Opium Poppy - Psychology
advertisement

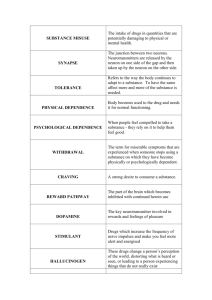
The problem with Opium Opium Poppy Papaver Somniferum Sleeping poppy Sedation Pain relief God’s own medicine Acts on brain’s opiate receptor Endorphins Endorphins Morphine Opium and its derivatives raw opium extract Natural components (1800) morphine heroin (1898) codeine thebaine Percadan Routes of Administration Upon until 1850 Smoking opium Landanum: opium dissolved into spiced wine Often called opium eaters Really opium drinkers Thomas DeQuincey Confessions of an Opium Eater (1822) “ I do not readily believe that any man, having once tasted the divine luxuries of opium will afterward descent to the gross and moral enjoyments of alcohol I take it for granted that those eat now who never ate before and those who always ate now eat more” Later volume, Miseries of Opium, detailing his agony of addiction not as widely remembered. Samuel Taylor Coleridge English Poet 1772-1834 Kubla Khan written in landanum dream In Xanadu did Kubla Khan A stately pleasure-dome decree : Where Alph, the sacred river, ran Through caverns measureless to man Down to a sunless sea. Hector Berlioz French Composer 1803-1869 Symphonie Fantastique Program notes refer to artist “poisoned with opium” who has visions, including: March to the scaffold Dream of a witches' sabbath American Civil War Hypodermic needle came into use 1850 Morphine had been extracted early 1800’s Thought no addiction with injection because it bypassed stomach. Soldier’s disease among veterans Morphine as cure for alcoholism Dr. Black (1889) “morphine calms in place of exciting the baser passions, and hence is less productive of acts of violence and crime. In short, the use of morphine in place of alcohol is but a choice of evils, and, by far, the lesser.” Patent Medicines Lydia Pinkham’s Vegetable Compound Most successful patent medicine of the 1800’s “Female complaint” nostrum 15-20% alcohol and vegetable extracts Sold until 1968 Many Patent Medicines: Contained large amounts of alcohol (up to 47%) Narcotics, such as morphine, cocaine, and opium Caffeine Vegetable extracts Journalists make an impact Samuel Hopkins Adams. 1905. The Great American Fraud. Patent medicines attacked in a series of 11 articles in Collier’s magazine Upton Sinclair. 1906. The Jungle. Book about the meat packing industry. 1906: Pure Food and Drug Act passed Temperance movement Concern about the impact of liquor on society Pledge to give up: Hard spirits only Beer and Wine too Total temperance T totalers Opium Den Drug laws 1870-1890 First anti-drug laws passed in California eliminate opium dens of Chinese immigrants. Connecticut law: addicts incompetent to handle personal affairs. Harrison Narcotic Act Harrison Narcotic Act Tax act 1914 First national narcotic act Trumped state laws Chief proponent was William Jennings Bryan Language of Harrison Act “An act to provide for the registration of, and collection of internal revenue, and to impose a special tax upon all persons who produce, import, manufacture, compound, deal in, dispense, sell, distribute or give away opium or coca leaves, their derivatives or preparations, and other purposes.” Physicians were concerned What about our ability to write Rx for opiates? Many “medical addicts” Harrison Act: No problem Dr’s could register and freely prescribe opiates as long as it was “in the course of his professional practice.” Harry Anslinger Doctor’s rights didn’t mean much to new head of the Bureau of Narcotics. Part of Treasury Dept. Started arresting and charging physicians How could this be happening? What is Addiction? Anslinger’s view was that addiction was a moral weakness. Doctors are only enabling the addiction. Doctors should be curing illness, not perpetuating them. Addicts need to stop. Doctors arrested for writing prescriptions Behrman Case (1922) Prevented M.D.’s from legally supplying drugs to addicts for self administration. Addicts must be isolated and hospitalized. Led to creation of Public Service Hospitals Prohibition Volstead Act (1920) Non-medical use of alcohol prohibited. Bootleggers Rum runners Organized crime saw profit in distributing alcohol. Repeal of Prohibition In 1933, FDR signed bill repealing prohibition. Organized crime stops distributing alcohol and switches to heroin (now the drug of choice) Black market. Addiction becomes centered in cities. Public Service Hospitals Opening day at hospital in Lexington, Kentucky (5/15/35) Beginning of research on addiction. NIDA’s roots Success of the public hospitals Most admissions were voluntary (75%). 