PA2001: Waves and Interference
advertisement

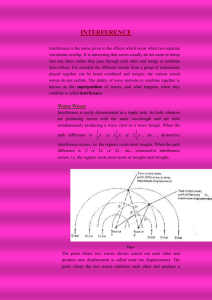
PA2001: Time and Energy Waves and Interference • Light as a wave • Fermat’s principle • Reflection • Refraction • Thin Film interference • Single slit diffraction • Young’s double slit experiment http://www.le.ac.uk/ph/mr6/lectures.html Tipler Chapters 16,33,35 Dr Mervyn Roy, S6 Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy The Electromagnetic Spectrum 1000 m Long-waves 10 m Radio, TV Wavelength 10 cm Microwaves 700 nm Infra-red 600 nm 1 mm 10 mm 100 nm Visible 500 nm 1 nm X-rays 0.1 nm Gamma rays Waves and Interference 400 nm PA2001: Time and Energy Fermat’s principle The path taken by light in travelling from one point to another is such that the time of travel is a minimum. Explains the law of reflection: Euclid Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Phase changes wave incident on a barrier incident wave: Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Phase changes wave incident on a barrier incident wave: reflected wave: phase change of upon reflection (note: phase change of only for reflection at rare/dense interface) Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Refraction some reflection rare medium (air) some reflection dense medium (glass) note: phase change of only at rare / dense interface Snell’s Law - derived using Fermat’s principle – shortest path is not the fastest as v < c Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Refraction some reflection phase change rare medium (air) some reflection no phase change dense medium (glass) note: phase change of only at rare / dense interface Snell’s Law - derived using Fermat’s principle – shortest path is not the fastest as v < c Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Refraction 2 Or, why shooting fish in a barrel isn’t easy nwater = 1.3 Fish are always deeper than you think Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Dispersive media - waves of different wavelength travel at different velocity and therefore refract differently Newton’s prism © The Exploratorium www.exploratorium.edu Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Interference Add coherent harmonic waves with phase difference 0, 2 /2 Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Interference Add coherent harmonic waves with phase difference 0, 2 /2 Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Interference Add coherent harmonic waves with phase difference 0, 2 /2 Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Interference Add coherent harmonic waves with phase difference 0, 2 /2 Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Interference 2 Add coherent harmonic waves with phase difference Intensity, With constant amplitude as before, In general (Hecht, Optics 2nd Ed. 9.1), Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Interference 3 Add coherent harmonic waves with path difference, Phase difference is related to path difference Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Thin film interference 1 travels further than difference in path length introduces phase difference interferes with type of interference depends on To find type of interference: Calculate path and phase difference, then: Note: have to be careful with possible phase changes of at each interface Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Thin film interference 2 travels further than difference in path length introduces phase difference interferes with type of interference depends on At normal incidence: Maximum in the intensity if Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Thin film interference 3 At normal incidence see interference fringes with films of varying thickness © The Exploratorium, www.exploratorium.edu Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy B Thin film interference 4 D C D C A B combine Waves and Interference A A D with Snell’s law PA2001: Time and Energy Thin film growth In-situ monitoring of film thickness At fixed, angle of incidence, Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Diffraction (single slit) Water wave slit width, a screen • aperture size ~ wavelength © The Exploratorium, www.exploratorium.edu Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Diffraction (single slit) Laser light slit width, a screen Screen Intensity -2/a Waves and Interference -/a /a 2/a PA2001: Time and Energy Young’s slits slit separation, d Laser light Interference fringes Screen far away, rays ~ parallel d Path difference, Constructive interference: Waves and Interference PA2001: Time and Energy Diffraction gratings © The Exploratorium, www.exploratorium.edu Angle of maxima is wavelength dependent: Waves and Interference