents QUIZ! Decide if the following scenarios will go to • DISTRICT COURT • COURT OF APPEALS • SUPREME COURT Determine what jurisdiction the court will use • ORIGINAL • APPELLATE Table of Contents QUIZ 1. Jessica is arrested for stealing a car and crossing state lines. ▫ ▫ DISTRICT COURT ORIGINAL JURISDICTION 2. Donovan was found guilty of robbery but he was never given a lawyer. ▫ ▫ SUPREME COURT APPELLATE JURISDICTION Table of Contents QUIZ (cont.) 3. Deisha was sentenced to 80 years in prison for spraying graffiti in Charlotte and her appeal was denied. ▫ ▫ SUPREME COURT APPELLATE JURISDICTION 4. Jose was picked up by police for selling drugs at school. ▫ ▫ DISTRICT COURT ORIGINAL JURISDICTION Table of Contents Qualifications of Offices of the 3 Branches of Government House of Representatives (Legislative Branch) • Age: 25 • Citizenship/ Residency: Must be an American Citizen for 7 years and a resident of the state he or she represents • Length of Term: 2 Years • Term Limit: Unlimited as long as reelected Senate (Legislative Branch) • Age: 30 years old • Citizenship/ Residency: Must be a citizen for 9 years and must live in the state from which elected • Length of Term: 6 years • Term Limit: Unlimited as long as reelected Congressional Salaries President/ Vice President (Executive Branch) • Age: 35 years old • Citizenship/ Residency: Must have been born a citizen of the US and a resident of the United States for 14 years • Length of Term: 4 years • Term Limit: 2 terms Supreme Court Justice (Judicial Branch) • Age: No age limit • Citizenship/ Residency: No Residency requirement • Length of Term: Life • Term Limit: Life Guided Practice • The Branches of Government ▫ Your task is to see if you can identify the roles and duties of the three branches of government. Finish Testing Data and Current Events Warm Up • Who is the chief executive at the federal level? • Who leads the legislative branch of government? (think about each house) • Who is the chief executive at the state level? • What is the name of the legislative body at the state level? Current events are due tomorrow State and Local Government Vocabulary Charter: a document that creates a municipality (city) Veto: when an executive rejects a whole bill Line-item veto: when an executive rejects parts of a bill, the rest becomes law Vocabulary municipality: a city or a town government (ex: City of Charlotte, Town of Huntersville) Initiative: When citizens sign a petition to create a new law Referendum: When a legislature lets the citizens decide on a new law (ex: School bond, gay marriage) The 3 Branches of the N.C. and Local Governments Legislative-State • The General Assembly ▫ Senate ▫ HoR Legislative-County • Board of County Commissioners Legislative-City/Town • City Council / Town Council Executive Branch-State • Governor & Lieutenant Governor Executive Branch-County • County Manager ▫ not elected but hired by BoCC Executive-City/Town • Mayor & City Manager - The City of Charlotte operates under a council-manager form of government. The Mayor and Council are responsible for making policy decisions for the community. The City Manager is responsible for carrying out those decisions, as well as providing vision and leadership to the organization and for overseeing the daily operations of City government Not elected but hired by city council Judicial Branch-State • N.C. Supreme Court Judicial Branch-County • Superior & District Court Vocabulary annexation: taking land into an existing town/city zoning: setting aside areas of land for specific uses Vocabulary revenue: money collected by government through taxes expenditure: money spent by government on services for the people budget: a plan for spending the government’s revenue on expenditures Vocabulary statute: a state law, created by the General Assembly ordinance: a local (city/town) law, made by the city council. Government Agencies • 2a) Government agencies belong to the executive branch (Governor) • 2b) Government agencies assist the governor carry out the statutes of the General Assembly • 2c) Examples of State Government Agencies Dept. of Health Board of Elections Dept. of Transportation Dept. of Corrections Dept. of Labor Dept of Public Instruction General Assembly • Powers ▫ Makes statutes ▫ Approve Governor’s budget ▫ Approve municipal charters ▫ Sets state income & sales tax • Greatest source of Revenue ▫ Sales tax & Income tax • Greatest Expenditure ▫ Public Education County Commissioners • Powers ▫ Set county sales and property tax ▫ Approves school district budget ▫ Hires county manager • Greatest source of Revenue ▫ Sales tax & Property tax • Greatest Expenditure ▫ Public Education City Council • Powers ▫ Makes ordinances ▫ Hires city manager ▫ Makes changes to city charter • Greatest source of Revenue ▫ Sales Tax, Fines, and Fees • Greatest Expenditure ▫ Public Education Strong vs. Weak Mayor • Strong mayors oversee the day-to-day operations of a city. • Weak Mayors are figureheads for the city. City Manager • Manages the day-to-day operations of the city • Reports to the City Council • Carries out requests by the City Council Referendums • Most commonly used for Bonds (when the municipal gov’t borrows money) Annexation • Incorporating land allows a city to collect more taxes (but also has to provide more services) Gerrymandering • Gerrymandering is the drawing of district lines to favor one political party over another. NC 12th District- Mel Watt’s District Compare to NC 8th District Compare to NC 9th District Implications of Gerrymandering • Elections are less important • Unfair to minority voters. Zoning • Benefit ▫ It keeps industrial (factories), commercial (stores), and residential (houses) separate from each other. • Downside ▫ It prevents people from building anything they want wherever they want. ▫ Charlotte Zoning Map Chamber of Commerce • Its purpose is to attract new businesses to the area and promote business already in the city. Amending the NC Constitution • To PROPOSE an Amendment ▫ 3/5 of the House & Senate of the G.A. must approve • To RATIFY an Amendment ▫ 51% of NC voters must approve Happy Wednesday!!! Please pass up your homework then get started on your warm up! • Warm Up – READ!!! • Purpose: ERT – Everyone Reads to… ▫ Find out more about the roles and responsibilities the local government ▫ Figure out the difficulties involved with managing money and budgeting at the local level. • Silently read and annotate the text for 10 minutes ▫ “How do I annotate the text?” you may ask. Simply follow these directions and you will be on your way… • Evidence: As you read, underline information that helps you answer the above ERT questions • Question: Write on the side of the reading, the questions you have as you read and the points that make you think "oh that's like..."or "I wonder...“ (connections to prior and background knowledge) Build a city project • You and your group are responsible for creating a new city somewhere in the state of North Carolina. You must design this city from scratch, follow many of the realistic steps that are taken when cities are incorporated. When finished, you and your group will present your cities and attempt to convince citizens to move to your city. Each group member will be given the same grade so make sure everyone in your group is participating. This will count as a test grade! • What is your role? Observations from yesterday… 1. Be a little more creative as you describe your city in your final write up. 2. Physical Features = Geography (soil, harbors, lakes, ext.) 3. Look back over the services you are providing. You need to make sure your basic needs for a city are being met! 4. There should be at least 5 ordinances. You need to be creative. You can’t undo any state law. (We know we have the Bill of Rights in place as well as we can’t kill or steal) 5. Make sure you completely understand your government. Strong mayor v. weak major 6. While 2 are working on the map of your city, 2 should be working on the write up. – This is due today! Closure • What are the ways in which city governments can be organized? • Should a person be forced to pay taxes on personal property?