70% of those left against medical advice. Others federal prisoners on drug charges. Treatment: detox and abstinence 90% of those who completed treatment relapsed within a few years. Revolving door: addict detox, reduce tolerance, restart habit when released. Heroin problem gets worse Stronger laws More punishment Stop using 1951 Boggs Act set minimum sentences 1956 Narcotic Drug Control Act made penalties stiffer. Robinson vs California (1963) Supreme Court finds that addiction is a disease. Support from AA. Alcoholism began to be seen as disease. Heroin addiction not that different. Narcotic Addict Rehabilitation Act Congress passed act in 1966, following Supreme Court decision. Sought to rehabilitate rather than imprison. Short and long-term care. Develop new treatment programs. End dependence on addictive drugs End susceptibility to addiction Comprehensive Drug Control Act 1970 Controlled substance act Five schedules, I – V More stringent regulations Penalties for possession and sale Moved from Treasury to Justice In 1988, cabinet level drug “czar” To be continued Treatment for heroin addiction Heroin treatment In 1965, treatments were still detox and abstinence. Pubic Service Hospitals. Revolving door. Didn’t offer much hope. Relapse or death most likely outcomes. Therapeutic Communities Synanon most famous. Founded by Chuck Dedrich Life in Synanon Detox on your own. No medical help. Commit yourself to total abstinence Community would work on rebuilding you. Start at lowest rung of social ladder. Move up a step as more trust in gained. Become a supervisor or mentor. Reenter society in stages. Success of communities Work well for those who stay in program. Most dropouts happened during the early stages (50-90%). Begin to work outside, go to school. Many didn’t want to leave. Dependence transferred to the community. A few communities turned into cults. Daytop Village: success story Daytop is based on the therapeutic community (TC) concept: a highly structured, family environment where positive peer interaction is emphasized. Separate and individualized programs are available for adolescents, adults, and all family members. Limitations of TC’s Not for everyone. Radical change in living circumstances. Dropout rate high during early stages. What if you had a large number of people needing services? More rapid return to society. Vietnam Veterans Vets served in area ready access to heroin. Thousands were coming back with addiction. 1970 alone, 100 O.D. deaths. 1971 VA set up 32 clinics across the US to treat returning vets. What would be the treatment? Counter culture Another group of concern were the hippies. Experimented with many drugs, including Speed. Abbie Hoffman: “Speed kills” Transition junkies turned to heroin. Revolving door only path? Enter Methadone Methadone is a synthetic opiate Developed during the 1940’s Opiate agonist Fills the receptor sites. Takes the place of heroin. Eliminates drug hunger Prevents withdrawal. New idea: Maintenance Rather than detox and abstinence. Substitute methadone for heroin. Maintain the patient on methadone. When the time is right and patient is ready, withdraw the methadone slowly. No dramatic withdrawal. Eventually drug free. Dole and Nyswander First treatment program using using methadone maintenance Advantage of Methadone Legal and inexpensive Accurate dose and purity Reduce criminal activity Slower acting Last 24 hours Given oral dose in orange juice Methadone as the “hook” Get addicts into treatment Drug screenings Provide them with other services Job training Individual and family counseling Parenting skills “Focus and families” (video) Success of methadone 70% of addicts who stayed in the program stopped IV drug use Reduction in drug related problems (80 to 25%) Reduction in criminal activity (20 to 10%) Slight increase is employment Short comings of methadone Moral question: not drug free Perpetuate addict mentality Substitute another drug or activity Methadone entering black market Attracts only 20% of addict community Other treatments Naltrexone Opiate antagonist Block effect of opiates if taken Takes away the high Reduces triggers Used for other drugs and gambling Harm Reduction For those addicts who continue to use IV drugs, how can we make use safer? Needle exchange programs Lower risk of infections: HIV Reduce the sharing of needles Make information available about treatment, safe sex, etc. What about heroin maintenance? Dutch, Swiss North America's first clinical trial of prescribed heroin begins today VANCOUVER (February 9, 2005) – Enrolment begins here today in North America's first clinical trial of prescribed heroin for people with chronic heroin addiction who have not been helped by available treatment options. The North American Opiate Medication Initiative (NAOMI) is a carefully controlled (clinical trial) that will test whether medically prescribed heroin can successfully attract and retain street-heroin users who have not benefited from previous repeated attempts at methadone maintenance and abstinence programs. Opium Trade Routes